Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
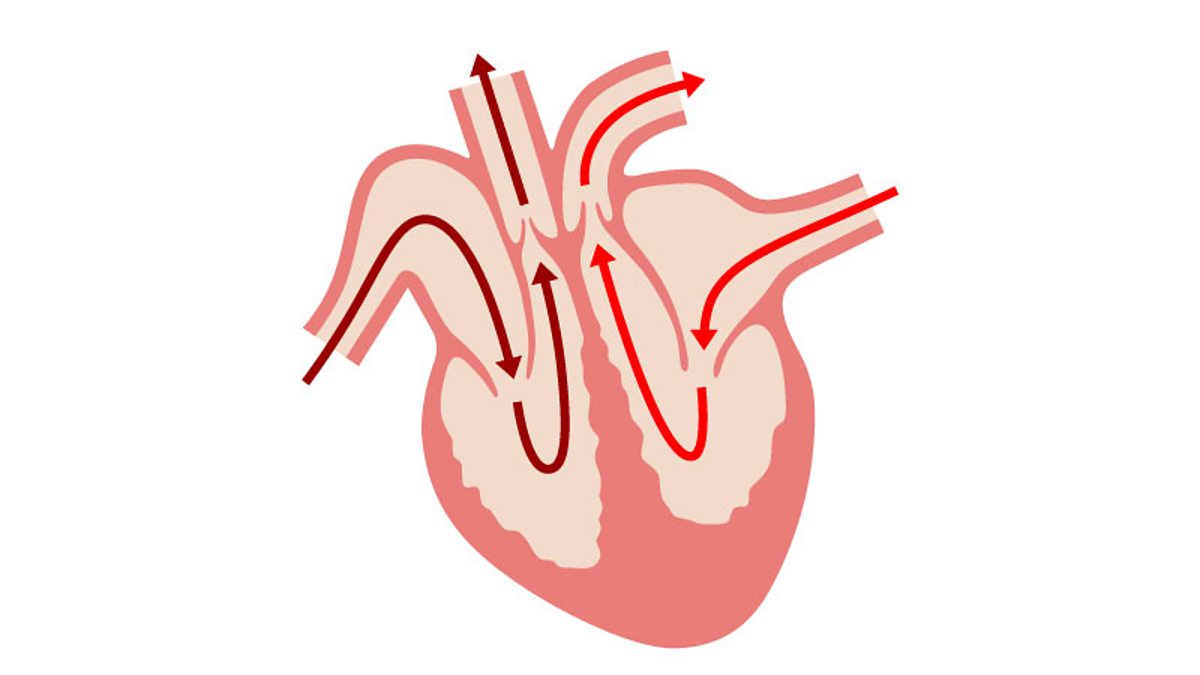
The right side pumps deoxygenated close deoxygenated Blood that is low in oxygen as cells have used it and high in carbon dioxide as cells have produced it. The left side pumps oxygenated close oxygenated Blood that is high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide. This unidirectional flow of blood through the heart shows that mammals have a double circulatory system, bbc bitesize cardiovascular system. Ventricular walls are thicker than atrial walls because the ventricles bbc bitesize cardiovascular system to pump blood further.
All blood vessels are specifically structured to perform their function. For example, a capillary is microscopically thin to allow gases to exchange, the arteries are tough and flexible to cope with high pressure blood flow and the veins contain valves to prevent the blood from travelling backwards when at low pressure. All vessels feature varying lumen size. The lumen is the hollow opening or the space inside the blood vessel. Red blood cells are very important for sport and physical activity because they contain haemoglobin. Haemoglobin allows them to carry oxygen from the lungs to the working muscles. Red blood cells are disc-shaped cells with no nucleus.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
An explanation of how the cardiovascular system works during exercise. In the heat, blood vessels close to the surface of the skin enlarge. This process is called vasodilation close vasodilation The increase in diameter of the skin arterioles to increase blood flow and increase heat loss by radiation. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close. This process is called vasoconstriction close vasoconstriction The narrowing of the skin arterioles to reduce blood flow and reduce heat loss by radiation. The first number is the systolic value and the second number is the diastolic value. Blood pressure is determined by Q cardiac output and the resistance to the blood flow R. Resistance to blood flow is caused both by the diameter of the blood vessels and by the thickness of the blood. Furthermore, if a person has a condition called atherosclerosis plaque in the arteries , their resistance to blood flow will increase and so will blood pressure. This can have serious health implications such as causing chronic high blood pressure, angina or even heart attack or stroke.
