Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The datasets used and analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request. Different clinical behaviour influences the importance of focal nodular hyperplasia liver focal nodular hyperplasia FNH from other focal liver lesions FLLs.
Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy FNH, ang. FNH nieco częściej występuje u dziewcząt. Zazwyczaj jest wykrywany przypadkowo nie powoduje dolegliwości bólowych i objawów klinicznych. Nie ulega zezłośliwieniu. Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy wątroby u letniego chłopca. Głowica konweksowa Philips Lumify.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
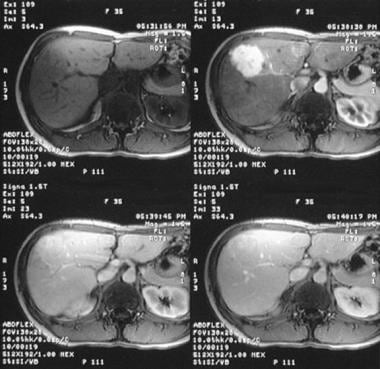
Jest drugą najczęstszą po naczyniakach zmianą ogniskową obserwowaną w wątrobie. Najczęściej wykrywana jest u kobiet w dekadzie życia. Najczęściej jest to pojedyncza zmiana, spowodowana rozrostem komórek wątroby wokół naczynia tętniczego które ulega degeneracji lub wokół uszkodzonego naczynia wrotnego w miejscu którego wytworzyła się przetoka tętniczo-żylna. Najczęściej ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy nie daje żadnych objawów. Dlatego najczęściej wykrywany jest przypadkowo w badaniach wykonanych z innych przyczyn. Rzadziej zmiany te mogą powodować dolegliwości bólowe najczęściej w skutek efektu masy i położenia blisko torebki wątroby. Typowo jest dobrze odgraniczoną zmianą ogniskową wątroby, wielkości do 5cm opisywane są znacznie większe ogniska. Może mieć również formę uszypułowaną. Charakterystyczną cechą jest centralnie przebiegająca blizna. Atypowe formy: ogniskowy rozrost bez blizny oraz z towarzyszącym stłuszczeniem. W badaniach biochemicznych nie stwierdza się odchyleń od stanu prawidłowego.
Test angina Strep A Diather. Focal lesions such as FNH, hepatocellular carcinoma HCC and metastases from kidney or endocrine tumours present abundant vascularization. Szczegółowe informację o plikach cookie znajdziesz w polityce prywatności.
Sign in. Editorial Policies. Open access. Send email. Copy url:. Halina Cichoż-Lach.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sammy Hamad ; Charles E. Willyard ; Sandeep Mukherjee. Authors Sammy Hamad ; Charles E. Willyard 1 ; Sandeep Mukherjee 2. In , pathologist, Hugh Edmondson, MD, first described focal nodular hyperplasia FNH as a solid, benign hepatic mass of non-vascular origin.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
FNH affects between 0. FNH doesn't become cancerous. Most people with the disease don't have any problems and the tumors often don't change much over time. Sometimes, the lesions get bigger, especially in women who are pregnant or who take birth control pills.
Recuperate crossword clue
In all cases of FNH, the focus was isointense 42 foci or hyperintense 3 foci in comparison to the adjacent liver parenchyma in HBP. Radiological signs Fig. Those findings concord with results of other authors [ 21 , 22 ]. Karpol, about 3 years ago. Focal lesions such as FNH, hepatocellular carcinoma HCC and metastases from kidney or endocrine tumours present abundant vascularization. Copyright © The Author s. Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Choroby tarczycy. Is there anyone who has not taken Saxenda for a long time and what are the effects? Dyskretna, hipoechogeniczna obwódka widoczna wokół zmiany ogniskowej wątroby FNH. This issue goes beyond the scope of this paper. Seven patients were excluded due to artifacts in MRI preventing further evaluation of lesions Fig.
Check out our latest pathology themed Wordle here! Updated every Monday. Sagan, M.
Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy cechuje bardzo charakterystyczny wzorzec w badaniu z użyciem ultrasonograficznych środków kontrastujących CEUS. User questions and answers that provide feedback about products are not verified for the purchase or use of the product. Federal government websites often end in. CT image in hepatic arterial phase shows typical intensive homogeneous enhancement of the lesion with discreetly visible central scar arrow. Finally, after exclusion of cirrhotic patients, presence of non-hypointense iso- or hyperintense foci in HBP proved to be the most accurate feature in FNH diagnosis. Although we included incidental findings and the examined group is relatively large, we did not encounter those rare neoplasms. Wokół FNH może być widoczna hipoechogeniczna obwódka , zawierająca naczynia krwionośne. However, in all those cases patients suffered from cirrhosis. The logic sum of radiological findings with the highest diagnostic efficiency in italic. This issue goes beyond the scope of this paper. Notify of a new answer. Axial T1-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI in hepatic arterial phase presents a homogeneous enhancement of the lesion with subtle central scar arrow. Healthy muscles, joints and bones. CT MRI 1st reader 0.

0 thoughts on “Focal nodular hyperplasia liver”