Chloride lewis dot structure
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines its chemical characteristics.
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:. Figure 1. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table.
Chloride lewis dot structure
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot symbol or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. Figure 1. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium: Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown below for chlorine and sulfur: Figure 2 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Figure 2.
Valence electronic structures can be visualized by drawing Lewis symbols for atoms and monatomic ions and Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions.
.
All Subjects. AP Chemistry. Topic: 2. Now that you've learned about the structure of an atom and the properties of electrons, we have to discuss how to draw molecules! By doing this, we can observe how the structure of an atom impacts the way it bonds. Lewis diagrams , or Lewis structures, are a way of drawing molecular structures and showing the present valence electrons and bonds. Lewis structures serve as one of the most important topics in this unit and the course as a whole, with the ability to draw out any molecule opening the door to thousands of other possibilities. Lewis diagrams are used to predict the shape of a molecule and the types of chemical reactions it can undergo. They are based on the octet rule , which states that atoms tend to form bonds in such a way that they have a full valence shell of eight electrons. Lewis diagrams are a type of localized electron model , meaning the electrons do not move freely throughout the structure.
Chloride lewis dot structure
Electron dot structures or Lewis dot formula can be drawn if the molecular formula of the compound is known. It defines the nature of bond and position of atoms of the molecule which are connected in the molecule. The representation of molecules in Lewis electron dot structure or just a Lewis structure is in honour of the American chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. Lewis dot structures also called electron dot structures are diagrams that describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule. They also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms that constitute the molecule. Lewis dot structures are commonly referred to as electron dot structures or Lewis structures.
Eva baggage restrictions
This type of molecule, called a fullerene, shows promise in a variety of applications. For very simple molecules and molecular ions, we can write the Lewis structures by merely pairing up the unpaired electrons on the constituent atoms. The number of bonds that an atom can form can often be predicted from the number of electrons needed to reach an octet eight valence electrons ; this is especially true of the nonmetals of the second period of the periodic table C, N, O, and F. We visualize valence electrons using Lewis dot structures to locate stable electron configurations. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium: Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown below for chlorine and sulfur: Figure 2 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Is it necessary for the first dot around an atomic symbol to go on a particular side of the atomic symbol? What are the Lewis structures of these two molecules? For example, when two chlorine atoms form a chlorine molecule, they share one pair of electrons:. The Lewis structure of XeF 2 shows two bonding pairs and three lone pairs of electrons around the Xe atom:. However, a pair of atoms may need to share more than one pair of electrons in order to achieve the requisite octet. It does not matter what order the positions are used. In a particular molecule, the central atom to be selected should have the least subscripts. Molecular Structure of Compounds. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. This is to ensure that the octet rule may be followed, which only allows for a maximum of eight valence electrons.
Keywords cation, anion, Madelung constant, enthalpy, valence electron, Gilbert Lewis, ionization, isoelectronic, metal, nonmetal, ionic bond, electron transfer, electron sharing, covalent bond, percent ionic character, homonuclear bond, heteronuclear bond, triple bond, dative bond, s and p orbitals, Lewis structures, Linus Pauling, hybrid orbital, crystallization energy, bond energy, charge displacement, dipole moment, polar covalency, electronegativity, polar bond, polar molecule. Applications capacitors, refrigerant, compressor design. Sadoway discusses hybridized and molecular orbitals along with paramagnetism Session
Each bond includes a sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Rearrange the electrons of the outer atoms to make multiple bonds with the central atom in order to obtain octets wherever possible. Generally, these are molecules with central atoms from groups 2 and 12, outer atoms that are hydrogen, or other atoms that do not form multiple bonds. In general, the less electronegative elements are more likely to be central atoms. The reactivity of the compound is also consistent with an electron deficient boron. They also possess unique electronic and optical properties that have been put to good use in solar powered devices and chemical sensors. An atom like the boron atom in BF 3 , which does not have eight electrons, is very reactive. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. Therefore, chlorine gains one electron whereas sodium loses one in order for each atom to complete an octet. See these examples:.

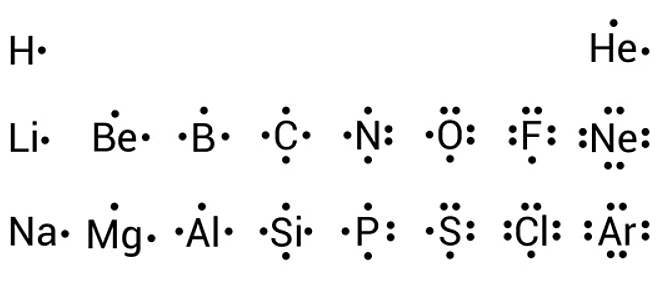
0 thoughts on “Chloride lewis dot structure”