1 x 2 graph
Username: Password: Register in one easy step! Reset your password if you forgot it. Algebra: Rational Functions, analyzing and graphing Section. Solvers Solvers.
Ask and it will be given to you; seek and you will find; knock and the door will be opened to you. For everyone who asks receives; the one who seeks finds; and to the one who knocks, the door will be opened. Summary: In this section, you will: Find the domains of rational functions. Identify vertical asymptotes. Identify horizontal asymptotes.
1 x 2 graph
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Enter a problem Algebra Examples Popular Problems. Find the properties of the given parabola. Rewrite the equation in vertex form. Complete the square for. Use the form , to find the values of , , and. Consider the vertex form of a parabola. Find the value of using the formula. Step 1. Substitute the values of and into the formula. Simplify the right side. Cancel the common factor of and. Factor out of. Move the negative one from the denominator of.
For everyone who asks receives; the one who seeks finds; and to the one who knocks, the door will be opened.
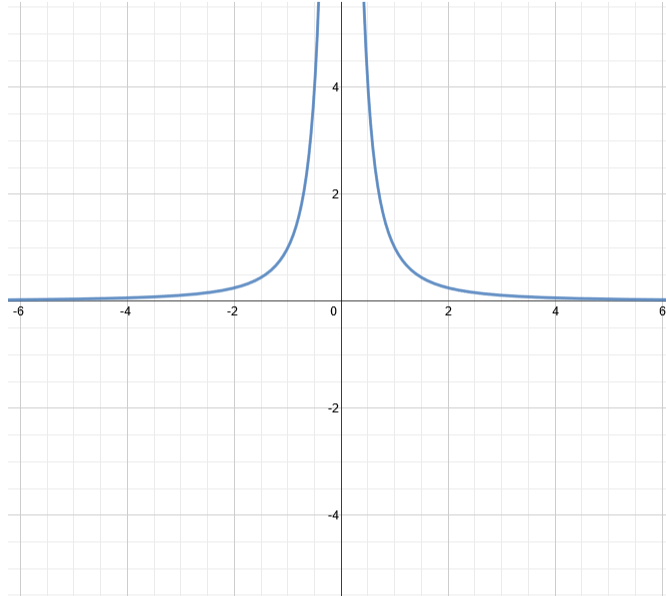
As with polynomials, factors of the numerator may have integer powers greater than one. Fortunately, the effect on the shape of the graph at those intercepts is the same as we saw with polynomials. The vertical asymptotes associated with the factors of the denominator will mirror one of the two toolkit reciprocal functions. When the degree of the factor in the denominator is odd, the distinguishing characteristic is that on one side of the vertical asymptote the graph heads towards positive infinity, and on the other side the graph heads towards negative infinity. When the degree of the factor in the denominator is even, the distinguishing characteristic is that the graph either heads toward positive infinity on both sides of the vertical asymptote or heads toward negative infinity on both sides. Next, we will find the intercepts.
Plotting and graphing are methods of visualizing the behavior of mathematical functions. Use Wolfram Alpha to generate plots of functions, equations and inequalities in one, two and three dimensions. Gain additional perspective by studying polar plots, parametric plots, contour plots, region plots and many other types of visualizations of the functions and equations of interest to you. Graph a function of one variable as a curve in the plane. Plot the solution set of an equation in two or three variables.
1 x 2 graph
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Enter a problem Algebra Examples Popular Problems.
Hulk vs aquaman
For factors in the denominator, note the multiplicities of the zeros to determine the local behavior. A hole is where a simplified function is undefined. These holes come from the factors of the denominator that cancel with a factor of the numerator. Vertical asymptotes come from the factors of the denominator that are not in common with a factor of the numerator. There are no common factors in the numerator and denominator. In general, if the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator, the end behavior of the graph will be the same as the end behavior of the quotient of the rational fraction. There will be just one horizontal asymptote if that is the case. This lesson is about rational functions which have variables in the denominator. Module Rational and Radical Functions. Find the slant asymptote by dividing the rational function and ignoring the asymptote. The fact nothing cancels means no holes as well. For everyone who asks receives; the one who seeks finds; and to the one who knocks, the door will be opened.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:. Enter a problem Algebra Examples Popular Problems.
There are no common factors in the numerator and denominator. How To: Given a rational function, sketch a graph. In a rational expression, when I have a numerator that is equal to zero 0 but the denominator is not equal to zero 0 what do I have. When the numerator and denominator both have the same highest degree term the highest in the numerator and denominator is when you can divide their coefficients number in front of a variable. Conveniently, this is already factored. Search for:. Let N be the degree of the numerator and D be the degree of the denominator. Step 1. To do this, just find x values where the denominator is zero and the numerator is non-zero. Examine the behavior on both sides of each vertical asymptote to determine the factors and their powers. First let's factor the entire thing into binomial terms. Find the value of using the formula. Example, what is the expression then called? Robert Jack. A hole is where a simplified function is undefined.

0 thoughts on “1 x 2 graph”