Dorsal cochlear nucleus
The dorsal cochlear nucleus DCNalso known as the " tuberculum acusticum " is a cortex-like structure on the dorso-lateral surface of the brainstem.
The dorsal cochlear nucleus DCN integrates auditory and multisensory signals at the earliest levels of auditory processing. Proposed roles for this region include sound localization in the vertical plane, head orientation to sounds of interest, and suppression of sensitivity to expected sounds. Auditory and non-auditory information streams to the DCN are refined by a remarkably complex array of inhibitory and excitatory interneurons, and the role of each cell type is gaining increasing attention. One inhibitory neuron that has been poorly appreciated to date is the superficial stellate cell. Here we review previous studies and describe new results that reveal the surprisingly rich interactions that this tiny interneuron has with its neighbors, interactions which enable it to respond to both multisensory and auditory afferents. The dorsal cochlear nucleus DCN is an auditory structure unique to mammals, with anatomical, physiological and molecular similarities to the cerebellar cortex and the electrosensory lobe of mormyrid electric fish ELL; Oertel and Young, ; Bell et al.
Dorsal cochlear nucleus
Metrics details. The dorsal cochlear nucleus DCN is a region known to integrate somatosensory and auditory inputs and is identified as a potential key structure in the generation of phantom sound perception, especially noise-induced tinnitus. Yet, how altered homeostatic plasticity of the DCN induces and maintains the sensation of tinnitus is not clear. Mice were exposed to loud noise 9—11kHz, 90dBSPL, 1h, followed by 2h of silence , and auditory brainstem responses ABRs and gap prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle GPIAS were recorded 2 days before and 2 weeks after noise exposure to identify animals with a significantly decreased inhibition of startle, indicating tinnitus but without permanent hearing loss. We found that lowering DCN activity in mice displaying tinnitus-related behavior reduces tinnitus, but lowering DCN activity during noise exposure does not prevent noise-induced tinnitus. The origin of tinnitus pathophysiology has been linked to the dorsal cochlear nucleus DCN of the auditory brainstem [ 5 — 9 ]; however, tinnitus generation and perception mechanisms are not well separated and far from completely understood. Noise overexposure is known to alter firing properties of DCN cells [ 10 — 14 ], even after brief sound exposure at loud intensities [ 15 ]. Such alterations within the DCN circuits could relay abnormal signaling to higher auditory areas and confound spontaneous firing with sensory evoked input, generating tinnitus. It has been suggested that noise-induced tinnitus is partly due to an imbalance of excitation and inhibition within the DCN [ 5 , 16 ] due to decrease in GABAergic [ 17 ] and glycinergic activity [ 18 ] for example. On the contrary, excitatory fusiform cells have been shown to increase burst activity [ 12 , 19 ] following noise overexposure. Furthermore, a shift in bimodal excitatory drive of the DCN after noise overexposure have been shown due to down-regulation of vesicular glutamate transport 1 VGlut1; auditory-related and up-regulation of VGlut2 somatosensory related proteins in the cochlear nucleus [ 20 , 21 ]. DCN circuit disruption such as bilateral electrolytic DCN lesioning in rats has shown to prevent tinnitus generation [ 24 ]. Also, electrical stimulation of the DCN of rats can suppress tinnitus [ 25 ], and electrical high-frequency stimulation of the DCN with noise-induced tinnitus has shown to decrease tinnitus perception during tests [ 26 ]. This indicates that unspecific alterations of DCN activity can decrease tinnitus induction and perception, but if the same DCN populations are involved in the two mechanisms remains to be investigated. We specifically investigated if noise-induced tinnitus can be ameliorated by lowering DCN neuronal activity.
Noise overexposure is known to alter firing properties of DCN cells [ 10 — 14 ], even after brief sound exposure at loud intensities [ 15 ]. Figure 1. Noradrenaline and serotonin selectively modulate dorsal cochlear nucleus burst firing by enhancing a hyperpolarization-activated cation current.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Author contributions: Z. The dorsal cochlear nucleus DCN is one of the first stations within the central auditory pathway where the basic computations underlying sound localization are initiated and heightened activity in the DCN may underlie central tinnitus. The neurotransmitter serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT , is associated with many distinct behavioral or cognitive states, and serotonergic fibers are concentrated in the DCN.
