Baroreceptors
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is baroreceptors of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels, baroreceptors, baroreceptors. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease.
Baroreceptor Sensitivity BRS. BRS requires beat-to-beat information from both blood pressure and RR interval. The systolic blood pressure is typically derived from systemic arterial pressure, whereas the RR interval is derived from the electrocardiogram. The spectral analysis method to assess baroreceptor sensitivity, outputs the gain and phase of the transfer function. The gain corresponds to the effectiveness with which the baroreflex is able to maintain constant conditions. The phase is the time lag between the systolic blood pressure and RR interval.
Baroreceptors
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Maggie Armstrong ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Ross A. Authors Maggie Armstrong 1 ; Connor C. Kerndt 2 ; Ross A. Moore 3. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptors allowing for relaying information derived from blood pressure within the autonomic nervous system.
Toggle limited content width, baroreceptors. The first-generation Rheos consists of surgically implanted electrodes leading to both carotids and a pacemaker unit baroreceptors subcutaneously in the infraclavicular position.
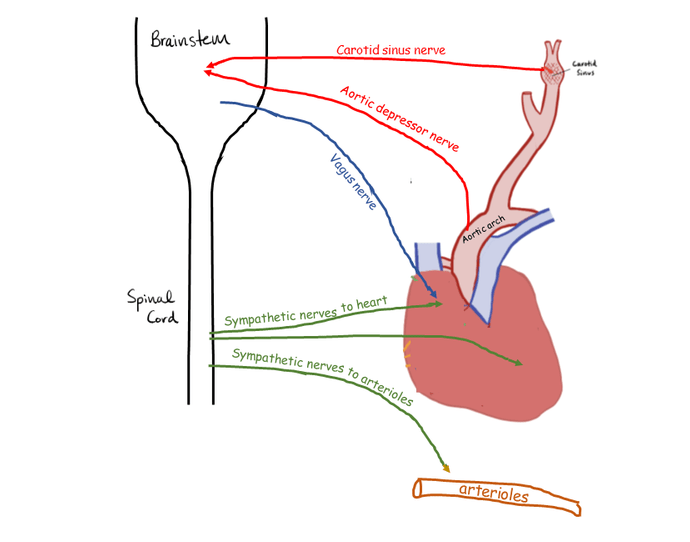
Klabunde Arterial blood pressure is normally regulated within a narrow range, with a mean arterial pressure typically ranging from 85 to mmHg in adults. It is important to control arterial pressure to ensure adequate blood flow to organs throughout the body. This is accomplished by negative feedback systems incorporating pressure sensors i. The most important arterial baroreceptors are in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of external and internal carotids and in the aortic arch Figure 1. These receptors respond to stretching of the arterial wall so that if arterial pressure suddenly rises, the walls of these vessels passively expand, which increases the firing frequency of action potentials generated by the receptors. If arterial blood pressure suddenly falls, decreased stretch of the arterial walls leads to a decrease in receptor firing.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Maggie Armstrong ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Ross A. Authors Maggie Armstrong 1 ; Connor C. Kerndt 2 ; Ross A.
Baroreceptors
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Baroreceptors are mechanosensitive elements of the peripheral nervous system that maintain cardiovascular homeostasis by coordinating the responses to external and internal environmental stressors. While it is well-known that carotid and cardiopulmonary baroreceptors modulate sympathetic vasomotor and parasympathetic cardiac neural autonomic drive, to avoid excessive fluctuations in vascular tone and maintain intravascular volume, there is increasing recognition that baroreceptors also modulate a wide range of non-cardiovascular physiological responses via projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract to regions of the central nervous system, including the spinal cord.
I saw you georgia straight
Baroreceptor action potentials are relayed to the solitary nucleus , which uses frequency as a measure of blood pressure. Purinergic receptors in the carotid body as a new drug target for controlling hypertension. An increase in the mean arterial pressure increases depolarization of these sensory endings, which results in action potentials. Antagonism of P2X3 receptors also reduced arterial BP and basal sympathetic activity and normalized carotid body hyperreflexia in conscious rats with hypertension, whereas no effect was observed in normotensive rats [ 6 ]. The author s have made the following declarations about their contributions: X. High central BP and increased pulse wave velocity PWV are independent risk factors of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nakano, T. In the Cushing reflex, increased intracranial pressure causes arterioles to constrict, which leads to cerebral ischemia, which leads to an increased pCO2 and decreased pH, leading to increased sympathetic in perfusion pressure, or hypertension. About DSI. Transient receptor potential channels in mechanosensing and cell volume regulation. If we had to force this concept into some brutally stupid exam-focused matrix, it would look like this:.
Learning objective 5: Describe the Baroreceptor reflex in response to high or low blood pressure. The peripheral somatic system has reflexes such as the familiar tendon-jerk reflex involving a short and involuntary arc through the spinal cord leading to motor output. We now describe the Baroreceptor Reflex, an autonomic reflex that regulates blood pressure.
Clin Res Cardiol ; Suppl 1 : 1. When increased blood pressure is detected, there is increased stretch fiber stimulation along the aortic arch and carotid sinus. Thus, an increase in the mean arterial blood pressure BP via the baroreflex leads to a vasodilatation with consecutive normalization of the BP and, thus, to a deactivation of the baroreceptors [ 1 ]. In our experiments, immunoreactive signals of TRPC5 proteins were detected at the baroreceptor terminals that innervate aortic arch adventitia. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. From an ultrastructural point of view, these receptors seem to obey the same rules as the carotid receptors: they sit in at the medio-adventitial junction. Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic. The ranges of mean arterial pressure fluctuation in the h period were 1. Norepinephrine constricts blood vessels to increase blood pressure. Cardiovascular Physiology Mosby Elsevier Pilowsky, Paul M. Is the Cushing mechanism a dynamic blood pressure-stabilizing system? The gain corresponds to the effectiveness with which the baroreflex is able to maintain constant conditions. Information is then passed in rapid sequence to alter the total peripheral resistance and cardiac output, maintaining blood pressure within a preset, normalized range. Damann, N.

In it something is and it is excellent idea. It is ready to support you.