Guttation diagram
Use app Login.
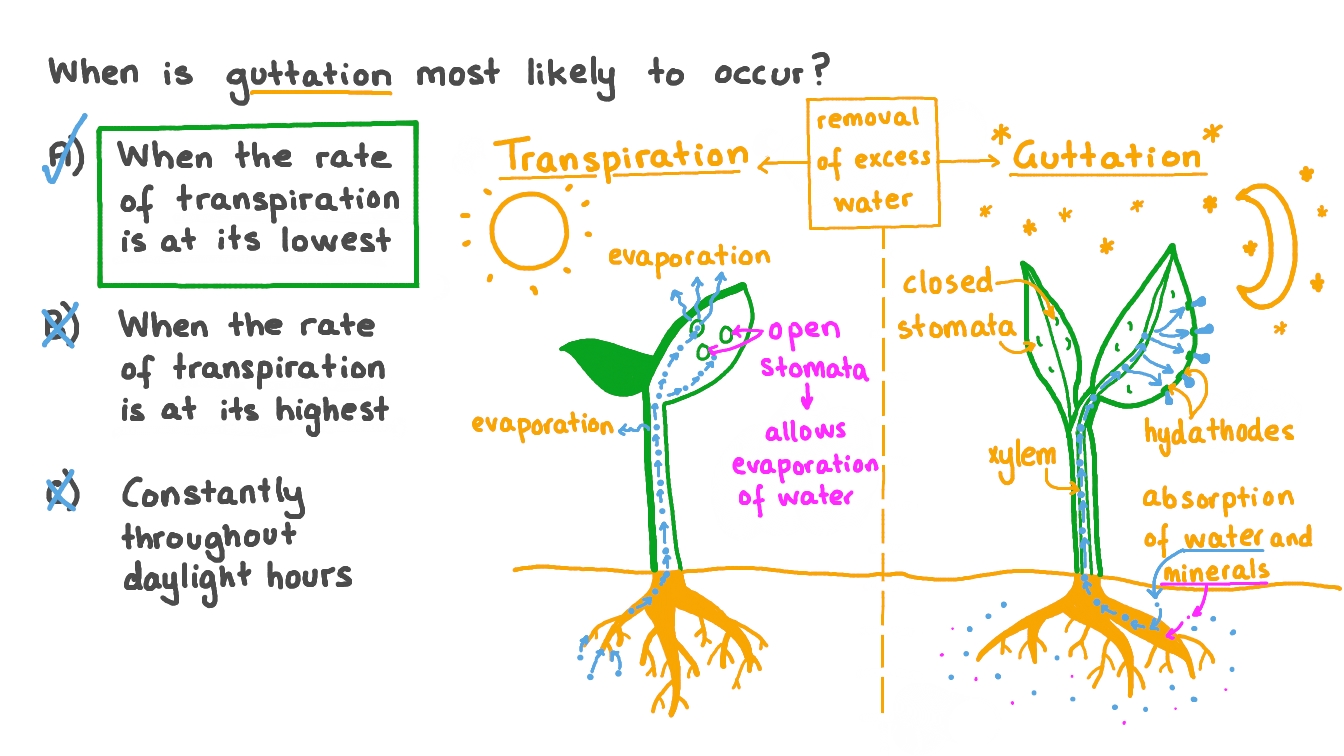
Guttation is a process by which plants release excess water from leaves as droplets. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. In this article, we will read about the demonstration, its mechanism, and demonstration , the role of hydathodes in guttation , the composition of water released during guttation , the difference between guttation and transpiration , and the importance of guttation. Guttation is a process that occurs in the case of vascular plants, in which excess water is removed from the leaf tips. Pores similar to stomata called hydathodes are present on the leaf tips that aid in this process.
Guttation diagram
.
Work Experiences.
.
Guttation is how plants expel excess water or nutrients through tiny openings on leaves and stems. Name — guttation Common name — crying plant, weeping leaves, teary plant, dewdrop Type — plant physiological process. This biological process enables plants to restore balance between their nutrient intake and needs. Guttation occurs when a plant oozes water and minerals out from perfectly healthy leaves , stems, and sometimes even flower petals. It takes place when roots of a plant absorb more water than the plant actually needs. Tiny, specialized cells on the surface of a leaf or stem are connected to veins and sap channels of the plant. This cluster of cells works as a nozzle. This process where excess pressure is released from inside the plant is called guttation. To understand why plants developed guttation as they evolved, it helps to brush up the following:. Hydathode nozzles are one of the biological tools plants use to regulate pressure inside them.
Guttation diagram
Hydathodes form natural openings but, unlike stomata, are open permanently and offer little resistance to the flow of fluid out of leaves. The cells of epithem are soft and made of loosely arranged thin-walled parenchyma cells and without chloroplast, and are involved in absorption and secretion. Internally, they are connected by tracheary endings to a large chamber with masses of thin-walled parenchymatous tissue surrounded by a sheath layer.
Dmc dalby
Additional Information. Campus Experiences. Brain Teasers. Stomata help in transpiration. Table of Content. These minerals are essential for various physiological functions in the plant. Suggest changes. Guttation becomes more important during the night when the plant continues to absorb water from the soil. Explain with the help of diagram of the vertical section of hydathode present on apical part of tomato or primula leaf. Catalysis - Definition, Mechanism, Types, Characteristics. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. Improve Improve. Thank you for your valuable feedback! Admission Experiences. View Solution.
Guttation is the process of liquid exudation from hydathodes situated on the tip, along the margins and adaxial and abaxial surfaces of leaves. Hydathodes, also known as water stomata or water pores, unlike stomata, are always open representing the path of least resistance to the liquid outflow from them.
Verified by Toppr. Influenced by factors such as root pressure , and humidity. Transpiration occurs during the daytime. The hydathode is made up of epithelial cells and has multiple intercellular spaces that are filled with water. Report issue Report. Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism. Maximize your earnings for your published articles in Dev Scripter ! Contribute your expertise and make a difference in the GeeksforGeeks portal. Influenced by factors such as sunlight , temperature and humidity. Vote for difficulty :. It occurs during the night or early morning when there is high atmospheric humidity and transpiration is less. Hydathodes release water from the pores of the margin of leaves.

Cold comfort!