Bbc bitesize plant cell
Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. Plants capture light from the sun and use it to build up chemical stores of energy.
There are many different types of cells in animals. Each type is specialised for a particular role. These ensure that the organism functions as a whole. The head of the sperm contains the genetic material for fertilisation. The acrosome in the head contains enzymes so that the sperm can penetrate an egg. The middle piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg. The tail enables the sperm to swim.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
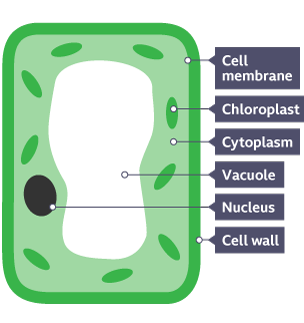
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. There are many different types of cells in plants. Each type is specialised to do a particular role and ensures that the organism functions as a whole. There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them. Strands of cytoplasm run through holes in the sieve plates, connecting the sieve tubes that make up the phloem. Companion cells, adjacent to the sieve tubes provide energy required to transport substances in the phloem. Plant cells can be observed in a laboratory, using a light microscope. Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds. Dr Alex Lathbridge breaks down the key facts about specialised animal and plant cells. In this guide. Light microscopes Electron microscopes Animal cells Plant cells Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Required practical - using a light microscope Measuring cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Maths - using units, decimals and standard form Maths - orders of magnitude. Plant cells. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common.
They are well adapted for this function because: they are towards the tops of leaves for maximum light they have lots of chloroplasts.
Learn about specialised plant cells. Like animal cells, basic plant cells have a nucleus, a cell membrane and cytoplasm. They've also got a vacuole, chloroplasts and a cell wall, which are only found in plant cells and they can be a bit bigger than animal cells. Plants also have some very specialised cells. Root hair cells don't have light absorbing chloroplast because they don't absorb light because they're underground. What they do have is a wide surface area to more efficiently absorb water and minerals. Xylem cells lose their end walls so they can form continuous tubes almost like pipes to transport that water up to stems and leaves.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with a transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Electron microscopes Animal cells Plant cells Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Investigating cells with a light microscope Measuring cell size Comparing sizes. Plant cells. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common. Cell structure How it is related to its function Cytoplasm A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. Plants capture light from the sun and use it to build up chemical stores of energy. This is called photosynthesis.
National treasure page 47
Has a tail. Structure Cell wall Function Made from cellulose fibres. The differences between animal and plant cells. Activity - Plant cell structure. Animal cells Plant cells Yeast cells - an example of a fungus Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Specialised cells Comparing sizes Cell measurement Required practical activity - microscopy Preparing biological samples for examination Using a microscope to measure cell size. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent - I agree - No thanks - Find out more. Describe the purpose and adaptations of xylem and phloem cells. Contains DNA which carries the genetic code for making enzymes and other proteins used in chemical reactions such as photosynthesis and respiration. Bacteria are single-celled organisms and were only discovered in the s. Working safely in the lab. The skeletal system.
Click to play the game. You can also play the full game. Find out how to observe cells under a microscope.
The four components of the blood. In skeletal muscle, the cells merge so that the muscle fibres contract in unison. All cells require oxygen to release energy. This video can not be played To play this video you need to enable JavaScript in your browser. Plant cells. Cell wall Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant. Biology was probably my favourite subject funnily enough. Cell wall Made from cellulose fibres. More guides on this topic. Contains haemoglobin. Plants feel firm because of their cellular walls. Cell membrane. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. More guides on this topic.

0 thoughts on “Bbc bitesize plant cell”