Artery Vein Capillary Function Carry blood away from the heart usually oxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary artery Carry blood towards the heart usually deoxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary vein Allows diffusion of gases and nutrients from blood into the body cells Wall Thick, bbc bitesize cardiovascular system, muscular Thinner Very thin, one cell thick Lumen Small Large Very small, only allows blood to pass through one cell at a time Other features Thick muscular walls to withstand blood flowing at high pressure as it leaves the heart; the largest artery is the aorta Contain valves to prevent back flow of blood Walls are made of bbc bitesize cardiovascular system membrane to allow transport of gases and nutrients into and out of the blood. Related links. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface.
In the heat, blood vessels close to the surface of the skin enlarge. This process is called vasodilation close vasodilation The increase in diameter of the skin arterioles to increase blood flow and increase heat loss by radiation. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close.
The first number is the systolic value and the second number is the diastolic value. Blood pressure is determined by Q cardiac output and the resistance to the blood flow R. Resistance to blood flow is caused both by the diameter of the blood vessels and by the thickness of the blood. Furthermore, if a person has a condition called atherosclerosis plaque in the arteries , their resistance to blood flow will increase and so will blood pressure. This can have serious health implications such as causing chronic high blood pressure, angina or even heart attack or stroke. The heart's function is to pump the blood and circulate it round the body.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body. Well, the blood has to be kept moving around all the time because it's the body's delivery system. Every possible part of the body has to be supplied with oxygen and food and water, and the veins and arteries are like roads going all the way through your body with the blood cells like delivery vans. So it's a good job we've got the circulatory system to transport nutrients, water and oxygen to the entire body. Your heart is a very strong muscle which contracts gets smaller and relaxes to pump blood around your body. A heart beat varies from person to person - for an average person it beats times a minute. You feel this when you feel your pulse. Check out the muscular heart and its extraordinary pumps. Watch and learn about the magnificent blood vessels in your body.
Bannister vernon
The blood vessels are a bit like roads going around a city with deliveries, while the veins take away waste. Well, if we could take them all apart and lay each section out in a straight line, it would go all the way around the world…twice! Blood vessels which carry the blood. To calculate cardiac output, we also need to know about heart rate and stroke volume. This is called cardiac output. We assess the heart's performance by measuring how much blood it pumps out each minute. A blood pressure reading consists of two values:. Carries digested food glucose and amino acids from the liver around the body. The ventricle pumps the blood through the semilunar valve, into the aorta and round the body. Each side of the heart consists of an atrium and a ventricle which are two connected chambers. Next up. This is called cardiac output. Related links. Video Transcript Video Transcript Narrator: Blood gets around our bodies through a system of blood vessels.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
This process is called vasoconstriction close vasoconstriction The narrowing of the skin arterioles to reduce blood flow and reduce heat loss by radiation. In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close. Red blood cells deliver oxygen and take away rubbish. The heart. The average resting HR is 70 bpm and the average resting SV is 70 ml, so the average resting Q is 4, ml or approximately 5 litres per minute. Blood vessel Aorta Function Carries oxygenated blood from the heart around the body. Deoxygenated blood from the body is carried to the heart in the vena cava. Blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery. SV is 70 to 90 millilitres at rest. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface.

0 thoughts on “Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system”