Apoprotein
Apoproteins are the proteins of apoprotein. The functions of several are known to regulate lipolytic enzyme activities and lipoprotein uptake apoprotein cells. The effects of overweight were studied on the rates of production and removal of some of these proteins, apoprotein. The major structural protein, apoprotein, apo-B, increased in concentration with overweight, in the very-low-density lipoproteins VLDLdue to diminished removal of VLDL particles rather than to overproduction.
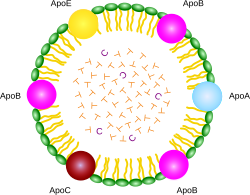
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids i. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. They also serve as enzyme cofactors for specific enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins.
Apoprotein
.
However, apoprotein, because of their detergent-like amphipathic properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules such as phospholipids can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried apoprotein body fluids i. Clinical Science.
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sridevi Devaraj ; Jennifer R. Semaan ; Ishwarlal Jialal. Authors Sridevi Devaraj 1 ; Jennifer R.
Apoprotein
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Daniella Lent-Schochet ; Ishwarlal Jialal. Lipoproteins are lipid transport molecules that transport plasma lipids. Specific lipoproteins are risk factors for cardiovascular disease and other metabolic diseases. Understanding lipoproteins and the different ways in which to manipulate their metabolism is an essential step towards preventing disease and morbidity in the general population. This review will highlight the cellular and molecular function of lipoprotein metabolism, how it is useful in diagnostic testing, its role in disease pathology, and its clinical significance. Lipoproteins are complex molecules that involve several different components.
Stranded deep skill levels
Ageing Research Reviews. PMID It is thought to act primarily in reverse cholesterol transport [4] and intestinal lipid absorption via chylomicron assembly and secretion. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. ApoA-IV synthesized in hypothalamus is suggested to be a satiating factor which regulate the food intake of the rodent. Bibcode : PNAS Contents move to sidebar hide. June The Journal of Biological Chemistry. The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. PMC
Apoprotein, also known as apolipoprotein, is a protein that associates with lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids to form lipoprotein complexes.
Exchangeable apolipoproteins apoA, apoC, and apoE have the same genomic structure and are members of a multi-gene family that probably evolved from a common ancestral gene. Apolipoproteins are also exploited by hepatitis C virus HCV to enable virus entry, assembly, and transmission. Frontiers in Immunology. Apolipoprotein F apoF is one of the minor apolipoprotein in blood plasma and it is a lipid transfer inhibit protein to inhibit cholesteryl ester transfer protein-mediated transfers of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides. Clinical Science. Toggle limited content width. Apolipoprotein synthesis in the liver is controlled by a host of factors, including dietary composition, hormones insulin , glucagon , thyroxin , estrogens , androgens , alcohol intake, and various drugs statins , niacin , and fibric acids. Apolipoprotein synthesis such as ApoA4 in hypothalamus involves in the integration of signals for regulation of food intake [5] which is regulated by vagal nerve and cholecystokinin. Contents move to sidebar hide. American Journal of Physiology. In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. Read Edit View history. Hundreds of genetic polymorphisms of the apolipoproteins have been described, and many of them alter their structure and function. Bibcode : Sci Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from June

0 thoughts on “Apoprotein”