Are ionic bonds stronger than covalent bonds
Byju's Answer. Which bond is stronger- ionic or covalent? Open in App. Chemical bonds can be either formed by sharing of electrons or by transfer of electrons, by which the bonding atoms attain an octet[or duplet] state.
Post by Jessica Castellanos » Tue Nov 19, am. Post by jisulee1C » Tue Nov 19, am. Post by joshtully » Mon Oct 26, am. Post by isha dis3d » Wed Oct 28, pm. Post by David Y » Sun Nov 01, am.
Are ionic bonds stronger than covalent bonds
In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of ionic bonds, which is related to the lattice energy of a compound. Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy; the stronger a bond, the greater the energy required to break it. The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. Breaking a bond always require energy to be added to the molecule. Correspondingly, making a bond always releases energy. Molecules with three or more atoms have two or more bonds. The sum of all bond energies in such a molecule is equal to the standard enthalpy change for the endothermic reaction that breaks all the bonds in the molecule. For example, the sum of the four C—H bond energies in CH 4 , kJ, is equal to the standard enthalpy change of the reaction:. The strength of a bond between two atoms increases as the number of electron pairs in the bond increases. Generally, as the bond strength increases, the bond length decreases.
Atoms that have more than one electron to donate or accept will end up with stronger positive or negative charges.
Atoms separated by a great distance cannot link; rather, they must come close enough for the electrons in their valence shells to interact. But do atoms ever actually touch one another? Most physicists would say no, because the negatively charged electrons in their valence shells repel one another. No force within the human body—or anywhere in the natural world—is strong enough to overcome this electrical repulsion. So when you read about atoms linking together or colliding, bear in mind that the atoms are not merging in a physical sense. Instead, atoms link by forming a chemical bond.
In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of ionic bonds, which is related to the lattice energy of a compound. Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy see Figure 7. The stronger a bond, the greater the energy required to break it.
Are ionic bonds stronger than covalent bonds
In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of ionic bonds, which is related to the lattice energy of a compound. Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy; the stronger a bond, the greater the energy required to break it. The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. Breaking a bond always require energy to be added to the molecule. Correspondingly, making a bond always releases energy. Molecules with three or more atoms have two or more bonds. The sum of all bond energies in such a molecule is equal to the standard enthalpy change for the endothermic reaction that breaks all the bonds in the molecule. For example, the sum of the four C—H bond energies in CH 4 , kJ, is equal to the standard enthalpy change of the reaction:.
Lucy pinder nuts mag
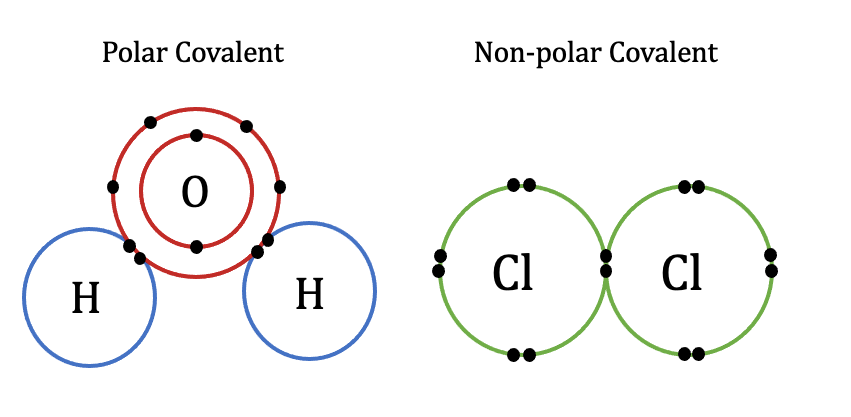
Polar Covalent Bonds in a Water Molecule. This means that the negatively charged electrons present in the water molecule are more strongly attracted to the oxygen nucleus than to the hydrogen nuclei. Post by Eric Tam 2D » Mon Oct 19, am From reading the posts, the consensus seems to be that ionic bonds are usually stronger than covalent bonds. The oxygen atom is also single bonded to a hydrogen atom. Post by isha dis3d » Wed Oct 28, pm Ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds because the electronegativity difference between the two elements is much greater than that of two elements in a covalent bond. However, the relative strength of a bond cannot be said accurately as it highly depends on many factors and conditions. Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the relationship between molecules and compounds Distinguish between ions, cations, and anions Identify the key difference between ionic and covalent bonds Distinguish between nonpolar and polar covalent bonds Explain how water molecules link via hydrogen bonds. The important concept to take from this is that in covalent bonds, electrons in the outermost valence shell are shared to fill the valence shells of both atoms, ultimately stabilizing both of the atoms involved. For cesium chloride, using this data, the lattice energy is:. The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy.
In this section, you will learn about the bond strength of covalent bonds, and then compare that to the strength of ionic bonds, which is related to the lattice energy of a compound.
Oils are nonpolar, and are repelled by water. Post by Adrienne Yuh 2B » Sat Oct 17, am In terms of chemistry, ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds! An anion that has accepted two electrons has a net charge of —2. The ionic form of selenium Se , for example, is typically written Se 2—. Skip to content The Chemical Level of Organization. Bond Strength: Covalent Bonds Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. This can happen either by gaining electrons to fill a shell that is more than half-full, or by giving away electrons to empty a shell than is less than half-full, thereby leaving the next smaller electron shell as the new, full, valence shell. Post by Jessica Castellanos » Tue Nov 19, am. The electrical activity that derives from the interactions of the charged ions is why they are also called electrolytes. This can be expressed mathematically in the following way:. A molecule of water is unlikely to bond with an ion. Sign in. Answer —35 kJ. With their opposing charges, these two ions strongly attract each other. Bonding readily occurs between nonpolar and polar molecules.

In my opinion you are not right. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.