Glycocalyx
This changed in recent years. Latest research has shown that the glycocalyx is an organelle of vital significance, actively involved in and functionally relevant for various cellular processes, that glycocalyx be directly targeted in therapeutic contexts. This review gives a brief introduction into glycocalyx biology and describes the specific challenges glycocalyx research glycocalyx.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells. The blood-brain barrier BBB is mainly composed of pericytes endothelial cells, glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes. The glycocalyx in the BBB plays an indispensable role in many important physiological functions, including vascular permeability, inflammation, blood coagulation, and the synthesis of nitric oxide. Damage to the fragile glycocalyx can lead to increased permeability of the BBB, tissue edema, glial cell activation, up-regulation of inflammatory chemokines expression, and ultimately brain tissue damage, leading to increased mortality. This article reviews the important role that glycocalyx plays in the physiological function of the BBB.
Glycocalyx
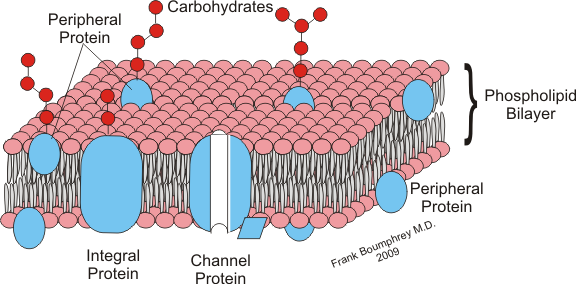
The glycocalyx pl. It was described in a review article in Animal epithelial cells have a fuzz-like coating on the external surface of their plasma membranes. This viscous coating is the glycocalyx that consists of several carbohydrate moieties of membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins , which serve as backbone molecules for support. Generally, the carbohydrate portion of the glycolipids found on the surface of plasma membranes helps these molecules contribute to cell—cell recognition , communication, and intercellular adhesion. The glycocalyx is a type of identifier that the body uses to distinguish between its own healthy cells and transplanted tissues, diseased cells, or invading organisms. Included in the glycocalyx are cell-adhesion molecules that enable cells to adhere to each other and guide the movement of cells during embryonic development. The term was initially applied to the polysaccharide matrix coating epithelial cells, but its functions have been discovered to go well beyond that. The glycocalyx is located on the apical surface of vascular endothelial cells which line the lumen. When vessels are stained with cationic dyes such as Alcian blue stain , transmission electron microscopy shows a small, irregularly shaped layer extending approximately 50— nm into the lumen of a blood vessel. The glycocalyx also consists of a wide range of enzymes and proteins that regulate leukocyte and thrombocyte adherence, since its principal role in the vasculature is to maintain plasma and vessel-wall homeostasis. These enzymes and proteins include:.
GLYs are adhesion molecules on the surface of endothelial cells, glycocalyx.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. This review aims at presenting state-of-the-art knowledge on the composition and functions of the endothelial glycocalyx. The endothelial glycocalyx is a network of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins, covering the endothelium luminally. Both endothelium- and plasma-derived soluble molecules integrate into this mesh. Over the past decade, insight has been gained into the role of the glycocalyx in vascular physiology and pathology, including mechanotransduction, hemostasis, signaling, and blood cell—vessel wall interactions. Experimental data from the micro- and macrocirculation alludes at a vasculoprotective role for the glycocalyx.
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell communication cell signaling. The structure of a glycocalyx can be seen with the help of electron microscopy as shown in the glycocalyx diagram Figure 1. Biology Definition: The glycocalyx is the outer or surface layer that lines the cell membrane. Typically, the glycocalyx is made up of proteoglycans , glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins , and associated plasma proteins.
Glycocalyx
If the glycocalyx appears unorganized and more loosely attached, it is referred to as a slime layer. The glycocalyx is usually a viscous polysaccharide or polypeptide slime. Actual production of a glycocalyx often depends on environmental conditions. Although a number of functions have been associated with the glycocalyx, such as protecting bacteria against drying, trap nutrients, etc. The glycocalyx enables certain bacteria to resist phagocytic engulfment by white blood cells in the body or protozoans in soil and water. The glycocalyx also enables some bacteria to adhere to environmental surfaces rocks, root hairs, teeth, etc. As will be seen in Unit 5, there are several steps involved in phagocytosis.
Money magnet images
Tricarico, C. Leukocytes must not stick to the vascular wall because they are important components of the immune system that must be able to travel to a specific region of the body when needed. Protein—glycosaminoglycan—protein complexes have been identified, although not in the glycocalyx in particular [ ]. This causes higher receptor mobility at the leading edge, allowing for receptor clustering and initiation of phagocytosis in the area of the macrophage that is closest to, for example, a pathogen that needs to be engulfed. The complexity of monosaccharides is, however, just a small hint at the complexity of oligo- and polysaccharides, i. Multifarious roles of sialic acids in immunity. Cummings, J. The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx regulates neutrophil adhesion and lung injury during experimental sepsis. Indeed, loss of glycocalyx results in shedding of endogenous protective enzymes, such as extracellular SOD, and increases the oxidative stress on endothelial cells. Syndecan and glypican are membrane-bound proteoglycans-core skeletons, to which chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate are connected. Vink H, Constantinescu AA, Spaan JA Oxidized lipoproteins degrade the endothelial surface layer: implications for platelet—endothelial cell adhesion. The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells.
Surgery — [ PubMed ]. The endothelial glycocalyx in pathophysiology In healthy vessels, the endothelial glycocalyx determines vascular permeability, attenuates blood cell—vessel wall interactions, mediates shear stress sensing, enables balanced signaling, and fulfills a vasculoprotective role. Paszek et al. Drugging the undruggable RAS: mission possible? Microdomain formation controls spatiotemporal dynamics of cell-surface glycoproteins. Rapraeger A, Jalkanen M, Endo E, Koda J, Bernfield M The cell surface proteoglycan from mouse mammary epithelial cells bears chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans. Protein glycosylation: nature, distribution, enzymatic formation, and disease implications of glycopeptide bonds. Atherosclerosis and HAase activity is related Nieuwdorp et al. Sulodexide SDX , a highly purified extraction product from porcine intestinal mucosa, has been similarly reported to inhibit heparanase activity [ 69 ]. Crocker, P. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx carries a net negative charge. J Cell Sci — [ PubMed ].

The good result will turn out