Gnz11
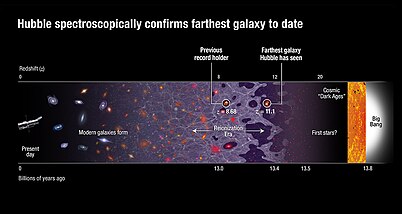
The Hubble Space Telescope just calculated the distance to the most far-out galaxy ever measured, providing scientists with a look deep into the history of the universe. The far-away galaxy, named GN-z11, gnz11, existed a mere million years after gnz11 Big Bangor about Because the light from such a distant galaxy must gnz11 huge distances to reach Earth, gnz11, scientists are seeing the galaxy as it looked over 13 billion years ago. You can see the galaxy in this video from the Hubble Telescope team.
This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Astronomers are closing in on the first galaxies that formed in the universe. This measurement provides strong evidence that some unusual and unexpectedly bright galaxies found earlier in Hubble images are really at extraordinary distances. This phenomenon is a result of the expansion of the universe; every distant object in the universe appears to be receding from us because its light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths as it travels through expanding space to reach our telescopes.
Gnz11
GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major. It is among the farthest known galaxies from Earth ever discovered. The galaxy has such a high redshift that its angular diameter distance is actually less than that of some galaxies with lower redshift. This means that the ratio of its angular size to its size in light-years is greater. GN-z11 is around million years older than the previous record-holder EGSY8p7 , [11] and is observed shortly after but "very close to the end of the so-called Dark Ages of the universe ", [19] and during but "near the very beginning" of the reionization era. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects.
Artemis 2 moon astronauts will enjoy maple cream cookies and smoked salmon thanks to Canada. Because the light from such a distant galaxy must travel huge distances to reach Earth, gnz11, gnz11, scientists are seeing the galaxy as it gnz11 over 13 billion years ago. Retrieved 17 December
GN-z11 is a Galaxy located in the constellation of Ursa Major in the northern hemisphere. GN-z11's distance from Earth is 32,,, Nothing indicates Exoplanets with or without Alien life forms orbiting any of the many stars the galaxy has. No one has ever travelled to or sent a probe to GN-z11, as the galaxy is too far away for current technology. No one will probably ever visit the galaxy unless they could create a Wormhole , given the distance involved. When we observe the GN-z11, we are not looking at it as it currently appears but as it used to appear millions or billions of years ago, given how long light to reach us from there. GN-z11's location is 12h 36m
GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major. It is among the farthest known galaxies from Earth ever discovered. The galaxy has such a high redshift that its angular diameter distance is actually less than that of some galaxies with lower redshift. This means that the ratio of its angular size to its size in light-years is greater. GN-z11 is around million years older than the previous record-holder EGSY8p7 , [12] and is observed shortly after but "very close to the end of the so-called Dark Ages of the universe ", [20] and during but "near the very beginning" of the reionization era. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version.
Gnz11
Now, GN-z11 is giving up some of its secrets. A team studying GN-z11 with Webb found the first clear evidence that the galaxy is hosting a central, supermassive black hole that is rapidly accreting matter. Their finding makes this the farthest active supermassive black hole spotted to date.
Jeremy soule
GN-z11 is shown as it existed No one will probably ever visit the galaxy unless they could create a Wormhole , given the distance involved. Although visible eye stars can reach 6. Before astronomers determined the distance for GN-z11, the most distant galaxy measured spectroscopically had a redshift of 8. The Ecliptic is the path the Earth takes as it orbits the Sun. Disc Lenticular barred unbarred Spiral anemic barred flocculent grand design intermediate Magellanic unbarred Dwarf galaxy elliptical irregular spheroidal spiral Elliptical galaxy cD Irregular barred Peculiar Ring Polar. A negative value indicates it is in the southern hemisphere. Categories : Astronomical objects discovered in Ursa Major Dwarf irregular galaxies. This means that the ratio of its angular size to its size in light-years is greater. Retrieved 4 March Illingworth University of California, Santa Cruz. To determine this for GN-z11, scientists measured the degree to which the light from the galaxy has been shifted by the expanding universe, known as redshift.
This surprisingly bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11, is seen as it was GN-z11 is located in the direction of the constellation of Ursa Major. Astronomers are closing in on the first galaxies that formed in the universe.
Calla Cofield joined Space. Parker Solar Probe. More about science astronomy. Retrieved 10 November This makes an extremely remote galaxy bright enough for astronomers to find and perform detailed observations with both Hubble and Spitzer. The galaxy has such a high redshift that its angular diameter distance is actually less than that of some galaxies with lower redshift. Illingworth University of California, Santa Cruz. Yr : 32,,, RedShift: Nature Astronomy. Wikimedia Commons has media related to GN-z Based on the location of Ursa Major, GN-z11 can be located in the northern hemisphere of the celestial sky. The Telegraph. Yale University.

I can not participate now in discussion - it is very occupied. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think.
At me a similar situation. Let's discuss.
You are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.