How many valence electrons does n have
Nitrogen is present in almost all proteins and plays important roles in both biochemical applications and industrial applications. Nitrogen forms strong bonds because of its ability to form a triple bond with itself and other elements. Thus, there is a lot of energy in the compounds of nitrogen. Before years ago, little was known about nitrogen.
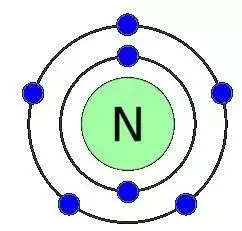
Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons. The thing to remember about main-group elements is that the group number gives you the element's number of valence electrons. In your case, nitrogen, "N" , is located in group 1color red 5 , which means that it has color red 5 valence electrons. Each nitrogen molecule consists of two atoms of nitrogen that are bonded by a triple covalent bond. This is a direct consequence of the fact that each nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons. Each atom can thus complete its octet by sharing three electrons.
How many valence electrons does n have
The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. There is a quick way of identifying the number of valence electrons - it is the same as the Group number not for d-block elements , though. Nitrogen is in Group 5, so it has 5 outer shell electrons. How many valence electrons does nitrogen have? Doc Croc. Jun 8, Five The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. Related questions How do valence electrons affect chemical bonding? How do valence electrons determine chemical properties? How do valence electrons determine chemical reactivity? How many valence electrons are in a silicon atom?
Enantiomeric Excess. Substitution Reactions 1h 47m. Carbocation Stability.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. A Review of General Chemistry 5h 9m. Intro to Organic Chemistry. Atomic Structure.
In chemistry and physics , valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom , and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond , a shared pair forms with both atoms in the bond each contributing one valence electron. The presence of valence electrons can determine the element 's chemical properties, such as its valence —whether it may bond with other elements and, if so, how readily and with how many. In this way, a given element's reactivity is highly dependent upon its electronic configuration. For a main-group element , a valence electron can exist only in the outermost electron shell ; for a transition metal , a valence electron can also be in an inner shell. An atom with a closed shell of valence electrons corresponding to a noble gas configuration tends to be chemically inert. Atoms with one or two valence electrons more than a closed shell are highly reactive due to the relatively low energy to remove the extra valence electrons to form a positive ion. An atom with one or two electrons fewer than a closed shell is reactive due to its tendency either to gain the missing valence electrons and form a negative ion, or else to share valence electrons and form a covalent bond.
How many valence electrons does n have
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Introduction to the periodic table.
Just dance 2016 tracklist
EAS:Halogenation Mechanism. Alkane Halogenation. Side-Chain Halogenation. Oxidizing Agent. It is often used in medical research and preservation. Imine vs Enamine. Condensed Structural Formula. Purpose of Analytical Techniques. Malonic Ester Synthesis. Carboxylic Acid to Acid Chloride.
The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. There is a quick way of identifying the number of valence electrons - it is the same as the Group number not for d-block elements , though.
Sigmatropic Rearrangement. Now, nitrogen is commonly used to preserve food and as a fertilizer. Nitrogen has two naturally occurring isotopes, nitrogen and nitrogen, which can be separated with chemical exchanges or thermal diffusion. Malonic Ester Synthesis. Free Radical Polymerization. R and S Configuration. Ether Cleavage. Almost all the oxides that form are gasses, and exist at 25 degrees Celsius. Claisen Condensation. Radical Synthesis. Aromatic Heterocycles. It only appears in 0. Electron Withdrawing Groups. Thomas, Jacob. Calculations with Enantiomeric Percentages.

Very much the helpful information
The authoritative point of view, funny...