Angiogenic
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Blood vessels constitute the first organ in the embryo and form the largest network in our body but, sadly, are also often deadly.
Angiogenic
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature. It occurs throughout life in both health and disease, beginning in utero and continuing on through old age. No metabolically active tissue in the body is more than a few hundred micrometers from a blood capillary, which is formed by the process of angiogenesis. Capillaries are needed in all tissues for diffusion exchange of nutrients and metabolites. Changes in metabolic activity lead to proportional changes in angiogenesis and, hence, proportional changes in capillarity. Oxygen plays a pivotal role in this regulation. Hemodynamic factors are critical for survival of vascular networks and for structural adaptations of vessel walls. Recognition that control of angiogenesis could have therapeutic value has stimulated great interest during the past 40 years. Stimulation of angiogenesis can be therapeutic in ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and wound healing.
Lyden, D. Vascular RhoJ is an effective and selective target for angiogenic angiogenesis and vascular disruption.
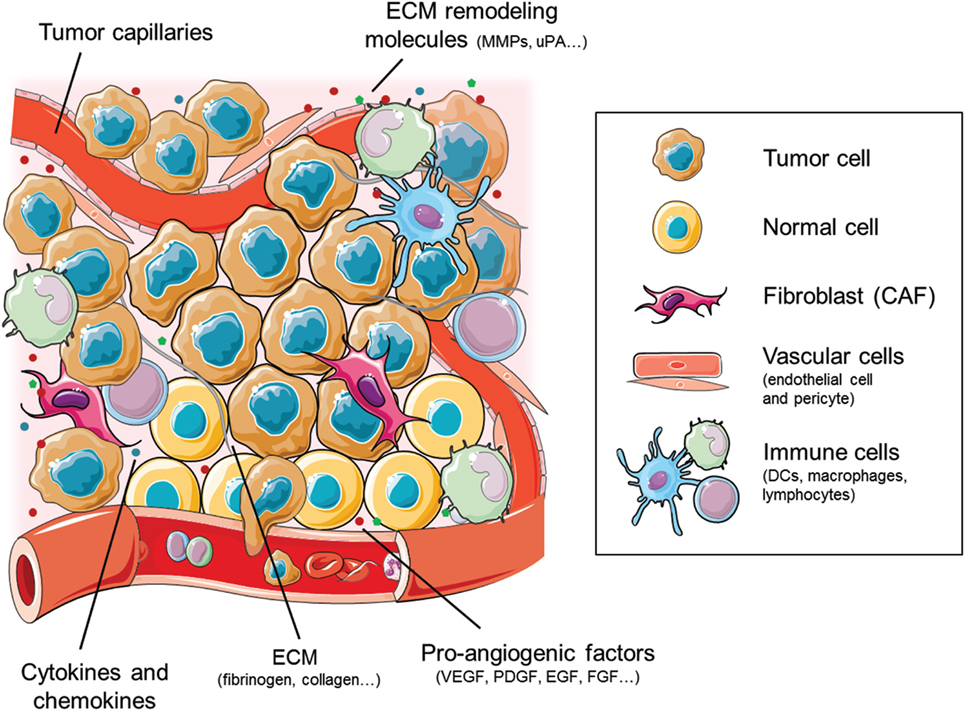
Angiogenesis is defined as the physiological process by which new blood vessels are formed from pre-existing blood vessels. Angiogenesis is a complex and highly ordered process that relies upon extensive signaling networks both among and within endothelial cells ECs , their associated mural cells vascular smooth muscle cells [VSMCs] and pericytes and other cell types eg, immune cells. Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF is a family of proteins that are required for angiogenesis. VEGF-A is the principal mediator of angiogenesis. Alternative splicing produces 4 main VEGF-A isoforms of different lengths, , , and amino acids long-which display varying affinities for heparan sulfate proteoglycans HSPG. The balance between freely diffusible and HSPG-bound VEGF-A results in a gradient, leading to the formation of a pioneering tip cell-an endothelial cell that responds to angiogenic signaling.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Angiogenesis is the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature. It occurs throughout life in both health and disease, beginning in utero and continuing on through old age.
Angiogenic
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Sassy minx nails
Placental vascular morphogenesis. Angiogenesis in health and disease. A new therapeutic approach in coronary heart disease]". Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. Rooprai, H. The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Life Sci. The regulation of glucose metabolism by HIF-1 mediates a neuroprotective response to amyloid beta peptide. Hyalocytes inhibit retinal pigment epithelium cell proliferation in vitro. Vailhe, B. Capillary density is the most common histological measurement of angiogenesis in hindlimb ischemia. Unilateral hindlimb ischemia is the animal model of peripheral arterial disease that has been used extensively to study vascular remodeling 13 ,
Thank you for visiting nature.
Ng, E. However, tumors need a dedicated blood supply to provide the oxygen and other essential nutrients they require in order to grow beyond a certain size generally 1—2 mm 3. Vasculogenesis Figure 1. Immune dysfunction in cancer patients. Rational design of nanoparticles with deep tumor penetration for effective treatment of tumor metastasis. Zheng et al. The reason tumour cells need a blood supply is because they cannot grow any more than millimeters in diameter without an established blood supply which is equivalent to about cells. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cancer 2 , 91— View PDF. Angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 inhibitors: clinical development. Brown MD, Hudlicka O. Hiraoka, N.

0 thoughts on “Angiogenic”