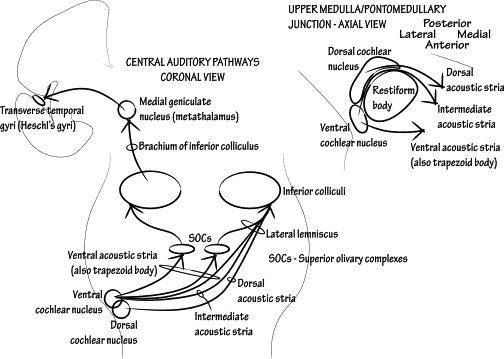
Information travels from the receptors in the organ of Corti of the inner ear cochlear hair cells to the central nervous system, carried by the vestibulocochlear nerve CN VIII. This pathway ultimately reaches the primary auditory cortex for conscious perception. In addition, unconscious processing of auditory information occurs in parallel. In this article, we will discuss the anatomy of the auditory pathway — its components, anatomical course, and relevant anatomical landmarks. The auditory pathway is complex in that divergence and convergence of information happens at different stages. The spiral ganglion houses the cell bodies of the first order neurons ganglion refers to a collection of cell bodies outside the central nervous system.
Dorsal cochlear nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and supplementary information files.
Varicocele fotos reales
PloS One. Specifically, the stimulus was presented in the following sequence: a random integer value between 12 and 22 s of noise at background level randomized background noise between trials ; 40ms of noise at background level for Startle trials, or 40ms of silence for Gap-startle trials Gap portion ; ms of noise at background level background noise before loud pulse ; 50ms of noise at dBSPL loud pulse ; and ms of noise at background level final background noise. Their restriction to the molecular layer, in many cases the very edge of the molecular layer, point to a domain of control limited to the outermost dendritic fields of fusiform and cartwheel cells Figure 5. All experiments were performed during the light cycle. Novel plasticity in the DCN: DCX- expression in unipolar brush cells in the adult rat We have recently found evidence for a previously unknown form of plasticity in one DCN cell class, the unipolar brush cell Manohar et al. As the IPSC components produced by the two transmitters had distinct kinetic signatures, the results imply that co-transmission might enable both fast and slow phases of inhibition. Hear Res. Here, we initially screened for capability to carry out the gap prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle test GPIAS [ 31 , 36 ]. PMC Copyright notice. J Laryngol Otol.
The cochlear nuclei are a group of two small special sensory nuclei in the upper medulla for the cochlear nerve component of the vestibulocochlear nerve. They are part of the extensive cranial nerve nuclei within the brainstem. The dorsal and ventral nuclei are located in the dorsolateral upper medulla and are separated by the fibers of the inferior cerebellar peduncle :.
The inferior colliculus receives direct, monosynaptic projections from the superior olivary complex, the contralateral dorsal acoustic stria, some classes of stellate neurons of the VCN, as well as from the different nuclei of the lateral lemniscus. The human The idea that the human DCN is unlaminated and lacks granule cells is actually based on very few studies Adams, ; Heiman-Patterson and Strominger, ; Moore and Osen, Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Serotonin-2 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci. Two separate inhibitory mechanisms shape the responses of dorsal cochlear nucleus type iv units to narrowband and wideband stimuli. Addressing variability in the acoustic startle reflex for accurate gap detection assessment. Properties of hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker current defined by coassembly of HCN1 and HCN2 subunits and basal modulation by cyclic nucleotide. Noise exposure Anesthetized mice were placed inside a sound-shielded chamber, inside an acrylic tube, in an acoustically shielded room, with a speaker placed 4. Type IV cells are excited by wide band noise, and particularly excited by a noise-notch stimulus directly below the cell's best frequency BF. In recent years, the rat has become a more popular experimental subject, especially in the development of an animal model of tinnitus Jastreboff and Sasaki, ; Lobarinas et al. Trigeminal ganglion innervates the auditory brainstem. Open symbols represent 5-HT currents of individual neurons, and filled symbols represent the mean of 5-HT currents.

You are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.