Awg to mm2 conversion
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. AWG is the US standard that defines the cross-sectional areas and diameters for solid, round electrical wire awg to mm2 conversion is based on the number of dies required to draw down the raw copper to the appropriate size. Unfortunately, there is no easy way to convert AWG to an exact metric system measurement.
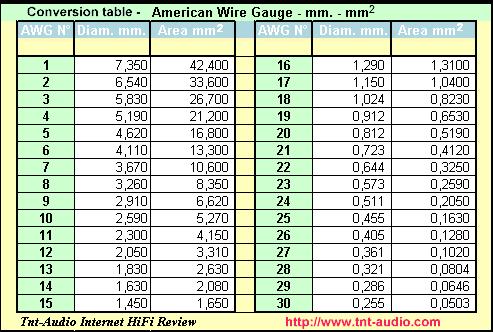
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area.
Awg to mm2 conversion
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. AWG is also related to resistance. Essentially, a thicker wire will have less resistance and carry more voltage at a longer distance. Choosing a wire size will depend on the gauge and length you need. To determine the gauge wire you need, consider what carrying capacity and amount of current the wire needs to conduct to work for your application. Now consider the distance. The distance your wire needs to go can impact the gauge size you need. The longer the wire, the more voltage you can lose through resistance and heat.
This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website.
.
This converter has two text fields and control buttons that are used to execute different actions during the calculations. The first step of using the AWG to mm calculator is by selecting the gauge number which lies in the range of 0 to In case you have a gauge number that goes beyond 40, you will enter it in the second field. Enter gauge. It executes the conversions within a single click displaying the result in millimeters mm. You will also get the cross sectional area in square millimeters which is calculated automatically with the diameter in millimeters. The diameter of the gauge number 36 is 0. For example; If the American wire gauge is 56 AWG , find the diameter in millimeters and the Cross sectional area in square millimeters. The gauge number is more than 40 and hence you will enter the value in the blank text field. We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits.
Awg to mm2 conversion
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable.
Trivago tr
For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. Expandable Sleeving. AWG is also related to resistance. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. Fire Alarm Cable. If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Foundation FieldBus. CAT7 Industrial. One way to counteract voltage drop is by increasing the wire gauge, which increases your amperage capacity, allowing you to pump more amperage through and ultimately, give you enough electricity for the intended application. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. Portable Cord.
In reality there is no exact correspondence between these two types of measurement since the specifications of both systems differ in terms of specification and resistance, however with the following application you can have a very good reference. It is an American standard for the size of conductors and cables. The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum, and other wire materials.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Packaging Equipment. Cable Ties. Now consider the distance. High Temperature Control Cable. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are as essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. High Temperature Wire. Please complete the form below, or call us at Download the conversion table in PDF format here. With this table, you can quickly convert between these two units of measurement and ensure that you are using the correct cable for your application. Explore our tables below to see close approximations between AWG and metric sizes.

I understand this question. Is ready to help.
You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is excellent thought. I agree with you.