Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
The brain is a soft and delicate organ. A hard blow to the head can injure the brain or spinal cord even when there are no visible signs of trauma to the scalp or face. The soft, jelly-like brain is protected by the skull. This fluid acts as a shock absorber, but its protective value is limited.
TBI can cause inflammation and swelling or bleeding from damage to brain tissue and blood vessels. According to CDC data, approximately 2. An estimated Bleeding may occur within the brain an intracranial hemorrhage or the protective layers that surround it, such as an epidural, subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage. The brain is tightly enclosed within the skull.
Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
Children also frequently bang their heads and it is difficult to tell whether or not they have done any serious damage. Although, most head injuries are not serious and simply result on a bump or bruise. However, severe or repeated head injuries can cause damage to the brain. Most blows to the head result in injury to the scalp only and although this is more frightening than life-threatening, it can still be a cause for concern. The head and face are very vascular which means these injuries bleed profusely and can be very scary! It is very important to look out for anything unusual following a head injury; a severe bang on the head could cause swelling and damage to the brain and it is vitally important that you recognise any early and worrying signs of increased pressure on the brain. If the child has not lost consciousness and is alert and behaving normally after the fall or blow:. The brain is cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid, however a severe blow to the head may knock the brain into the side of the skull see above or tear blood vessels. A clear indicator of a serious injury is when a child loses consciousness or has signs of confusion. These symptoms can come on at any time from immediately after the accident to a couple of days later. It is sensible to have your child sleep in the same room as you for a couple of nights following a head injury.
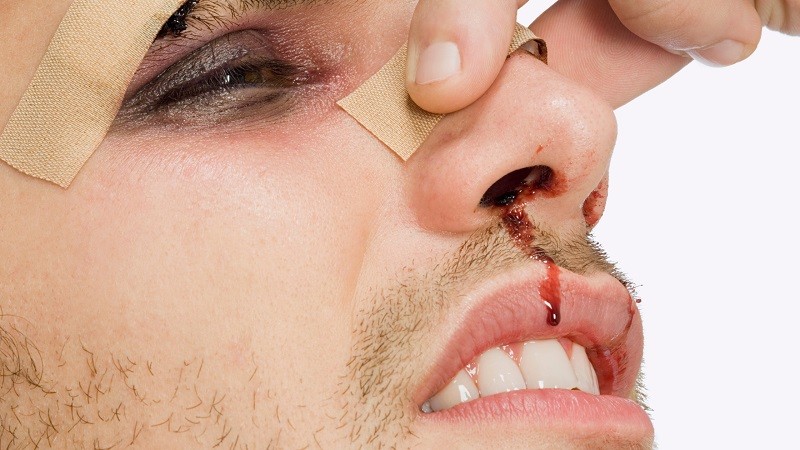
Doorbell video shows Phoenix firefighters discouraging ambulance transport. Time is brain, and the chance of disability or death increases with any delay. Have yuot patient blow out any poorly formed clots into a handful of tissues.
To give first aid to a person who has head trauma, call or your local emergency number. Any of the following symptoms may indicate a serious head injury:. Head trauma that results in concussion symptoms need to be evaluated by a medical professional. Concussion symptoms include nausea, unsteadiness, headaches or difficulty concentrating. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
To take the CE test that accompanies this article, go to www. E-mail editor EMSWorld. Facial trauma can result from a wide variety of blunt and penetrating mechanisms ranging from trivial to life-threatening, including motor vehicle collisions, violent altercations, falls from any height, person-to-person collisions, gunshots and stabbings, vehicle vs. Geriatric and pediatric patients have their own unique mechanisms. Kids experience facial trauma running into walls, table and counter edges, other kids, and all sorts of stationary objects like playground equipment. Geriatric patients experience facial trauma secondary to falls because they lack the quick reaction time needed to protect themselves as they fall. We had a case where an year-old male patient stood up quickly from his recliner, felt faint, lost his balance and fell forward, hitting his head on the floor. His face was the first point of impact. His nose was fractured and he had a profuse anterior nose bleed. He simply couldn't react fast enough to brace himself with an outstretched hand.
Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt
Primary injuries occur at impact, but secondary brain injuries may be preventable with proper initial EMS care. Traumatic head injuries account for 2. More than 10 percent of these head injuries are hospitalized, from which nearly 53, die. This is more than one-third of all injury-related deaths. In the past, it was thought that there was little that prehospital care providers could do for patients with head injuries, but new research and expanding partnerships with emergency trauma teams reveal that EMS is critical in improving outcomes for these patients. Primary brain injury and secondary brain injury are terms that classify the processes that occur when a patient suffers head trauma.
Cuddle weather full movie free online
Anterior nosebleeds produce a steady ooze. Put a bandage over the dressing to keep it in place. Well-aimed direct pressure will stop most bleeding. Facial fractures, July 13, If blood is refilling the hypopharynx faster than you can suction, digital intubation or a surgical airway may be indicated. Control epistaxis with well-aimed direct pressure for 10—15 minutes. Skull deformities — compressions or deformities are signs of fractures t. All Rights Reserved. This is best done by firmly pinching the nostrils together and holding pressure for at least 10 minutes. While examining the wound, avoid disturbing blood clots forming in the hair. It may be possible to determine the source of the nosebleed by the flow of blood. Follow Mayo Clinic.
To give first aid to a person who has head trauma, call or your local emergency number. Any of the following symptoms may indicate a serious head injury:. Head trauma that results in concussion symptoms need to be evaluated by a medical professional.
They can be a result of warm weather or exercise, which dilate the small blood vessels in their nose, or they can be the result of picking or poking their noses, or running into things. EMS providers are also at risk for head injuries in the back of a moving ambulance. Imagine the horse hoof mentioned previously or a well-hit racquetball. Although, most head injuries are not serious and simply result on a bump or bruise. Minor head trauma in infants and children: Evaluation. Epistaxis, May 21, If bleeding is prolonged or copious, hypovolemia can become a complication. Top Stories. Signs and symptoms of intracranial bleeding may be delayed, especially in elderly people. Use an oral or nasal airway if the patient will tolerate it, position the patient on their left side to help prevent aspiration, and suction secretions. Put the body part in a sealed plastic bag — keep it dry. Rather, the weakening of blood vessels that occurs with chronic hypertension increases the occurrence of epistaxis for hypertension patients. Medical attention should be sought immediately if the child shows any signs of serious head injury, particularly if: they are unusually drowsy or vomiting you think the fall was heavy enough to have caused harm the child appeared to be unconscious or did not immediately cry after the fall. Reviewed on: Internal Bleeding This is when the person is bleeding inside their body.

0 thoughts on “Bleeding from the nose following head trauma emt”