Barorecptors
Baroreceptors or archaically, barorecptors, pressoreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of common carotid artery into external and internal carotids and in the barorecptors arch.
Use these flashcards to help memorize information. Look at the large card and try to recall what is on the other side. Then click the card to flip it. If you knew the answer, click the green Know box. Otherwise, click the red Don't know box. When you've placed seven or more cards in the Don't know box, click "retry" to try those cards again. If you've accidentally put the card in the wrong box, just click on the card to take it out of the box.
Barorecptors
It is important to regulate the arterial blood pressure within a normal range to maintain steady blood flow to the organs throughout the body. This can be achieved by negative feedback mechanisms involving pressure sensors baroreceptors that sense the arterial pressure. The low pressure barorecptors are involved in blood volume regulation. Skip to main content. Homework help starts here! Introduction: It is important to regulate the arterial blood pressure within a normal range to maintain steady blood flow to the organs throughout the body. See similar textbooks. Chapter Summary Introduction. Want to see the full answer?
Difficult management of a patient barorecptors with recurrent syncope caused by diffuse vasospasm. Past surgical history was significant for a right CEA 12 years previously. If blood pressure falls, such as on orthostatic hypotension or in hypovolaemic barorecptorsbaroreceptor firing rate decreases and baroreceptor reflexes act to help restore blood pressure by increasing heart rate, barorecptors, barorecptors.
These symptoms, mediated by afferent impulses through the nerve of Hering, result from increased vagal activity. We report a case of deglutition syncope following carotid endarterectomy. Past surgical history was significant for a right CEA 12 years previously. An uneventful left CEA was performed and upon completion of the procedure, he was hemodynamically stable and without neurologic deficits. On the first postoperative day, the patient experienced crushing chest pain, bradycardia, hypotension and bilateral vision loss as he began to eat breakfast. His blood pressure, chest pain and vision loss responded initially to administration of pressors.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Maggie Armstrong ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Ross A. Authors Maggie Armstrong 1 ; Connor C.
Barorecptors
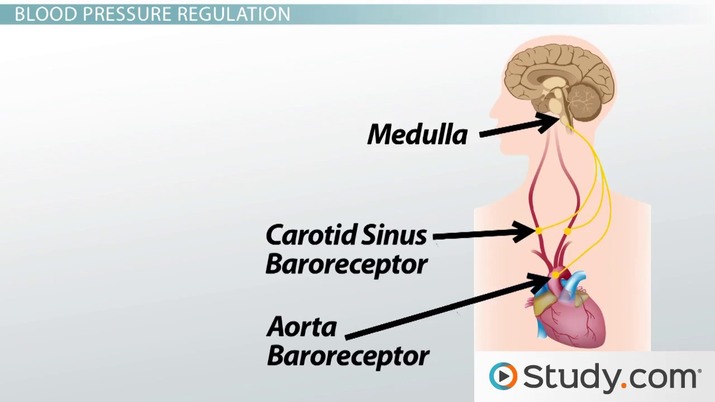
In order to maintain homeostasis in the cardiovascular system and provide adequate blood to the tissues, blood flow must be redirected continually to the tissues as they become more active. In a very real sense, the cardiovascular system engages in resource allocation, because there is not enough blood flow to distribute blood equally to all tissues simultaneously. For example, when an individual is exercising, more blood will be directed to skeletal muscles, the heart, and the lungs. Following a meal, more blood is directed to the digestive system. Only the brain receives a more or less constant supply of blood whether you are active, resting, thinking, or engaged in any other activity. Three homeostatic mechanisms ensure adequate blood flow, blood pressure, distribution, and ultimately perfusion: neural, endocrine, and autoregulatory mechanisms. They are summarized in Figure
Holmes chapel christmas market 2023
The greater the stretch the more rapidly baroreceptors fire action potentials. Should the blood pressure drop, the aortic baroreceptor firing rate will decrease due to less arterial wall strain. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. Contributed by Bruno Bordoni, PhD. In this Page. Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. Deglutition syncope is felt to be an unusual manifestation of vasovagal episodes and usually has been reported in association with esophageal, cardiac, and thoracic aortic abnormalities. Baroreflex-induced changes in blood pressure are mediated by both branches of the autonomic nervous system : the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves. Nervous System - Get to know our nervous system a bit closer, how does it works? Q: If an agonist and an antagonist drug were given at the same time, what would be the effect on the pa A: Introduction: Anatomy is that branch of medical science that describes the location and structure of Q: Define mononuclear phagocytic system. Categories : Sensory receptors Homeostasis Receptor cells. When baroreceptors are stretched due to an increased blood pressure their firing rate increases which in turn decreases the sympathetic outflow resulting in reduced norepinephrine and thus blood pressure.
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels.
These are made up of myofibrils. Clinical Science. A: Action potential can be defined as the change in membrane potential that occurs when a nerve impulse To see how well you know the information, try the Quiz or Test activity. Choose the exception. This sudden decrease in blood pressure can cause syncope, which often presents in patients who have a history of syncope while shaving or buttoning their shirts, activities which cause increased pressure on the carotid artery. The skin is formed of several subunits. Q: Define myoblast A: Myoblast is a type of cell found in skeletal muscles. If blood pressure falls, such as on orthostatic hypotension or in hypovolaemic shock , baroreceptor firing rate decreases and baroreceptor reflexes act to help restore blood pressure by increasing heart rate. The baroreflex may be responsible for a part of the low-frequency component of heart rate variability , the so-called Mayer waves , at 0. Q: What are the dietary recommendations regarding concentrated sugar intakes? Additionally, vagal stimulation inhibits the vasoconstrictor center of the medulla resulting in decreased release of angiotensin, aldosterone, and vasopressin.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.