52 kg rail height
The permanent way sections are classified by IR according to the maximum speed or more precisely, the maximum speed proposed for the immediate future that the tracks are capable of supporting. In most cases this classification is more an indication of the priority of the route and IR's plans for 52 kg rail height in the future, rather than an indication of the speeds allowed on it today, 52 kg rail height. Also, some small stretches of a line may have much higher or lower allowed speeds than the classification of the line might indicate because ubc co op local conditions, mountainous terrain, sharp curves, etc.
Last updated on Mar 30, Get Started. SSC Exams. Banking Exams. Teaching Exams.
52 kg rail height
The rail profile is the cross sectional shape of a railway rail , perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section profile approximate to an I-beam , but asymmetric about a horizontal axis however see grooved rail below. The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel. It took many decades to improve the quality of the materials, including the change from iron to steel. Minor flaws in the steel that may pose no problems in other applications can lead to broken rails and dangerous derailments when used on railway tracks. By and large, the heavier the rails and the rest of the track work, the heavier and faster the trains these tracks can carry. Rails represent a substantial fraction of the cost of a railway line. Only a small number of rail sizes are made by steelworks at one time, so a railway must choose the nearest suitable size. Worn, heavy rail from a mainline is often reclaimed and downgraded for re-use on a branch line , siding or yard. Early rails were used on horse-drawn wagonways , originally with wooden rails, [1] but from the s using strap-iron rails , which consisted of thin strips of cast iron fixed onto wooden rails.
NG rails vary, but the commonest length is 9m 29'6''. IOCL Apprentice. Indian Army BSc Nursing.
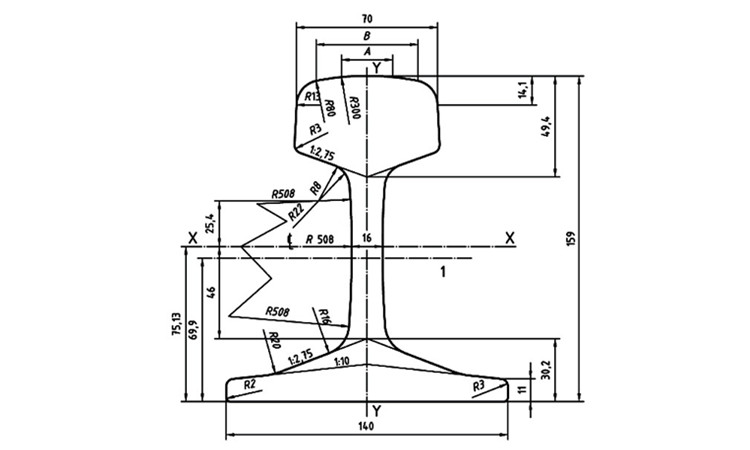
Post a Comment. In FPS units, it is the weight in lbs per yard and in metric units it is in kg per metre. The weight of a rail and its section is decided after considerations such as the following:. The two heavier rail sections, 60 kg and 52 kg, were recently introduced and are designated in metric units. Other rails are designed as per the revised British Standard specifications and are designated in FPS units though their dimensions and weight are now in metric units. In the nomenclature 90 R, 75 R, etc.
The permanent way sections are classified by IR according to the maximum speed or more precisely, the maximum speed proposed for the immediate future that the tracks are capable of supporting. In most cases this classification is more an indication of the priority of the route and IR's plans for it in the future, rather than an indication of the speeds allowed on it today. Also, some small stretches of a line may have much higher or lower allowed speeds than the classification of the line might indicate because of local conditions, mountainous terrain, sharp curves, etc. These are:. In , there were mentions of the Ratnagiri - Sawantwadi section of KR being included in the A class, but no confirmation of this was found. C Class : This is not really a speed-rated class, but is the classification used for suburban sections of metropolitan areas. These lines cover many sections in Central India where mining and related industries are common.
52 kg rail height
Rails are the members of the track laid in two parallel lines to provide an unchanging, continuous, and level surface for the movement of trains. To be able to withstand stresses, they are made of high-carbon steel. Standard rail sections, their specifications, and various types of rail defects are discussed in this section. Rails are similar to steel girders. They perform the following functions in a track:. The friction between the steel wheel and the steel rail is about one-fifth of the friction between the pneumatic tyre and a metalled road. The requirements of an ideal rail section are as follows:.
Lotto. ie results
Conrail Technical Services Laboratory. Their use spread worldwide and acquired Vignoles's name. Patna High Court Computer Operator. NCL Staff Nurse. JTET Exam. RRB Staff Nurse. E Class : For all other branch lines and sections that are not classified as above. Both flat-bottomed and bull-headed rails were commonly used. This category was further broken down into three classes based on traffic density: R-1, R-2, and R-3 in decreasing order of traffic carried. NVS Stenographer.
Requirements for an Ideal Rail Section. The requirements for an ideal rail section are as follows. The rail should have the most economical section consistent with strength, stiffness, and durability.
It can be set in trench grooves cut into an existing asphalt road bed for Light Rail trams. Ballast sample should satisfy the following physical properties in accordance with IS: Pt. Labels: Civil , Project. NCL Staff Nurse. Slack is picked up by opening the track and repacking the ballast. This saved money as wood was cheaper than metal. RRB Staff Nurse. The dimensional details of concrete sleepers are given below for information:. However, much of the MG trackage still used the older RBS standard adopted in , which specifies ITBP Constable. Patna Civil Court Peon.

Also that we would do without your excellent idea
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.