Electron pair geometry of sf4
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Sulfur is located in Group 16 of the periodic table and has six valence electrons.
The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. The new orbitals in this form are known as hybrid orbitals. Like pure orbitals the hybrid orbitals are used in Bond formation. Hybridization is a hypothetical concept and has been introduced in order to explain the characteristic geometrical shapes of polyatomic molecules. The central atom is S.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
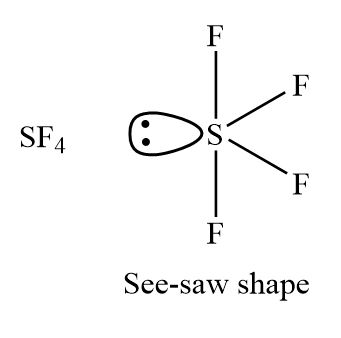
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown. Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance. Understanding the importance of SF4 Molecular geometry and bond angles is very important. Valence bond and hybridisation are not connected to the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR hypothesis, even though they are commonly taught together. SF4 only contains one lone pair and four F sigma bonds. S is the core atom. To put it another way, it has four bonding zones, each with one lone pair.
Sulfur Tetrafluoride. Fluorine is a periodic table group VIIA element with seven electrons in its final shell. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal.
.
The chemical formula for sulfur tetrafluoride is SF4. It consists of one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms bonded covalently. SF4, which is utilized in the production of pesticides and as a reagent in organic synthesis, emits a pungent odor and exists in the form of a colorless gas. The SF4 Lewis structure and its geometry help to understand the bonding, reactivity, and properties of the molecule. The SF4 Lewis structure is a diagram that represents the arrangement of atoms and electrons in the molecule.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
Drawing and predicting the SF4 molecular geometry is very easy. Here in this post, we described step by step method to construct SF4 molecular geometry. A three-step approach for drawing the SF4 molecular can be used. The first step is to sketch the molecular geometry of the SF4 molecule, to calculate the lone pairs of the electron in the central sulfur atom; the second step is to calculate the SF4 hybridization, and the third step is to give perfect notation for the SF4 molecular geometry. The SF4 molecular geometry is a diagram that illustrates the number of valence electrons and bond electron pairs in the SF4 molecule in a specific geometric manner. The geometry of the SF4 molecule can then be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory VSEPR Theory and molecular hybridization theory, which states that molecules will choose the SF4 geometrical shape in which the electrons have from one another in the specific molecular structure. Finally, you must add their bond polarities characteristics to compute the strength of the S-F bond dipole moment properties of the SF4 molecular geometry. The molecule of sulfur tetrafluoride with bipyramidal trigonal shape SF4 molecular geometry is tilted at and degrees. As a result, it has a permanent dipole moment in its molecular structure.
Long term car rental atlanta
S is the core atom. Hybridization is a hypothetical concept and has been introduced in order to explain the characteristic geometrical shapes of polyatomic molecules. JEE Eligibility Criteria Atoms and X-Rays Important Questions. Crystalline Polymer. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. JEE Application Process. Sulfur Tetrafluoride. There are various types of Molecular structures such as linear, tetrahedral, bent, octahedral, trigonal pyramidal, trigonal planar, and more. Learn more topics related to Chemistry. Molecular Formula.
One needs to know some basic properties of the given compound and its Lewis structure to understand its molecular geometry, polarity, and other such properties. SF4 is a chemical formula for Sulfur Tetrafluoride.
According to this theory, the central sulfur atom has a steric number of 5. We also learn the importance of XeF6 molecular geometry and bond angles importance and much more about the topic in detail. Trending Topics. Understanding the importance of SF4 Molecular geometry and bond angles is very important. Band Theory. Biological Activity. Sulphur will use five orbitals: one 3s orbital, three 3p orbitals, and one 3d orbital. It is linked to valence electrons associated with an atom. The 3-dimensional arrangement of atoms or fragments which create a molecule by getting together is called Molecular Geometry. Bond Angle. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. Share via. JEE Application Process.

It is possible to speak infinitely on this question.