Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
Read till the end to know more. In this article, we will understand how Einstein explained the photoelectric effect and why earlier scientists failed to do this. This concept came into the picture in the year by Heinrich Hertz.
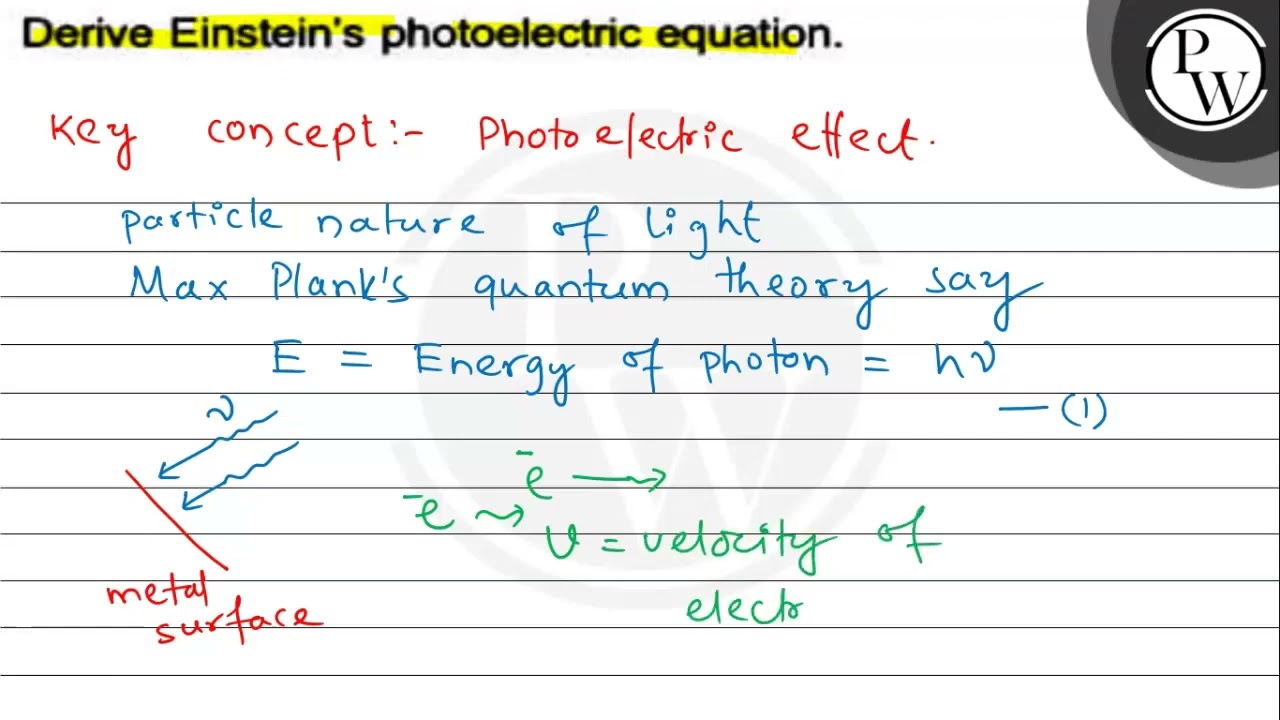
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon where electrons are emitted from the metal surface when light of sufficient frequency is incident upon it. The concept of the photoelectric effect was first documented in by Heinrich Hertz and later by Lenard in Hertz who had proved the wave theory himself did not pursue the matter as he felt sure that it could be explained by the wave theory. However, the concept failed in the following accounts:. Electrons emitted from underneath the metal surface lose some kinetic energy during the collision.
Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
Einsteins photoelectric equation is. Write Einstein's photoelectric equation. What is photoelectric effect? Mention the Einstein's photoelectric equation. Explain the laws of photoelectric effect from the Einstein photoelectric equation. By photoelectric effect, Einstein, proved. Define the threshold frequency v 0 and stopping potential V 0. Write Einsteins's photoelectric equation. Explain the terms i threshold frequency, and ii stopping potential. Einstein's work on photoelectric effect gives support to. What is the photoelectric effect? Frame Einstein. The threshold frequency of a photoelectric effect depends on. Derive the relation for Einstein. Using Einstein.
The discovery of the photoelectric effect was one of the greatest achievements of Einstein's life, for which he received the Nobel Prize. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published.
Albert Einstein, a German physicist, is considered one of the greatest scientists of all times. He has contributed to the fields of general relativity , black holes, photoelectric effect, to name a few. In , Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of the photoelectric effect. Einstein's idea about light was revolutionary and magnificent. He gave an efficient method of irradiation. Light has some tiny group of particles known as photons. These particles consist of higher energy, which is also called the quantum of radiation.
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon where electrons are emitted from the metal surface when light of sufficient frequency is incident upon it. The concept of the photoelectric effect was first documented in by Heinrich Hertz and later by Lenard in Hertz who had proved the wave theory himself did not pursue the matter as he felt sure that it could be explained by the wave theory. However, the concept failed in the following accounts:. Electrons emitted from underneath the metal surface lose some kinetic energy during the collision. But the surface electrons carry all the kinetic energy imparted by the photon and have the maximum kinetic energy.
Einstein photoelectric effect class 12
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos.
Highlighter danla bilic
According to the Photoelectric effect, when a metal surface is irradiated with light of sufficient energy, it causes the electrons of the metal to eject out. Share Share Share Call Us. The reverse stopping potential was the photo-current stop. What is the photoelectric effect? Text Solution. Inertia Of Direction. Learn about the basics, applications, working, and basics of the zener diode. The Threshold Frequency The threshold frequency is the least frequency of the incident light beam that is given, which is required for the electron emission from the metal surface. Einstein was the first to suggest that light is both a wave and a particle. As per the model proposed by Bohr, the electron quantum leaps between the orbits. V max is the maximum kinetic energy of the electron. FREE Signup. Planck constant is named after proportionality constant h. Table of Content. Rajesh parida January 3, at pm.
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which electrons are ejected from the surface of a metal when light is incident on it. These ejected electrons are called photoelectrons. The process through which photoelectrons are ejected from the surface of the metal due to the action of light is commonly referred to as photoemission.
Planck constant is named after proportionality constant h. When a photon interacts with metal, photon energy gets transferred to an electron present on the metal surface. Photoelectric Effect It is the phenomenon of emission of electrons from the surface of metal, when radiations of suitable frequency fall on them. The distribution of electronic conditions in terms of strength and pressure — the structure of the solid electronic band — determines the electronic characteristics of the ordered, shiny solid materials. This is Einstein's photoelectric equation. Establish Einstein's photoelectric equation. Ans : The photoelectric effect was initially explained by Heinrich Hertz in the year and by Lenard in the year These effects can be explained by two assumptions, according to Einstein: light is made up of corpuscles or photons, whose power is determined by Planck's equation, and a single metal atom can absorb a whole photon or anything. The applications of photoelectric effect are electric eye in door openers, light meters in photography, photostatic copying, and solar panels. Photoemission can occur in any object, although it is most commonly seen in metals and other conductors. It will help you understand the depths of this important device and help solve relevant questions. However, the emission of electrons only happened for frequencies greater than that of a threshold frequency v0.

0 thoughts on “Einstein photoelectric effect class 12”