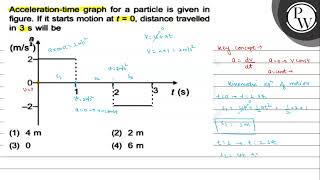
Acceleration time graph for a particle is given in figure
Learn from their 1-to-1 discussion with Filo tutors. Total classes on Filo by this tutor - 9,
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. See what we can learn from graphs that relate acceleration and time. What does the vertical axis represent on an acceleration graph?
Acceleration time graph for a particle is given in figure
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. Ask students to use their knowledge of position graphs to construct velocity vs. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. Ask—Is it the same information as in a position vs. How is the information portrayed differently? Is there any new information in a velocity vs. Earlier, we examined graph s of position versus time. Now, we are going to build on that information as we look at graphs of velocity vs. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity; we will discuss acceleration more in another chapter.
Teaches : Physics, Biology, Organic Chemistry. The position x of a particle moving along x - axis veries with time I believe it represents a negative derivative of displacement.
Position - time graph for a particle is shown in figure. The position - time graph for a particle moving along a straight line is shown in figure. The acceleration-time graph of a particle moving along x-axis is shown in the figure. Acceleration-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is as shown in figure. The acceleration versus time graph of a particle is shown in the figure. The acceleration time graph of a particle is shown in the figure Assume motion is 1 dimension :.
The Learning Objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Acceleration, as well as the following standards:. Review graphical analysis, including axes, algebraic signs, how to designate points on a coordinate plane, i. Explain that these equations can also be represented graphically. We are studying concepts related to motion: time, displacement, velocity , and especially acceleration. We are only concerned with motion in one dimension. The kinematic equations that we will be using apply to conditions of constant acceleration, except where noted, and show how these concepts are related. Constant acceleration is acceleration that does not change over time. This equation, which is the definition of average velocity and valid for both constant and non-constant acceleration, says that average velocity is displacement per unit time.
Acceleration time graph for a particle is given in figure
In this article, you will learn about acceleration graphs in detail. Acceleration-Time Graph shows the acceleration plotted against time for a particle moving in a straight line. The acceleration-time plots acceleration values on the y-axis and time values on the x-axis. The vertical axis in the acceleration-time graph represents the acceleration of the object. In the given graph below, reading the value of the graph at a particular time will fetch you the acceleration of the object in meters per second squared for that moment. Acceleration-Time Graph Slope of the acceleration graph The slope of the acceleration graph represents a quantity known as a jerk. Jerk is the rate of change of acceleration.
Free sex pinoy
The displacement is given by finding the area under the line in the velocity vs. If students are struggling with a specific objective, the Check Your Understanding will help direct students to the relevant content. If you would like, you can put it on the a setting, as well. The instantaneous velocity can just be read off of the graph. Essay review. Taught by Raj Shukla. We can see that the average velocity for the drive back is —0. Suppose the elevator is initially at rest. Answer:- As there is a graph that has the figure under the curve so you have to find the area under the acceleration time graph. What's the reasoning behind this?
.
Answer:- As there is a graph that has the figure under the curve so you have to find the area under the acceleration time graph. Describe the graph and explain what it means in terms of velocity and acceleration. If the rolling ball slowed down in the last snap lab, perhaps due to the ramp being too low, then the graph may not show constant velocity. Question 2. Total classes on Filo by this tutor - 9, Taught by Pramod Kumar Singh. Find a. But this is the change in velocity, so to find the final velocity, we'll use the definition of change in velocity. The area under any acceleration graph for a certain time interval gives the change in velocity for that time interval. As she nears the finish line, the race car driver starts to accelerate. This means the area under the curve of the acceleration time graph is equal to the change in the velocity of the object in the given time period. Was this answer helpful? One destination to cover all your homework and assignment needs. Like when we were working with a curved displacement graph, we will need to take a tangent line at the instant we are interested and use that to calculate the instantaneous acceleration.

Bravo, seems to me, is a brilliant phrase