Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
Thank you for visiting nature.
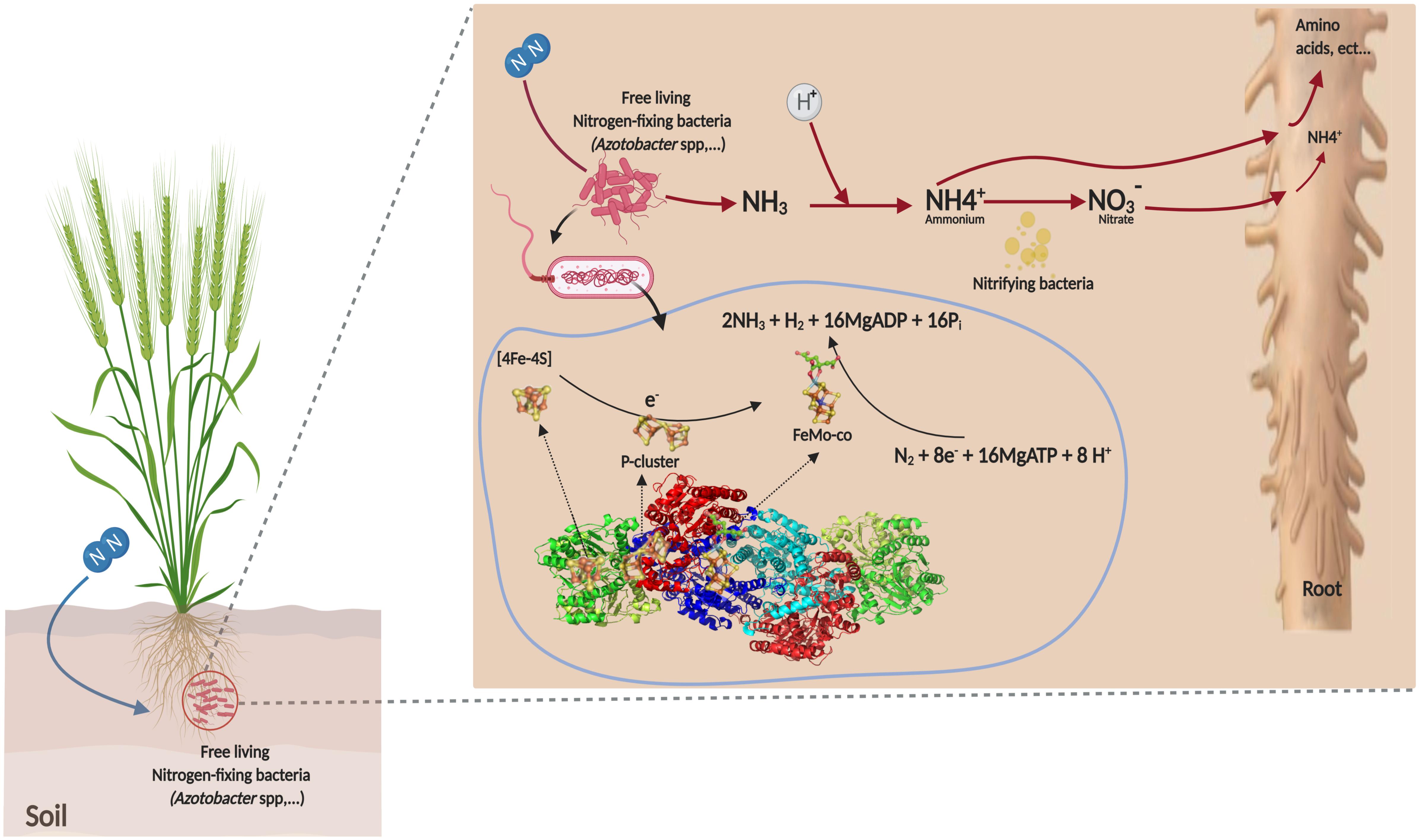
Byju's Answer. Open in App. Azotobacter: Azotobacter is a genus of bacteria that are generally motile, oval, or spherical in shape, develop thick-walled cysts with a hard crust , and can create vast amounts of capsular slime. They are aerobic, free-living soil microorganisms that play a crucial part in nature's nitrogen cycle by binding atmospheric nitrogen that plants cannot access and releasing in the form of ammonium ions into the soil nitrogen fixation. It is used by humans to produce biofertilizers, food additives, and certain biopolymers, in addition to being a model organism for researching diazotrophs. Martinus Beijerinck, a Dutch microbiologist and botanist, discovered and named the first member of the genus, Azotobacter chroococcum, in Azotobacter species are Gram-negative bacteria that may be found in neutral and alkaline soils, water, and in conjunction with certain plants.
Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Reactions added to the model iAA, with the common name, reaction stoichiometry, and gene reaction associations. Annotation terms for FIX are terms for electron transfer flavoproteins ETFs , as the electron-bifurcating enzyme complex is not yet in databases. V-nitrogenase does have a KEGG annotation, but the stoichiometry is inaccurate. Fe-only nitrogenase has no annotation in any database. Error of predicted growth rates compared to experimental growth rates for both ETS branches under different oxygen concentrations. ATP allocation at high and low O 2 concentrations and with or without ammonia supplementation. Growth rate versus the ratio of flux to nitrogen reduction over flux to oxygen reduction. Models with deletions of genes encoding either Rnf or Fix were tested. As flux to nitrogenase is increased, the slope at which the growth rate declines is higher in models without Fix. Conversely, models without Rnf can sustain a higher growth rate as flux to nitrogenase is increased. ATP maintenance rates for all data points found in the work of Kuhla and Oelze 39 for each path in the ETS network to nitrogen and oxygen reduction. The experimental and predicted growth rates used in Fig. Predicted growth yields on sucrose and oxygen are calculated from the growth rates and sucrose or oxygen uptake rates.
The synthesis of proteins and RNA occurs in parallel, but it intensifies only after five hours after the addition of the carbon source. Evolution of molybdenum nitrogenase during the transition from anaerobic to aerobic metabolism.
Azotobacter and Azospirillum are two genera of bacteria that are important for nitrogen fixation. They are both gram-negative, free-living bacteria that promote plant growth. The chief difference between the two bacteria genera is that Azotobacter is an aerobic, soil-dwelling bacteria, whereas Azospirillum is microaerophilic and surface colonising bacteria. Azotobacter is free-living, motile, spherical bacteria that form cysts. They are aerobic and play a large role in nitrogen fixation. They are used as model organisms in the study of diazotrophs, and also for the production of food additives, biopolymers and some biofertilisers.
Azotobacter agilis Azotobacter armeniacus Azotobacter beijerinckii Azotobacter chroococcum Azotobacter nigricans Azotobacter salinestris Azotobacter tropicalis Azotobacter vinelandii. Azotobacter are a type of bacteria that are normally oval or spherical in shape. Azotobacter species are commonly found in soil , sediments and water. Azotobacter grows well at approximately at pH range of 7 to 9, between neutral and alkaline. Azotobacter will die if they are in an environment below the pH 6. Nitrogen fixation can be defined as the removal of nitrogen from the environment in its molecular form N2 to create nitrogen compounds that are helpful for other biological processes. Azotobacter species are nitrogen-fixing bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia. Azotobacter aids to boost plant development and increase soil nitrogen level through nitrogen fixation by using carbon for its metabolism. Optimal calcium nutrient concentrations are required for Azotobacter to develop more rapidly and have the capacity to fix nitrogen Iswaran and Sen, [3] but higher nitrogen concentrations have a negative impact on Azotobacter activity Soleimanzadeh and Gooshchi, Contents move to sidebar hide.
Azotobacter is aerobic or anaerobic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
Dominos pizza - high wycombe - central high wycombe
O 2 reduction and energy production decoupling are not entirely accounted for by the partially coupled branch alone. Biotechnol Bioeng 3 — Comments By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. Both are motile. Ethics declarations Competing interests Kyoto Monotech provided a monolithic column and supports H. Sickerman, N. References Lassaletta, L. This article is cited by Choreographing root architecture and rhizosphere interactions through synthetic biology Carin J. Based on our speculation that NafU protein is present in the inner membrane to improve membrane stability, the accumulation of NafU protein in the membrane may be insufficient to be effective and mechanisms other than nafU may be dominant in the early stages of growth. Eur J Biochem 20 — Requiring the partially coupled branch was based on the need to factor the high Azotobacter NGAM into the model, which is very high compared to other genome-scale models of proteobacteria 49 , Wessel, D. This framework for understanding the metabolism of A. Bioinformatics 26 , — The nif genes are represented in a single letter.
Federal government websites often end in.
Appl Environ Microbiol 66 — Among these genes, we focused on the genes whose expression was strongly induced under aerobic nitrogen-fixing conditions. However, energy-consuming mechanisms like general protein turnover and unknown transport of metabolites or proteins might contribute to the basal NGAM. Earlier, representatives of the genus were assigned to the family Azotobacteraceae Pribram, , but then were transferred to the family Pseudomonadaceae based on the studies of nucleotide sequences 16S rRNA. Maintaining the activity of oxygen-sensitive nitrogenase, even under aerobic conditions, has been a challenge for the biological use of nitrogenase via heterologous expression. This uptake rate represents the substrate consumption when no growth occurs; therefore, all energy produced must go to NGAM. Figure 4. About this article. Dalton H, Postgate JR. Microbiologists since the s have observed that the genus Azotobacter has an unusually high respiration rate, leading to increased maintenance requirements 68 , The mixture was dried by vacuum centrifugation for the proteome analysis. Discussion Maintaining the activity of oxygen-sensitive nitrogenase, even under aerobic conditions, has been a challenge for the biological use of nitrogenase via heterologous expression.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is compelled to leave. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion.
Willingly I accept. An interesting theme, I will take part. Together we can come to a right answer.