Bond angle of bh3
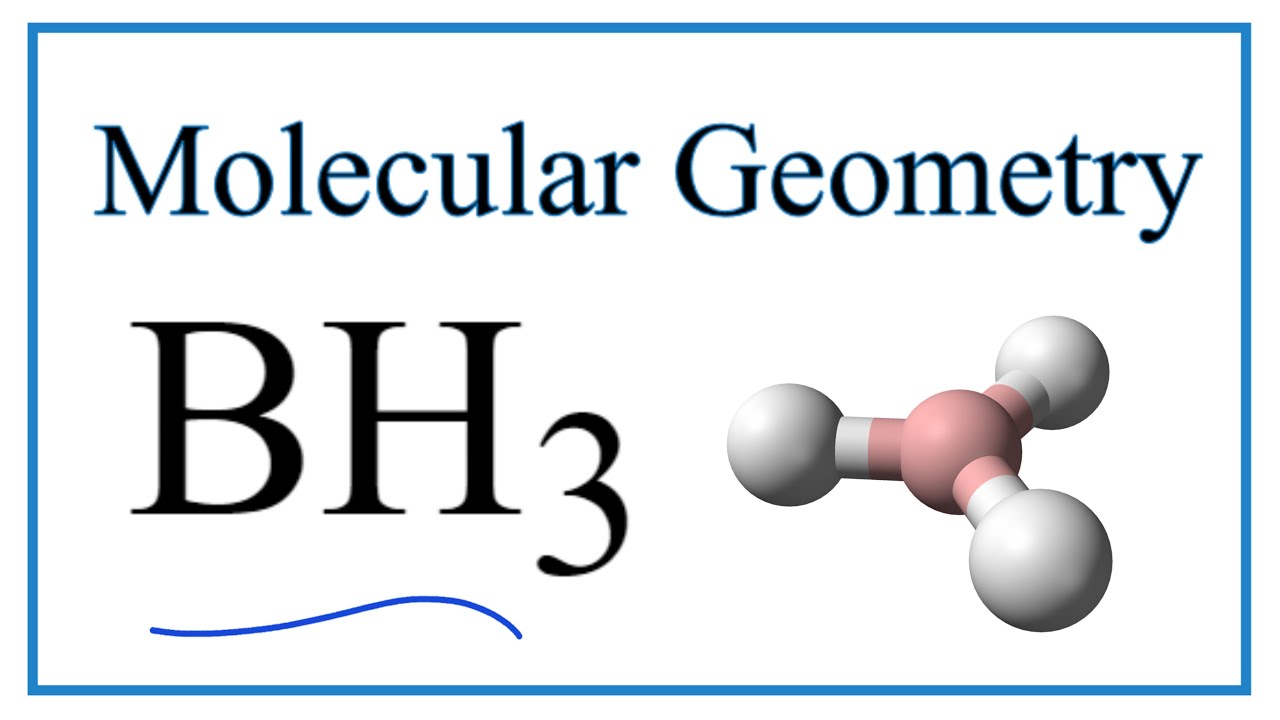
Wiki User. BH3 has a trigonal planar shape with angles.
In this video, you will learn about the different types of molecular geometry and their ideal bond angles from VSEPR theory. This video gives examples of different molecules that have different geometries, as well as helps give tips on how to identify the geometry and ideal bond angle of different molecules. The ideal bond angles are the angles that would be formed if all of the electron domains surrounding an atom were arranged in a perfectly symmetrical manner. Ultimately, these ideal bond angles are usually not quite correct , because lone electron pairs repel other electron pairs more strongly than bonding electron pairs. However, the ideal bond angles are still usually pretty close to the true bond angles. If there is 1 electron domain surrounding an atom, then there are no associated electron domain geometry and ideal bond angles.
Bond angle of bh3
Trending now This is a popular solution! General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry 3rd Edition. Skip to main content. Homework help starts here! Publisher: Cengage Learning. What is HCH bond angle implied by this Problem 17CTQ: Indicate the bond angle and shape about each central atom. Problem 20CTQ: A student who missed this class needs to know how to predict the bond angles and shape of amolecule Assume the atom is neutral, and write Problem 4E: How many valence electrons does a neutral a.
What is the molecular geometry of nh3o? Because they have access to the d - orbitals.
.
The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. This approach gives no information about the actual arrangement of atoms in space, however. Keep in mind, however, that the VSEPR model, like any model, is a limited representation of reality; the model provides no information about bond lengths or the presence of multiple bonds. The VSEPR model can predict the structure of nearly any molecule or polyatomic ion in which the central atom is a nonmetal, as well as the structures of many molecules and polyatomic ions with a central metal atom. The premise of the VSEPR theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. This theory is very simplistic and does not account for the subtleties of orbital interactions that influence molecular shapes; however, the simple VSEPR counting procedure accurately predicts the three-dimensional structures of a large number of compounds, which cannot be predicted using the Lewis electron-pair approach. We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of most polyatomic molecules and ions by focusing only on the number of electron pairs around the central atom , ignoring all other valence electrons present. According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups , which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, a lone pair of electrons, or even a single unpaired electron, which in the VSEPR model is counted as a lone pair. Because electrons repel each other electrostatically, the most stable arrangement of electron groups i. In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AX m E n designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group usually a lone pair of electrons , and m and n are integers.
Bond angle of bh3
Borane , also known as borine , is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula B H 3. The preparation of borane carbonyl , BH 3 CO , played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated the likely existence of the borane molecule. Consequently, it is highly reactive and can only be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen.
Best cavitation machine for home use
K atom have? Trending now This is a popular solution! Based on your model, draw a bond-line representation What is the formal charge on each atom in PH4 and the Lewis structure for it? So, it has two bond angles. Can you explain why the answer is NO3-? The bond angle between the N-O bonds is Dichlorine monoxide is a flat inverted v-shaped molecule. They want to be as far from each other as possible! BH3 has a trigonal planar shape with angles.
B atom in BH
Send Feedback. When we handle balloons, they build up a charge. Chemistry by OpenStax All Rights Reserved. This video gives examples of different molecules that have different geometries, as well as helps give tips on how to identify the geometry and ideal bond angle of different molecules. Dichlorine monoxide is a flat inverted v-shaped molecule. They need to minimize their energy. What is HCH bond angle implied by this Each hydrogen atom will spread out evenly. In this video, you will learn about the different types of molecular geometry and their ideal bond angles from VSEPR theory. K atom have? What is the molecular shape for n2f4? Electron domains are the most probable area for finding an electron. Trigonal pyramidal molecules such as ammonia NH3 have bond angle closer to degrees. Trending Questions.

Also that we would do without your very good phrase
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss it.