Agrobacterium ti plasmid
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, agrobacterium ti plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A.
Agrobacterium ti plasmid
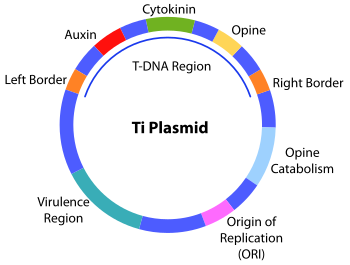
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell. The presence of this Ti plasmid is essential for the bacteria to cause crown gall disease in plants. These regions have features that allow the delivery of T-DNA into host plant cells, and can modify the host plant cell to cause the synthesis of molecules like plant hormones e. Because the T-DNA region of the Ti plasmid can be transferred from bacteria to plant cells, it represented an exciting avenue for the transfer of DNA between kingdoms and spurred large amounts of research on the Ti plasmid and its possible uses in bioengineering. They are also often termed replicons , as their replication begins at a single site. Members of this family have a characteristic repABC gene cassette. A key feature of Ti plasmids is their ability to drive the production of opines, which are derivatives of various amino acids or sugar phosphates , in host plant cells. These opines can then be used as a nutrient for the infecting bacteria, which catabolizes the respective opines using genes encoded in the Ti plasmid.
Acknowledgments The authors thank members of the Christie laboratory for helpful discussions, agrobacterium ti plasmid. EMBO J. Opine catabolism and conjugal transfer of the nopaline Ti plasmid pTiC58 are coordinately regulated by a single repressor.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell 1. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A. At the end of this chapter, we will describe how this natural genetic engineer has been adapted to spawn an entire industry of plant biotechnology and review its potential for use in future therapeutic applications of plant and nonplant species.
Agrobacterium ti plasmid
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A. At the end of this review, we will describe how this natural genetic engineer has been adapted to spawn an entire industry of plant biotechnology and review its potential for use in future therapeutic applications of plant and nonplant species. Abstract Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. Publication types Research Support, N.
Da luigi pizzeria
Binns AN, Castantino P. When delivered to plant cells and integrated into the plant nuclear genome, T-DNAs code for biosynthesis of auxins and cytokinins resulting in proliferation of plant tissues, and production of opines that serve as nutrients for the infecting bacterium Figure was adapted from Ref. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Conjugative DNA metabolism in Gram-negative bacteria. This binding reaction stimulates T-DNA processing and results in accumulation of many copies of free VirD2-T-strand transfer intermediates in a cell A small antisense RNA downregulates expression of an essential replicase protein of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. Toggle limited content width. Conjugal transfer system of the IncN plasmid pKM References 1. Other channel subunits, including the pilin subunit and a portion of VirB9 are postulated to form the distal portion of the channel within the core's central chamber This is thought to ensure a selective advantage of the infecting bacterium over other A.
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria.
A LuxR-type regulator from Agrobacterium tumefaciens elevates Ti plasmid copy number by activating transcription of plasmid replication genes. May Besides regulating expression of opine catabolism genes, opines serve another important regulatory function. However, when A. Both channels are assembled from at least 11 subunits whose stoichiometries for the most part are unknown Fig. The envelope-spanning core complex: In A. Schematic of octopine-type Ti plasmid pTiA6 showing locations of genes coding for plasmid maintenance rep , infection of plant cells vir region, T-DNA , cell survival in the tumor environment opine catabolism , and conjugative transfer of the Ti plasmid to recipient agrobacteria tra and trb. VirB3 interacts with VirB4 59 and might play a role in coordinating a biologically important interaction between this ATPase and other components of the translocase. The versatile bacterial type IV secretion systems. Ultimately, the regulatory cascade involving opine-mediated expression of traR and TraR—AHL-mediated expression of Ti plasmid transfer genes at high cell densities, results in enhanced Ti plasmid conjugative transfer to neighboring agrobacterial cells in the environment of the plant tumor. Bacterial type IV secretion: conjugation systems adapted to deliver effector molecules to host cells. The cotransfer of oncogenes ensures that transformed plant cells proliferate, resulting in enhanced opine synthesis. Agrobacterium and plant cell transformation. Frontiers in Microbiology.

It is simply matchless :)