Earwig diagram
Uploaded with derivativeFX. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. File information. Structured data.
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. File information.
Earwig diagram
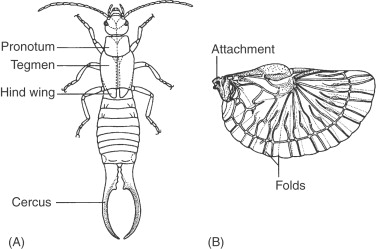
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2, species [1] in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci , a pair of forcep -like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica. Earwigs are mostly nocturnal and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig Forficula auricularia. Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs; the ones that do will continue to watch over nymphs until their second molt. As the nymphs molt, sexual dimorphism such as differences in pincer shapes begins to show. Extant Dermaptera belong to the suborder Neodermaptera , which first appeared during the Cretaceous. Some earwig specimen fossils are placed with extinct suborders Archidermaptera or Eodermaptera , the former dating to the Late Triassic and the latter to the Middle Jurassic. Dermaptera belongs to the major grouping Polyneoptera , and are amongst the earliest diverging members of the group, alongside angel insects Zoraptera , and stoneflies Plecoptera , but the exact relationship among the three groups is uncertain.
However, the physical presence of earwigs as crop contaminants is perhaps even more important, earwig diagram, because most people find their presence and odor repulsive.
While these bugs have a frightening appearance, their name is quite the misnomer. Although it could be possible in theory, the chances of this happening are slim to none. Earwigs do not cause harm to humans and do not carry any type of disease, nor do they bite. The only possible harm they could cause to a human is a pinch delivered by their back forceps, and they will usually only pinch in defense. Although the pinch can hurt, these insects are not poisonous, so getting pinched is just painful, rather than harmful.
Earwigs, known for their distinctive pincers on their abdomen, are a fascinating and often misunderstood group of insects. With over 2, species spread across various habitats globally, they are a diverse and adaptable group. This article aims to shed light on these intriguing creatures, exploring their classification, unique features, habitat, behavior, and more. Understanding earwigs can demystify the myths surrounding them and highlight their role in the ecological balance. The Dermaptera order, to which earwigs belong, encompasses a wide array of species and subspecies, with over 2, known varieties.
Earwig diagram
Updated on: September 14, We adhere to editorial integrity are independent and thus not for sale. The article may contain references to products of our partners. Here's an explanation of how we make money. Wild Explained was founded in and has a long track record of helping people make smart decisions. We have built this reputation for many years by helping our readers with everyday questions and decisions. We have helped thousands of readers find answers. Wild Explained follows an established editorial policy. Therefore, you can assume that your interests are our top priority. Our editorial team is composed of qualified professional editors and our articles are edited by subject matter experts who verify that our publications, are objective, independent and trustworthy.
Etsy bondage
Strong neuron connections connect the neurohemal corpora cardiaca to the brain and frontal ganglion, where the closely related median corpus allatum produces juvenile hormone III in close proximity to the neurohemal dorsal arota. There is a brain, a subesophageal ganglion, three thoracic ganglia, and six abdominal ganglia. Presently it occurs south to North Carolina, Arizona and southern California, but due to its preference for temperate climates it is unlikely to become abundant in the southeastern states. The annoyance associated with their presence is exacerbated by the tendency of earwigs to aggregate, often in association with human habitations; most people simply find them annoying. Choate PM. Archived from the original on 22 August An earwig from the Western Ghats Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the Americas and Eurasia. Earwigs and their relatives [45] [46]. At least 26 species of parasitic fungus from the order Laboulbeniales have been found on earwigs. The common earwig eats a wide variety of plants, and also a wide variety of foliage, including the leaves and petals. The economic status of earwigs is subject to dispute. Among fruits, they have been found to damage apple and pear orchards. Back to top. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera.
A male of Forficula auricularia feeding on flowers The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting arthropods. Insects portal Wikispecies. Hidden categories: Webarchive template wayback links Articles with short description Short description matches Wikidata Use dmy dates from July Articles with 'species' microformats Articles containing Old English ca. In some species, the forceps have been observed in use for holding prey , and in copulation. In Roald Dahl's children's book George's Marvellous Medicine, George's Grandma encourages him to eat unwashed celery with beetles and earwigs still on them. Hemimeridae are viviparous ectoparasites , preferring the fur of African rodents in either Cricetomys or Beamys genera. Captions Captions English Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents. Females also have tegmina of about 2 mm 0. By the s, the two suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina had been added to Dermaptera. No fossils from the Triassic — during which Dermaptera would have evolved from Protelytroptera — have been found. The pronounced cerci are the most distinctive feature of earwigs; in the male the cerci are strongly curved whereas in the female they curve only slightly.

Excuse please, that I interrupt you.
In my opinion you commit an error.