How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule.
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Chemistry Bonding Basics Bonding. Jan 29,
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
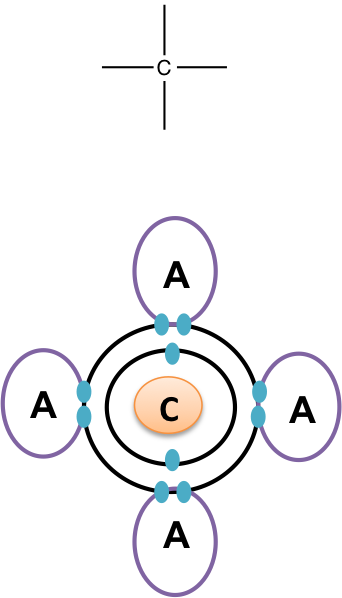
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule. The methane molecule provides an example: it has the chemical formula CH 4. Each of its four hydrogen atoms forms a single covalent bond with the carbon atom by sharing a pair of electrons. This results in a filled outermost shell. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, such as methane CH 4 described above. We often use hydrocarbons in our daily lives as fuels—like the propane in a gas grill or the butane in a lighter. The many covalent bonds between the atoms in hydrocarbons store a great amount of energy, which is released when these molecules are burned oxidized.
Search for:.
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things.
Inorganic Carbon. For more than years, chemists have divided compounds into two categories. Those that were isolated from plants or animals were called organic , while those extracted from ores and minerals were inorganic. Organic chemistry is often defined as the chemistry of carbon. But this definition would include calcium carbonate CaCO 3 and graphite, which more closely resemble inorganic compounds. Carbon therefore forms covalent bonds with many other elements. Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including N, O, P, and S.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things.
Bill nye atoms worksheet
In contrast to unsaturated fats, triglycerides without double bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated fats, meaning that they contain all the hydrogen atoms available. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Molecules must have a double bond to be cis - trans isomers. This diversity of molecular forms accounts for the diversity of functions of the biological macromolecules and is based to a large degree on the ability of carbon to form multiple bonds with itself and other atoms. When two carbon atoms form a double bond, the shape is planar, or flat. Try It. Carbon Bonding The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. The molecules may also form rings, which themselves can link with other rings Figure 2 c. Similarly, the D-form of glucose is the main product of photosynthesis and the L-form of the molecule is rarely seen in nature.
Well, carbon can form up to FOUR covalent bonds Carbon can also "catenate" ; i.
In this way, long and branching chains of carbon compounds can be made Figure 2 a. In nature, only the L-forms of amino acids are used to make proteins. Skip to main content. Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. In the trans configuration, the carbons form a more or less linear structure, whereas the carbons in the cis configuration make a bend change in direction of the carbon backbone. Skills to Develop Explain why carbon is important for life Describe the role of functional groups in biological molecules. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom. Figure 1. Geometric isomers , on the other hand, have similar placements of their covalent bonds but differ in how these bonds are made to the surrounding atoms, especially in carbon-to-carbon double bonds. Furthermore, individual carbon-to-carbon bonds may be single, double, or triple covalent bonds, and each type of bond affects the geometry of the molecule in a specific way.

I am am excited too with this question. Prompt, where I can read about it?
Here there's nothing to be done.
You are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.