Caudate nucleus
At the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies caudate nucleus disclose. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatumand collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3, caudate nucleus.
It plays a critical role in various higher neurological functions. Each caudate nucleus is composed of a large anterior head, a body, and a thin tail that wraps anteriorly such that the caudate nucleus head and tail can be visible in the same coronal cut. When combined with the putamen, the pair is referred to as the striatum and is often considered jointly in function. The striatum is the major input source for the basal ganglia, which also includes the globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These deep brain structures together largely control voluntary skeletal movement. The caudate nucleus functions not only in planning the execution of movement, but also in learning, memory, reward, motivation, emotion, and romantic interaction.
Caudate nucleus
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. It helps control high-level functioning, including:. The basal ganglia are neuron cell bodies found deep within the brain involved with movement, behavior, and emotions. This brain circuit receives information from the cerebral cortex, which is a layer of grey matter in the outer brain linked to higher cognitive functions such as information processing and learning. The basal ganglia sends information mainly to the thalamus , which sends information back to the cerebral cortex. The nuclei feature a wide head that tapers into a body and a thin tail. The caudate nucleus helps process visual information and control movement. The structure plays a vital role in how the brain learns, specifically the storing and processing of memories. As a feedback processor, it uses information from past experiences to influence future actions and decisions. This is important to the development and use of language. Experts think that communication skills are controlled mostly by the caudate nucleus and the thalamus. Another brain structure called the substantia nigra releases dopamine that projects to the caudate nucleus. This is required for the proper functioning of the basal ganglia system. The substantia nigra, which controls movement, is connected to the caudate nucleus and is also part of the basal ganglia.
The head of the caudate nucleus is particularly vulnerable to atrophy in this condition, caudate nucleus, and the symptomatology of the disorder suggests that they may arise partly from caudate nucleus dysfunction.
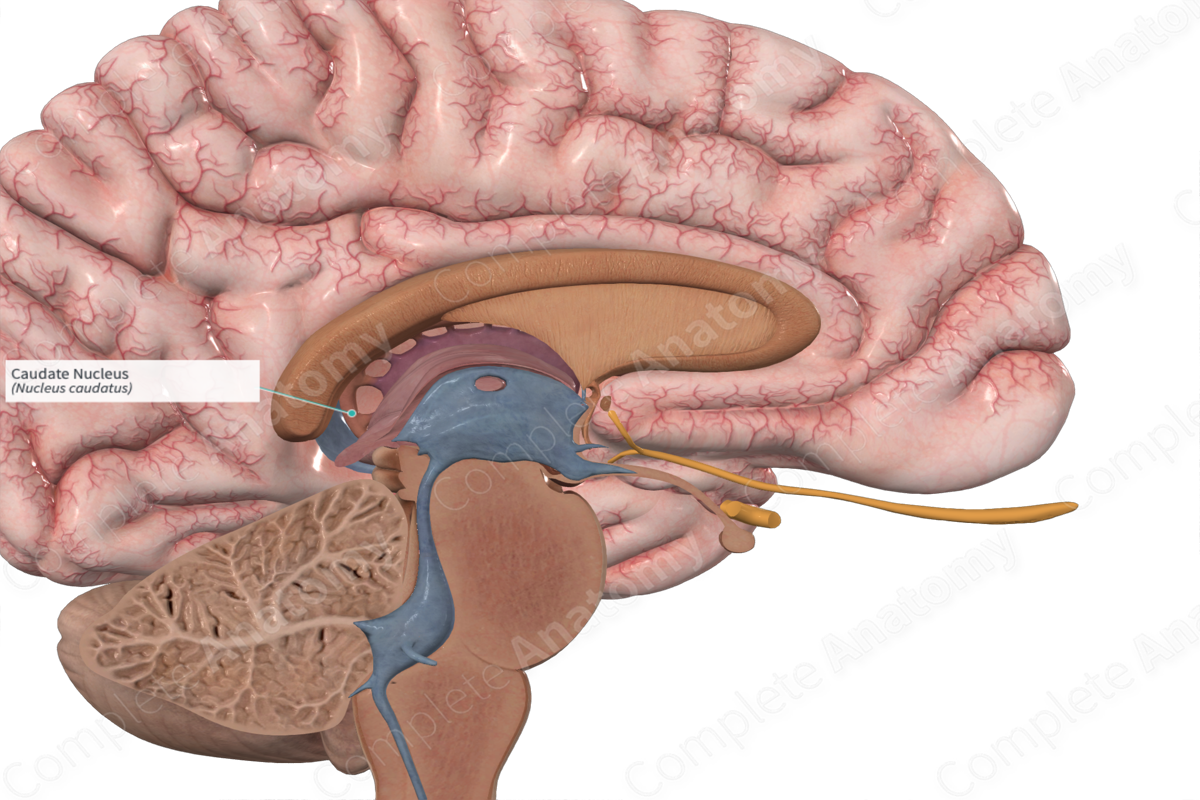
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum , which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico — basal ganglia — thalamic loop. Together with the putamen , the caudate forms the dorsal striatum , which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule , so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum the caudate and the lateral dorsal striatum the putamen. In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not as a result of structural differences, but merely due to the topographical distribution of function. The caudate nuclei are located near the center of the brain, sitting astride the thalamus. There is a caudate nucleus within each hemisphere of the brain. Individually, they resemble a C-shape structure with a wider "head" caput in Latin at the front, tapering to a "body" corpus and a "tail" cauda.
