Hybridization of carbon in co2
We will learn about the hybridization of CO 2 on this page. Carbon dioxide basically has a sp hybridization type. This type of hybridization occurs as a result of carbon being bound to two other atoms. We can determine this by closely observing each atom of CO 2.
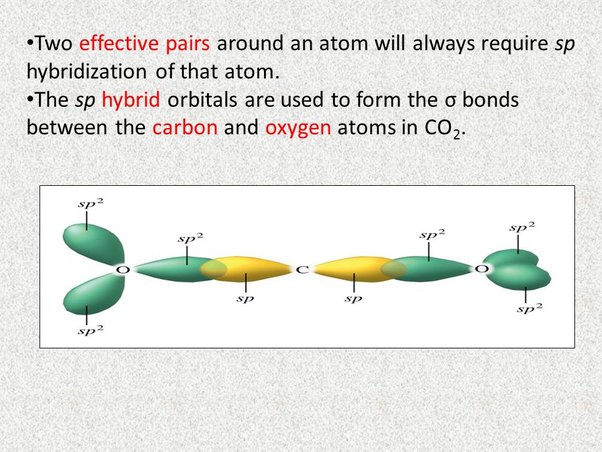
To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two double bonds, or two effective pairs exist in it. However, this is not enough to produce bonds with oxygen. So, then, one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to the 2p level that results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. They are used to form a pi bond as for the two remaining p electrons.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
The carbon dioxide or CO2 has sp type hybridisation. This type of hybridisation occurs as an outcome of the carbon being bound to two different atoms. The atom of the carbon comprises 2 double bonds, i. However, this is not sufficient for creating bonds involving the oxygen. Therefore, one electron from the 2s orbital shifts from the 2s level to 2p level, which leads to the creation of 2 hybrid orbitals. These hybridised sp orbitals belonging to the carbon atoms extend beyond 2p orbitals that belong to the atoms of oxygen for creating two sigma bonds. A pi-bond is formed between the 2 leftover p electrons. The oxygen hybridised its orbital for creating 3 hybrid orbitals of sp2 in the CO2 molecule. Moreover, the p orbital inside the atom of oxygen stays the same and is used primarily to create a pi-bond. However, only 1 sp hybrid orbital will be used from these 3 sp hybrid orbitals to make a bond with carbon atoms. Firstly, let us find out the types of bonds in the molecule by making the chemical structure of the molecule. Particularly, note down the number of single, double, and triple bonds made by each atom.
It will look like the following.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of chemistry to explore the hybridization of CO 2. Carbon dioxide is an interesting molecule, with carbon at its core exhibiting sp hybridization. This hybridization arises due to the carbon atom being bonded to two other atoms, which can be either two double bonds or a combination of one single and one triple bond. We can understand this better by scrutinizing each atom of CO 2 more closely. When we discuss the hybridization of carbon dioxide, we start with the central carbon atom. This atom has two effective pairs, or two double bonds. However, to form bonds with oxygen, this is not sufficient.
First, we need to draw the Lewis structure of CO 2. Write the correct skeletal structure for the molecule. Sum the valence electrons from all the atoms. Use a pair of electrons to form a bond between each pair of bound atoms. Add the remaining electrons to satisfy the octet for a more electronegative atom first. If any atoms lack an octet, make a double or triple bond to give them an octet. The oxygens have 8 electrons. However, the carbon has only four and in these cases, you need to move one of the lone pairs, from the element that has an octet to the element lacking an octet to make another bond:. At this point, all the atoms have 8 electrons.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of chemistry to explore the hybridization of CO 2. Carbon dioxide is an interesting molecule, with carbon at its core exhibiting sp hybridization. This hybridization arises due to the carbon atom being bonded to two other atoms, which can be either two double bonds or a combination of one single and one triple bond. We can understand this better by scrutinizing each atom of CO 2 more closely. When we discuss the hybridization of carbon dioxide, we start with the central carbon atom. This atom has two effective pairs, or two double bonds. However, to form bonds with oxygen, this is not sufficient. This is where the magic of hybridization comes into play. One electron from the 2s orbital hops to the 2p level, leading to the creation of two hybrid orbitals.
Moon lord drops
Band Theory. Similarly, if we talk about the oxygen atom also undergoes hybridization to form three sp2 types of hybrid orbitals. In Total, we used 16 valence electrons. Learn more topics related to Chemistry. This hybridization type occurs as a result of carbon being bound to the other two atoms. Lone pairs absorb the hybridised orbitals. First, calculate the atoms that carbon is bonded with. View Result. Does CO2 comprise sp2 hybridisation? Reserved Seats. The absence of the double bonds represents a hybridisation of sp3. Law of Thermodynamics. Preparation of Aluminium Chloride. Login To View Results.
Carbon Dioxide is one of the best compounds to start with learning the concepts of Lewis structure and Molecular Geometry. This molecule can be a good start for beginners who want to learn the fundamentals of such concepts and want to know how to draw Lewis dot structures for other molecules as well. Although this gaseous molecule is known for its contribution to the greenhouse effect and global warming , one cannot deny that there are quite a lot of uses for this gas in several industries.
An atom with 2 or more than 2 double bonds, or with a single-triple bond, comprises hybridisation of sp. Related articles. Law of Thermodynamics. The type of hybridization in CO 2 is sp hybridization, and each carbon atom forms two sp hybrid orbitals. Temporary Hardness of Water. In addition, the properties of CO2 are discussed in this article. Two 2p orbitals, such as the 2px as well as 2pz, hold just a single electron. If we talk about its uses, these are as follows:. It can also be found closely with the observation of every single atom of CO2. One of the electrons from the 2s electrons can be considered to be eager to fill the other unfilled 2p orbital to give a configuration of 1s2 2s1 2p3. Share via. Access more than.

Today I read on this theme much.