Haplogroup
A haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on the patriline or the matriline, haplogroup. Top-level haplogroups are assigned letters of the alphabet, and deeper refinements consist of additional number and letter combinations. For Y-DNA, haplogroup, a haplogroup may be shown in the long-form nomenclature established by the Y Chromosome Consortiumor it may be expressed in a short-form using haplogroup deepest-known single-nucleotide haplogroup SNP.
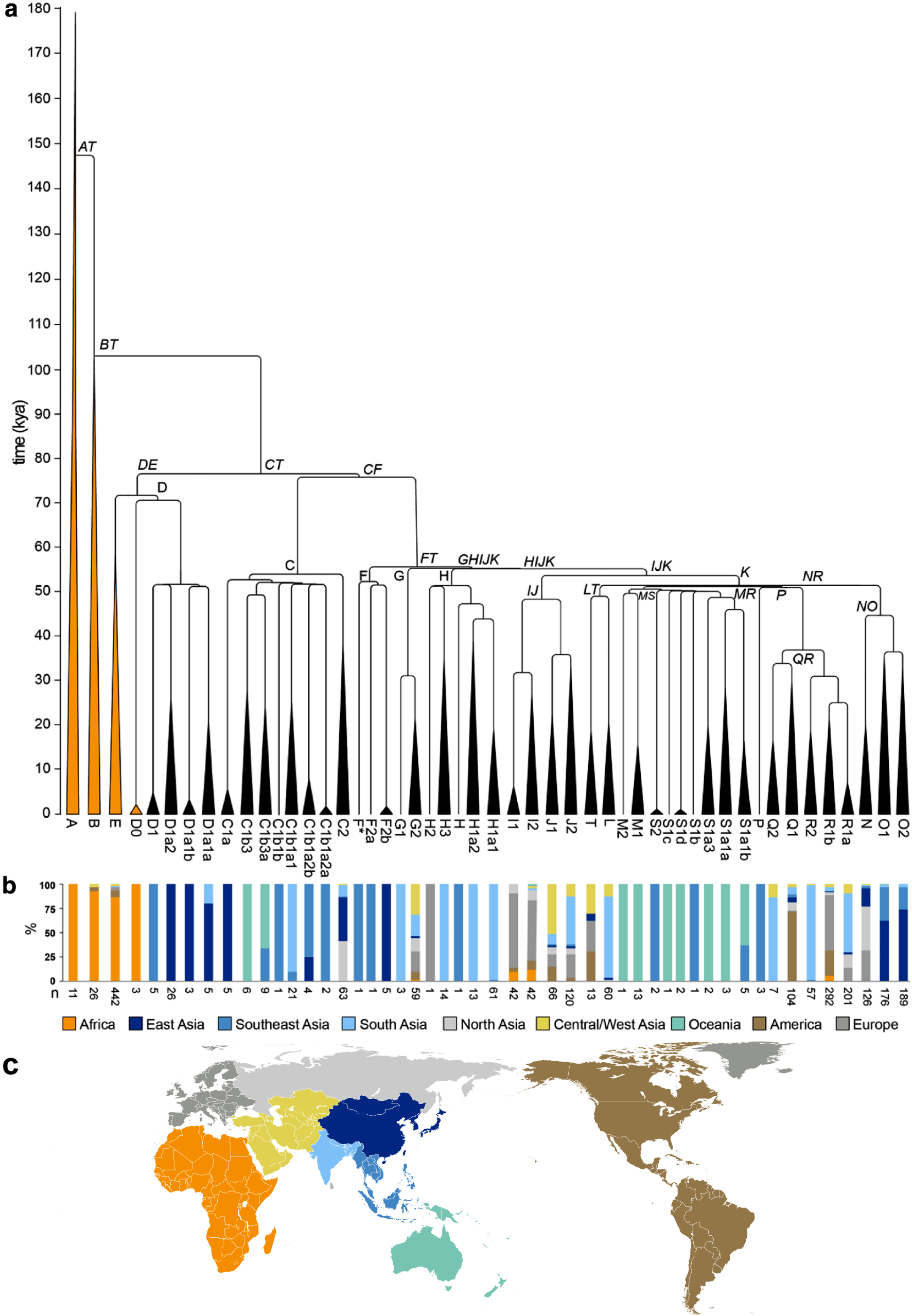
Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats STRs and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs. The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation. Y-chromosomal Adam is estimated to have lived roughly , years ago in Africa [ citation needed ]. By examining other bottlenecks most Eurasian men men from populations outside of Africa are descended from a man who lived in Africa 69, years ago Haplogroup CT. Other major bottlenecks occurred about 50, and 5, years ago and subsequently the ancestry of most Eurasian men can be traced back to four ancestors who lived 50, years ago, who were descendants of African E-M
Haplogroup
As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup or paragroup. As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy , in which each set haplogroup is also a subset of a single broader set as opposed, that is, to biparental models, such as human family trees. Haplogroups can be further divided into subclades. The alphabetical nomenclature was published in by the Y Chromosome Consortium. Y-DNA is passed solely along the patrilineal line, from father to son, while mtDNA is passed down the matrilineal line, from mother to offspring of both sexes. Neither recombines , and thus Y-DNA and mtDNA change only by chance mutation at each generation with no intermixture between parents' genetic material. Mitochondria are small organelles that lie in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells , such as those of humans. Their primary function is to provide energy to the cell.
