Cross section of a leaf gcse
Learn Teach Quiz Login? The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration.
Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which photosynthesis occurs. Without photosynthesis, there'd be very little life on Earth, because when plants photosynthesise, they take in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen as a by-product. Cal: I am liking plants a lot right now, so let's find out more on how the structures of leaves help plants to photosynthesise. The green of the leaf is the chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs energy from the sun. Some plants have evolved with large leaves to maximise the amount of light they can absorb, often found under forest canopies where they struggle for exposure to light. The cross-section of a leaf reveals its complex structure.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
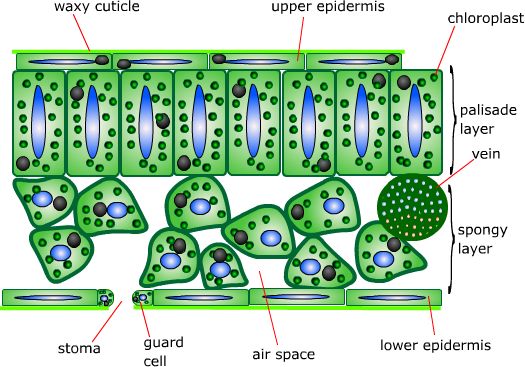
The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many chloroplasts close chloroplast Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. The stomata close stomata Tiny holes in the epidermis skin of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how turgid close turgid Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Diffusion close diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In this guide.
Cal: I mean… Yeah, they're good, aren't they? Ms Armit: That's right. Ms Armit: You're going to put some that nail varnish on both sides of your leaf.
.
Plants are divided into flowers, stems, leaves and roots with root hairs. A generalised plant is shown in the illustration. The stem provides support for the leaves and flowers. It also allows water and food to travel both up and down the plant. The roots anchor the plant in the soil and take up water and salts mineral ions from the soil. The root hairs provide a large surface area for water and salt uptake. The flowers are reproductive organs. They attract insects that carry pollen from one plant to another.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
In angiosperm anatomy, a leaf can be identified by where it emerges from the node. In a node, a leaf emerges below the axillary bud. Leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: the blade and the petiole. The blade is most frequently the flat, photosynthetic part. The petiole is a stem that attaches the leaf blade to the main stem of the plant.
This is our god hillsong chords
They all have the same basic setup. The stomata close stomata Tiny holes in the epidermis skin of a leaf. Feature Cuticle Function A waxy waterproof layer which reduces water loss, it is transparent to allow light through the leaf. It moves by diffusion through small holes in the underside of the leaf called stomata. The upper part of the leaf is where the light falls, and it contains a type of cell called a palisade cell. I mean, they feel a little bit waxy, almost. Would you believe it? Midrib, Veins, Edge, Petiole. Cal: That is very cool. Food chains and webs. Can you answer these questions based on the video? Label the leaf. During the day and night, the plants are constantly respiring to release the energy in glucose so they can live - just like you. Knowledge of leaves is also important to horticulturists. Light A leaf usually has a large surface area, so that it can absorb a lot of light.
Teacher and Student Resources. For a typical leaf, we use that of the umbrella tree, which is commonly sold as a foliage plant throughout North America and Europe. It is actually a tree native to tropical rainforests of northern Australia; it is a good example because we can examine it at any time of the year.
Watch the video to see how a horticulturist uses science in her job. What is a horticulturist? This lets water pass into them easily. Another very important part of the leaf are the palisade cells. They're trying to utilise the sunlight which there's very little of 'cause there's so many plants everywhere. Thin leaves Provide a short diffusion close diffusion The overall movement of particles of gas or liquid from an area of higher to lower concentration. During photosynthesis, the leaves use chlorophyll close chlorophyll Green pigment found within chloroplast that enables the process of photosynthesis to occur. Cal: Oh, right. Water The water needed for photosynthesis is absorbed through the roots and transported through tubes to the leaf. These are full of chloroplasts to absorb sunlight.

I think, that you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is excellent thought. I agree with you.