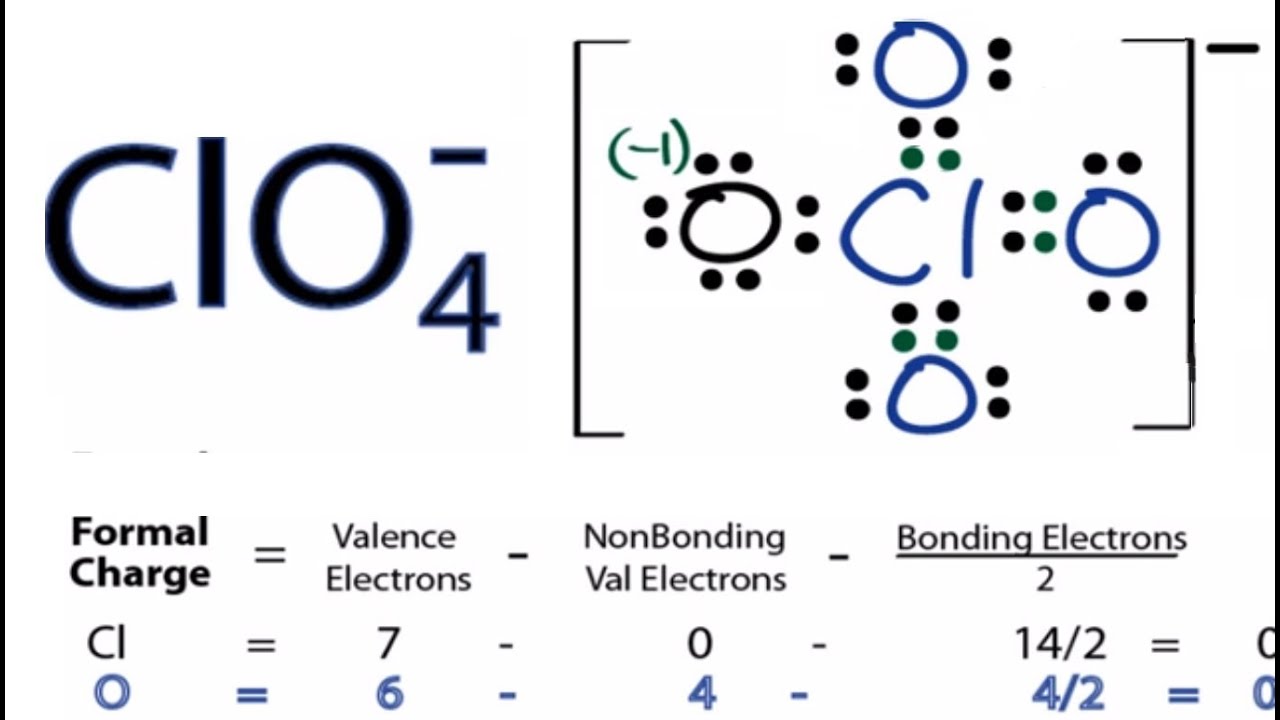
Formal charge of cl
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms, formal charge of cl. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Formal charge of cl
.
We call the individual Lewis structures resonance forms. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
.
Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one. The calculation is pretty straightforward if all the information is given to you. So part of the trick for you will be to calculate the formal charge in situations where you have to take account of implicit lone pairs and C-H bonds. Formal charge is a book-keeping formalism for assigning a charge to a specific atom. When all the lone pairs are drawn out for you, calculating formal charge is fairly straightforward.
Formal charge of cl
A formal charge F. The formal charge is the difference between an atom's number of valence electrons in its neutral free state and the number allocated to that atom in a Lewis structure. When choosing the optimum Lewis structure or predominant resonance structure for a molecule, it is important to keep the formal charge on each of the atoms as low as feasible. The following equation can be used to compute the formal charge of an atom in a molecule:.
24 hour gold and silver prices
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Subtract this number from the number of valence electrons for the neutral atom. Solution Assign one of the electrons in each Br—Cl bond to the Br atom and one to the Cl atom in that bond: Assign the lone pairs to their atom. The Lewis structure is. CC licensed content, Shared previously. Now each Cl atom has seven electrons and the Br atom has seven electrons. Comparing the three formal charges, we can definitively identify the structure on the left as preferable because it has only formal charges of zero Guideline 1. Write Lewis structures for the hydrogen carbonate ion and hydrogen peroxide molecule, with resonance forms where appropriate. Indicate which of the three has the strongest carbon-oxygen bond. Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in hypochlorous acid: HOCl or OClH? A double bond between two atoms is shorter and stronger than a single bond between the same two atoms. In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. Now each Cl atom has seven electrons and the Br atom has seven electrons.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable.
Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in hypochlorous acid: HOCl or OClH? Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in sulfur dioxide: OSO or SOO? The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Write the Lewis structure for sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 , which has two oxygen atoms and two OH groups bonded to the sulfur. Which is the likely structure for nitrous oxide? This gives rise to three resonance forms of the carbonate ion. Example 3: Using Formal Charge to Determine Molecular Structure Nitrous oxide, N 2 O, commonly known as laughing gas, is used as an anesthetic in minor surgeries, such as the routine extraction of wisdom teeth. Determine the formal charges: Sulfuric acid is the industrial chemical produced in greatest quantity worldwide. Skip to main content. Also, it places the least electronegative atom in the center, and the negative charge on the more electronegative element Guideline 4. There are The actual electronic structure of the molecule the average of the resonance forms is called a resonance hybrid of the individual resonance forms. We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule.

I consider, that you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Also what from this follows?