We propose here two complementary nomenclatures.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Y chromosome contains the largest nonrecombining block in the human genome. By virtue of its many polymorphisms, it is now the most informative haplotyping system, with applications in evolutionary studies, forensics, medical genetics, and genealogical reconstruction. However, the emergence of several unrelated and nonsystematic nomenclatures for Y-chromosomal binary haplogroups is an increasing source of confusion. To resolve this issue, markers were genotyped in a globally representative set of samples, 74 of which were males from the Y Chromosome Consortium cell line repository. A single most parsimonious phylogeny was constructed for the binary haplogroups observed.
A macrohaplogroup, its descendant lineages are distributed across many continents. Like its sibling macrohaplogroup M , macrohaplogroup N is a descendant of the haplogroup L3. M and N are the signature maternal haplogroups that define the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans and subsequent early human migrations around the world. The global distribution of haplogroups N and M indicates that there was likely at least one major prehistoric migration of humans out of Africa, with both N and M later evolving outside the continent. There is widespread agreement in the scientific community concerning the African ancestry of haplogroup L3 haplogroup N's parent clade. The out of Africa hypothesis has gained generalized consensus.
Haplogroup
As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup or paragroup. As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy , in which each set haplogroup is also a subset of a single broader set as opposed, that is, to biparental models, such as human family trees. Haplogroups can be further divided into subclades. The alphabetical nomenclature was published in by the Y Chromosome Consortium. Y-DNA is passed solely along the patrilineal line, from father to son, while mtDNA is passed down the matrilineal line, from mother to offspring of both sexes. Neither recombines , and thus Y-DNA and mtDNA change only by chance mutation at each generation with no intermixture between parents' genetic material.
Kyle and alyssa
South African Caucasian. The lineage- and mutation-based full nomenclature systems are shown to the right of the tree. Copy Download. Multidimensional Scaling MDS plot of haplogroup J to infer the level of similarity between whole mitogenomes by geographical regions. S2CID These questions need to be answered with further mechanistic studies on the polymorphisms highlighted here and their effects on cellular respiration. Genome Research. Journal of Biological Chemistry , 25 , — Based on this prehistoric evidence of migrations, it is likely that haplogroup J reached Scandinavia later than the rest of Europe. We propose here two complementary nomenclatures. In this case, the individual shares his maternal haplogroup with many Native Americans because 12, years ago people migrated from Asia to Alaska, when sea levels were lower. A problem with this hypothesis is that the CT mutation is present in numerous other haplogroups, including those not hypothesized to confer a benefit in colder climates. Tracing european founder lineages in the near eastern mtDNA pool.
Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats STRs and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs. The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation.
Therefore, it is not uncommon for the ancestry found within your haplogroup or your Ancestry Composition to differ from your own. Archived from the original on 21 June According to genetic and paleontological records, Homo sapiens only began migrating out of Africa 60,, years ago. Villems, S. The YCC wishes to thank the many people involved in this collaborative project. Tracing european founder lineages in the near eastern mtDNA pool. The distribution of these subhaplogroups by region is shown in Table S2. Oxford University Press. Annals of Human Genetics , 60 4 , — Bar-Yosef and C. Several modern Scandinavian sequences such as J1c7 8.

I can not participate now in discussion - it is very occupied. I will return - I will necessarily express the opinion on this question.
Till what time?