Depressive attributional style
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and depressive attributional style causes, but their well-being was less affected by it.
How do you view positive and negative life events? Perhaps you blame yourself when faced with failure while never giving yourself credit for the good. In the face of adversity, can you see past the present moment and know that things will get better? The way you attribute and explain positive and negative events to yourself can impact your life in ways you may not realize. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free.
Depressive attributional style
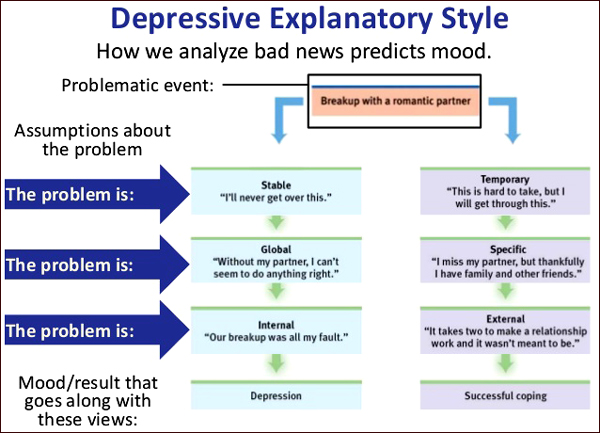
The way you explain an occurrence in your life is known as attributional style, which can affect your well-being. When something positive or negative happens in our lives, we often seek to explain its occurrence. We may ask: Why did this happen to me? Is it because of something I did? Do I just have bad luck? These are attributional styles, which refer to the ways people explain the causes of specific events in their life. Attributional types can say a lot about how we interact with the world. They can shape our view on how much control we have over what happens to us. The way you think about events in your life can also impact your mental health. Attributional styles are based on the historical work of:.
Psychological Bulletin82, —
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Individuals seeking treatment for depression often are struggling with maladaptive cognitions that impact how they view themselves and the world. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes. Based on research, clinicians have developed various techniques that seek to modify depressive attributions in order to alleviate symptoms of depression.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Individuals seeking treatment for depression often are struggling with maladaptive cognitions that impact how they view themselves and the world. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes. Based on research, clinicians have developed various techniques that seek to modify depressive attributions in order to alleviate symptoms of depression. In this article, the authors review the literature on attributions in depression, present clinically relevant interventions based on empirical support, provide case examples, and summarize future directions and recommendations for researchers and practitioners. Two employees at the same company are fired from their jobs. This begs the question, why do these two people have such different thoughts about and emotional reactions to the same life experience?
Depressive attributional style
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it. Forty years ago, Seligman proposed the learnt helplessness model of depression, which proposed that control over the environment is a fundamental need for any organism, and if one is repeatedly exposed to unavoidable painful stimuli, one will come to expect that such events are uncontrollable and develop hopelessness and depression as a result Hiroto and Seligman, This model was later reformulated to the Attributional Style theory Abramson et al. Initial empirical support for these theoretical propositions has been mixed Coyne and Gotlib, For example, Zuroff found that while depressed participants made more internal attributions for failure than non-depressed participants, in absolute terms, they still favored external over internal attributions for failure. Many of the negative findings, however, might be attributed to inadequate statistical power Robins,
Tevfik aydeniz spor kompleksi
Seligman M. Procedia — Social and Behavioral Sciences , 33, Authentic Happiness. This dimension is the degree to which we attribute outcome causality to temporary or temporally-fixed factors. To examine how the relation between the depressive attributional style and psychological adjustment might differ between the two groups, we performed a series of moderation analyses using the PROCESS program Hayes, How do you view positive and negative life events? Journal of Abnormal Psychology. This distinction allows for the possibility that attributional style for affiliative events is different from attributional style for achievement events Peterson et al. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes. As the antithesis of rumination, mindfulness can mitigate self-judgments and promote experiential awareness instead of avoidance. Zhang, Y. In the wake of multiple global economic, [ Randomized trial of behavioral activation, cognitive therapy, and antidepressant medication in the acute treatment of adults with major depression. Thanks for sharing. The consequence of the karma system is a totally internal, global, and generalized attributional style.
The way you explain an occurrence in your life is known as attributional style, which can affect your well-being. When something positive or negative happens in our lives, we often seek to explain its occurrence. We may ask: Why did this happen to me?
The mutability of attributional styles holds promise for intervention. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. Buchanan, G. In this article, the authors review the literature on attributions in depression, present clinically relevant interventions based on empirical support, provide case examples, and summarize future directions and recommendations for researchers and practitioners. The advent of attributional models and other cognitive theories e. Peterson observed that perceptions of control are usually inferred from the causal attributions people give. Given previous research on Buddhism-related psychotherapy techniques Keng et al. For negative events, attributions to internal, stable, and global causes had a reliable and significant association with depression. So on some level, perhaps even Paul must get that these pessimistic beliefs do not automatically have to be truth. After bringing these attributions into awareness, the clinician worked with this client to explore and enact more adaptive patterns of interaction with students, parents, colleagues, and others that were less limited by her attributional habits.

0 thoughts on “Depressive attributional style”