Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Check out our latest pathology themed Wordle here! Updated every Monday. Skin nonmelanocytic tumor Cysts Epidermal epidermoid type Authors: V. Claire Vaughan, M.
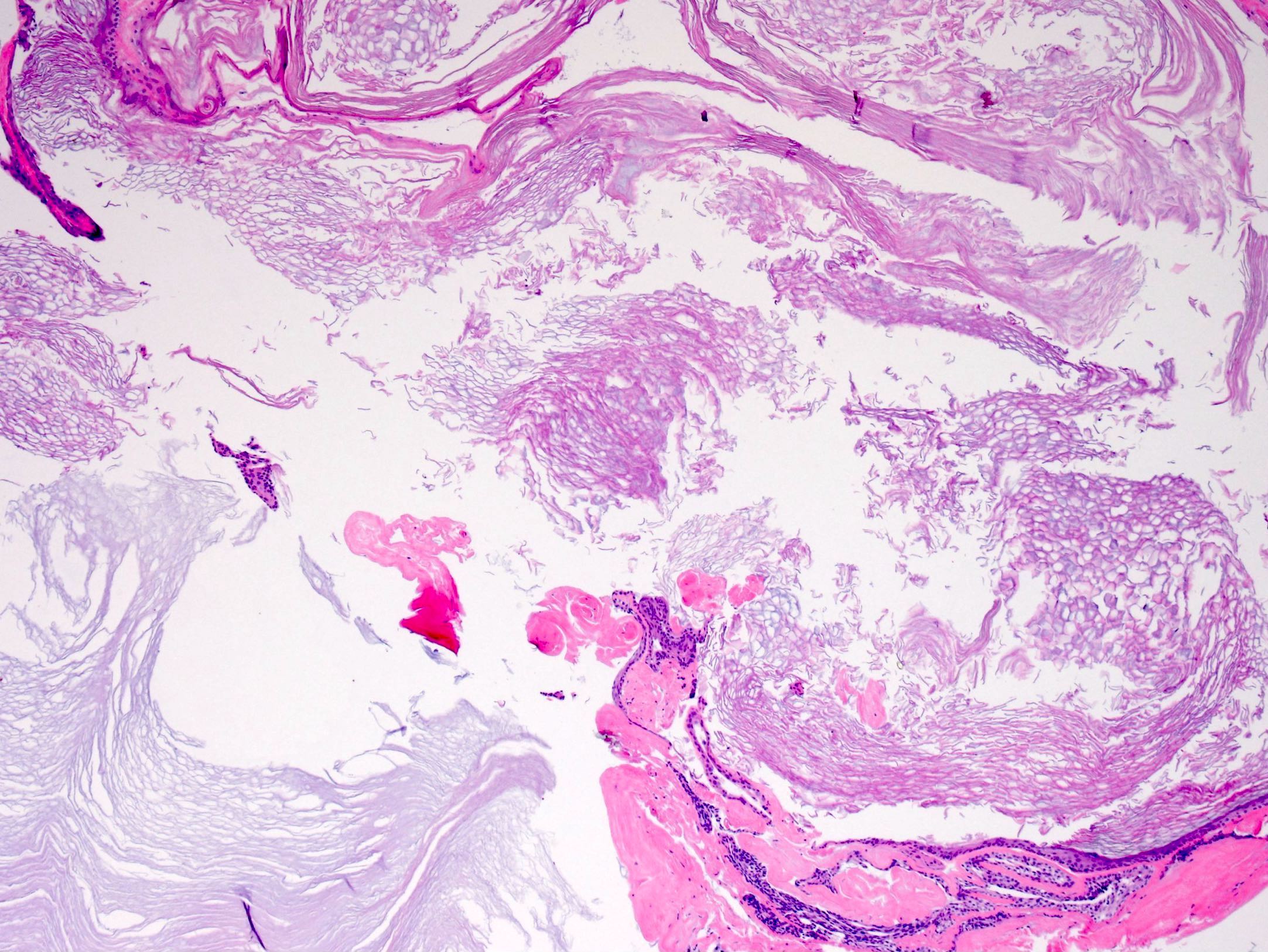
Also known as epidermal inclusion cyst EIC and sebaceous cyst. Typical findings: [1]. Trichilemmal cyst , containing, from external top to internal bottom : [image 1] [2] - Fibrous capsule - Small, cuboidal, dark-staining basal epithelial cells in a palisade arrangement, with no distinct intercellular bridging - Swollen pale keratinocytes, which increase in height closer to the interior - Solid eosinophilic-staining keratin There is no granular cell layer in contrast to an epidermoid cyst. Pilomatricoma : Stroma surrounding irregularly shaped islands containing basaloid cells darkly stained, round or elongated , which abruptly or gradually transitions into ghost cells having pale cytoplasm and a central clear area , which in turn may transition into necrosis. Further information: Skin cyst. Look for signs of cyst rupture, which may manifest as inflammation, including granulomas and microabscesses.
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Proliferating epidermoid cyst pathology. Proliferating epidermoid cyst has been poorly defined in the literature. The regular epidermoid cyst should be seen in at least part of the lesion in addition to an epidermal proliferation. Sections show a cyst in the dermis with a proliferating epidermal component figures 1, 2. Characteristically, the proliferative areas are made up of bland squamous epithelium with striking squamous eddies figures 2, 3, 4. These eddies are whorles of maturing squamous epithelium and are exactly the same as those seen in irritated seborrheic keratoses or inverted follicular keratoses. Proliferating epidermoid cyst pathology Figure 1. HPV-related epidermal cysts — These have a hyperplastic lining with viropathic nuclear and cytoplasmic changes. Cystic squamous cell carcinoma — Must be considered if there are nuclear atypia and adjacent infiltration into the surrounding dermis. This can be a challenging differential when cysts have partially ruptured or there is extensive proliferation. Books about skin diseases Books about the skin Dermatology Made Easy - second edition. DermNet does not provide an online consultation service.
Public Domain - Author info - Reusing images. Epidermoid cyst Trichilemmal cyst Proliferating trichilemmal cyst.
Check out our latest pathology themed Wordle here! Updated every Monday. Deputy Editor-in-Chief: Borislav A. Alexiev, M. Page views in 11,
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Epidermoid cyst pathology. Epidermoid cysts infundibular cysts are thought to be derived from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle. Some are derived from implantation of the epidermis.
Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines
Don't forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel! Skin nonmelanocytic tumor Cysts Epidermal epidermoid type Authors: V. Claire Vaughan, M. Page views in , Epidermal epidermoid type. Accessed March 22nd, Benign skin tumor Cystic mass containing keratin.
Ts jessyca ketlen
Epidermoid inclusion cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst, intraosseous epidermoid cyst. Foci of rupture are common and the keratin exposed to the adjacent dermis elicits a neutrophilic and then granulomatous reaction figures 5, 6. Comment Here Reference: Epidermoid inclusion cyst. Microscopic histologic images. Sections of an epidermoid cyst show a cystic structure occupying at least the upper dermis but larger lesions may grow to involve the entire dermis figure 1. DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Contributed by Jijgee Munkhdelger, M. Navigation menu Personal tools Log in. Table of contents arrow-right-small. Dermoid cyst differs from epidermoid inclusion cyst by the presence of skin appendages.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Cytology images. Board review style answer 2. Page views in , Ear pit cyst Epidermoid cyst. Feb This website is intended for pathologists and laboratory personnel but not for patients. However, we cannot answer medical or research questions or give advice. Positive stains. Radiology images. Epidermoid cysts infundibular cysts are thought to be derived from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle.

0 thoughts on “Epidermoid cyst pathology outlines”