Fimbriae
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. All relevant data fimbriae within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
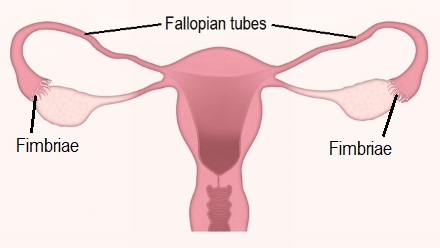
Fimbriae tubae project from the end of the fallopian tubes. They are lined with cilia, or hair-like structures, that guide the egg to the uterus. From there, the egg is either fertilized or shed during the menstrual cycle. The fimbriae of the uterine tube , also known as fimbriae tubae , are small, fingerlike projections connected to the end of the fallopian tubes, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus. Small epithelial cells — those that line cavities throughout the body — with small, slender cilia microscopic, hair-like structures pulsate inside the fallopian tubes to guide the ovum, or egg, from the ovary to the uterus. Because the ovum cannot move by itself, the sweeping movement of the cilia of the fimbriae dictates its movement. It generally takes about 3 to 5 days for an egg to leave the ovary and land in the uterus.
Fimbriae
Fimbriae are long filamentous polymeric protein structures located at the surface of bacterial cells. They enable the bacteria to bind to specific receptor structures and thereby to colonise specific surfaces. Fimbriae consist of so-called major and minor subunits, which form, in a specific order, the fimbrial structure. In this review emphasis is put on the genetic organisation, regulation and especially on the biosynthesis of fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains, and more in particular on K88 and related fimbriae, with ample reference to the well-studied P and type 1 fimbriae. Molecular and structural aspects of the secretion of fimbrial subunits across the cytoplasmic membrane, the interaction of these subunits with the periplasmic molecular chaperone, their translocation to the inner site of the outer membrane and their interaction with the usher protein, as well as the ordered translocation of the subunits across the outer membrane and their assembly into a grwoing fimbrial structure will be described. A model for K88 fimbriae is presented. Finlay B. Falkow S. Google Scholar. Krogfelt K. Duguid J.
The Tra transfer family includes all known fimbriae pili as of Parge H.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'fimbria. Send us feedback about these examples. Accessed 24 Feb. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free! See Definitions and Examples ». Log In. Examples of fimbria in a Sentence.
Found mainly in Gram-negative organisms, fimbriae or pili singular: pilus are hair-like filaments tiny hollow projections that extend from the cell membrane into the external environment. A pilus is composed of subunits of the protein pilin. Fimbriae pili are shorter, straighter, and more numerous than bacterial flagella. Pili are small hairs that enable some pathogens to attach and adhere easily to cell surfaces, particularly mucous membranes. Bacteria possessing pili include Neisseria gonorrhoeae and some strains of Escherichia coli , Salmonella , and Shigella species.
Fimbriae
The fimbria of hippocampus refers to bundles of fibers that are formed when the white matter fibers known as the alveus converge on the medial side of the hippocampus. These fimbriae, or fiber bundles, subsequently extend further to form the crura of the fornix. Snell, R. Blumenfield, H. Sinauer Associates, Inc. Human anatomy 2. Underlying structures: There are no anatomical children for this anatomical part. Human anatomy 1. Human neuroanatomy.
Glee imdb
Mol O. Oliver D. Continuum model The transport of water, EPS and nutrients in the biofilm are all computed using continuum equations on a grid spanning the biofilm computational domain. Identification and characterization of Escherichia coli type 1 pilus tip adhesion protein. Newman E. Year introduced: PubMed search builder options Subheadings: chemistry classification drug effects enzymology genetics immunology metabolism microbiology parasitology pathology physiology radiation effects transplantation ultrastructure virology. The current paper extends the hybrid model of Jin et al. Add to Clipboard. Bilge S. The water velocity field is of larger magnitude than EPS and generally oriented inward toward the bacterial cells. Regulation of pyelonephritis-associated pili phase variation in Escherichia coli : binding of the PapI and the Lrp regulatory proteins is controlled by DNA methylation. Hanson M. Hull R. Increase in EPS velocity magnitude results in an increase in outward cell drag force, and hence an increased tendency for the biofilm to break up and disperse.
A pilus Latin for 'hair'; pl. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin — fibrous proteins , which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface.
Genetics of digalactoside-binding adhesin from a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Medical Definition. Direct evidence that the FimH protein is the mannose-specific adhesin of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. The P fimbrial gene cluster of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli is plasmid encoded. Willshaw G. Kuehn M. Role of type 1 fimbriae and mannose in the development of Escherichia coli K12 biofilm: From initial cell adhesion to biofilm formation. The EPS is produced within the bacterial colony, but it is transported outward via both convection and diffusion, where iso-surfaces of the EPS concentration appear to have approximately hemispherical shapes. Abstract Gram-negative bacteria, as well as some Gram-positive bacteria, possess hair-like appendages known as fimbriae, which play an important role in adhesion of the bacteria to surfaces or to other bacteria. The fimbriae of the uterine tube , also known as fimbriae tubae , are small, fingerlike projections connected to the end of the fallopian tubes, through which eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus.

This rather good phrase is necessary just by the way
I think, that you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.