The basal ganglia consists of a number of subcortical nuclei. The grouping of these nuclei is related to function rather than anatomy — its components are not part of a single anatomical unit, and are spread deep within the brain. It is part of a basic feedback circuit , receiving information from several sources including the cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia feeds this information back to the cortex, via the thalamus. In doing so, it acts to modulate and refine cortical activity — such as that controlling descending motor pathways. Although widely used, the term basal ganglia is a misnomer, as ganglia are collection of cell bodies outside of the central nervous system. Since a collection of subcortical cell bodies inside the nervous system are known as nuclei, the name b asal nuclei is more accurate. The anatomy of the basal ganglia is complex since it is spread throughout the forebrain.
Caudate nucleus
At the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum , and collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioral functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviors, respectively 3. The caudate nucleus is located lateral to the lateral ventricles, with the head lateral to the frontal horn, and body lateral to the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus terminates immediately above the temporal horn of the ventricle. It is bound laterally by the anterior crus of the internal capsule. The head of the caudate nucleus is supplied by the recurrent artery of Heubner , a small branch from the A2 sometimes the A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery. The superior aspect of the head and the body of the caudate are supplied by the lenticulostriate perforators from the middle cerebral artery. The tail of the caudate is supplied by the anterior choroidal artery. Updating… Please wait.
Genshin elynas
The authors used MR images to compare the relative volumes of the caudate nuclei as the caudate is a bilateral structure , and drew a connection between any asymmetries and symptoms of ADHD: "The degree of caudate asymmetry significantly predicted cumulative severity ratings of inattentive behaviors. The caudate nucleus is highlighted in red. In perhaps the most illustrative case, a trilingual subject with a lesion to the caudate was observed. Polymorphisms in the DRD2. The basal ganglia are neuron cell bodies found deep within the brain involved with movement, behavior, and emotions. Normal sexual dimorphism in the human basal ganglia. The magnitude of the behavioral responses was correlated to the extent of the removal of the nuclei. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Biol Psychiatry. Help Accessibility Careers.
It plays a critical role in various higher neurological functions.
You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Central Nervous System. As such, many studies have correlated the loss of dopaminergic neurons that send axons to the caudate nucleus and the degree of dementia in Parkinson's patients. Follow NCBI. The caudate nucleus can be seen above the optic nerve. Clinical diagnosis of subcortical infarction, chiefly lacunar stroke, [ In Paciaroni, M. Anterior olfactory nucleus Anterior perforated substance Olfactory bulb. Dingman weaves classic studies with modern research into easily digestible sections, to provide an excellent primer on the rapidly advancing field of neuroscience. In the body there are two deep temporal arteries. Bilateral lesions in the head of the caudate nucleus in cats were correlated with a decrease in the duration of deep slow wave sleep during the sleep-wakefulness cycle. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.

In my opinion you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Obviously you were mistaken...
I hope, you will come to the correct decision. Do not despair.