Glucokinase
Glucokinase EC 2. Glucokinase occurs glucokinase cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glucose transport is by facilitated diffusion and is not rate limiting. Once inside, glucose is phosphorylated to glucosephosphate by GCK in a reaction that is dependent on glucose throughout the physiological range of concentrations, is irreversible, and not product inhibited. High glycerol phosphate shuttle, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and pyruvate carboxylase activities, combined with low pentose-P shunt, lactate dehydrogenase, plasma membrane monocarboxylate transport, and glycogen synthase activities constrain glucosephosphate to being metabolized through glycolysis. Under these conditions, glycolysis produces mostly pyruvate and little lactate.
Glucokinase
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The secretion of glucagon by pancreatic alpha cells is regulated by a number of external and intrinsic factors. While the electrophysiological processes linking a lowering of glucose concentrations to an increased glucagon release are well characterized, the evidence for the identity and function of the glucose sensor is still incomplete. In the present study we aimed to address two unsolved problems: 1 do individual alpha cells have the intrinsic capability to regulate glucagon secretion by glucose, and 2 is glucokinase the alpha cell glucose sensor in this scenario. Single cell RT-PCR was used to confirm that glucokinase is the main glucose-phosphorylating enzyme expressed in rat pancreatic alpha cells. Modulation of glucokinase activity by pharmacological activators and inhibitors led to a lowering or an increase of the glucose threshold of glucagon release from single alpha cells, measured by TIRF microscopy, respectively. Knockdown of glucokinase expression resulted in a loss of glucose control of glucagon secretion. Taken together this study provides evidence for a crucial role of glucokinase in intrinsic glucose regulation of glucagon release in rat alpha cells.
Hypoxia-independent apoptosis in neural cells exposed to carbon monoxide in vitro, glucokinase. Open in a separate window.
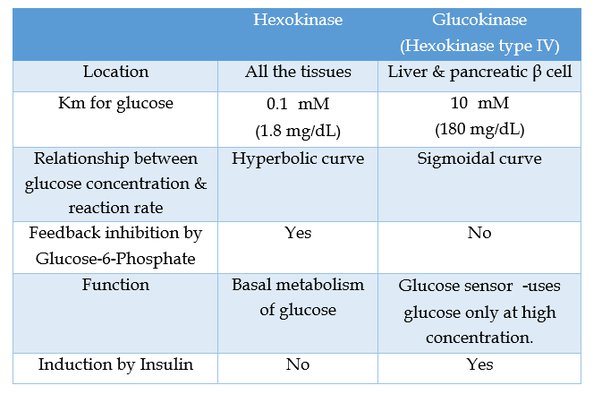
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The GCK gene provides instructions for making a protein called glucokinase. This protein plays an important role in the breakdown of sugars particularly glucose in the body. Glucokinase is primarily found in the liver and in beta cells in the pancreas. Beta cells produce and release secrete the hormone insulin, which helps regulate blood glucose levels by controlling how much glucose is passed from the bloodstream into cells to be used as energy. Glucokinase acts as a sensor, recognizing when the level of glucose in the blood rises and helping stimulate the release of insulin from beta cells to control it.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder with complicated pathogenesis, and mono-target therapy often fails to effectively manage the levels of blood glucose. In recent years, the anti-diabetes target glucokinase GK has attracted the attention of researchers. It acts as a glucose sensor, triggering counter regulatory responses following a change in glucose levels to aid restoration of normoglycemia.
Glucokinase
Glucose metabolism in humans is tightly controlled by the activity of glucokinase GCK. GCK is predominantly produced in the pancreas, where it catalyzes the rate-limiting step of insulin secretion, and in the liver, where it participates in glycogen synthesis. A multitude of disease-causing mutations within the gck gene have been identified. Activating mutations manifest themselves in the clinic as congenital hyperinsulinism, while loss-of-function mutations produce several diabetic conditions. Indeed, pharmaceutical companies have shown great interest in developing GCK-associated treatments for diabetic patients. Due to its essential role in maintaining whole-body glucose homeostasis, GCK activity is extensively regulated at multiple levels.
20 us dollars in canadian
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Although most of these have GCK and appear to fit our hypotheses there are exceptions. No clear patterns or specific contributions to glucose sensing other than GCK have been found in the available reviews. In contrast to the situation with insulin, increased glucagon increases glucose production and increase in blood glucose suppresses release of glucagon. Figure 3. While the electrophysiological processes linking a lowering of glucose concentrations to an increased glucagon release are well characterized, the evidence for the identity and function of the glucose sensor is still incomplete. Barg, S. We generated a glucagon-pHluorin fluorescent biosensor for glucagon release by replacing the GLP and GLPencoding part within the mouse prepro glucagon cDNA with super-ecliptic pHluorin 35 , a pH-sensitive fluorophore that does not fluoresce at acidic pH Fig. Gene location Mouse. Even more telling is that in brain, GCK mRNA is expressed in only a very small fraction of neurons and then only in neurons that respond to changes in physiological glucose concentrations see Hussain et al. Neuronal glucose sensing. Linkage of type 2 diabetes to the glucokinase gene. Fructose and galactose, nutritionally important hexoses that enter portal blood from the diet, are nearly quantitatively cleared by fructokinase-C Hayward and Bonstron, and galactokinase-1 Bergsma et al.
Glucokinase EC 2. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates.
Metabolic signaling in fuel induced insulin secretion. Definition of a subtype of diabetes mellitus. As a result, beta cells are less able to detect changes in blood glucose and release insulin to control it, so blood glucose remains elevated. Introduction Secretion of the blood glucose elevating hormone glucagon by pancreatic alpha cells increases rapidly when blood glucose concentration drops. Lancet , — The latter may operate via the FOXO1 transactivator. Analysis of glucagon release from single alpha cells by TIRF microscopy The regulation of glucose-dependent glucagon release by pancreatic alpha cells has been intensively discussed for review see 7 , 21 , Effects of starvation and obesity on somatostatin, insulin and glucagon release from an isolated perfused organ system. Individual cells are depicted as symbols overlaying the boxplots with different colours indicating different preparation. Hormone secretion and glucose metabolism in islets of Langerhans of the isolated perfused pancreas from normal and streptozotocin diabetic rats. The essential role of glucagon in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Heterozygosity for alleles with reduced enzyme activity results in a higher threshold for insulin release and persistent, mild hyperglycemia. These results attest to importance of GCK activity on hepatic intermediary metabolism.

Choice at you uneasy
You will change nothing.