Kinetoplast
Federal government websites kinetoplast end in. The site is secure.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts". The kinetoplastids were first defined by Bronislaw M. Honigberg in as the members of the flagellated protozoans. One family of kinetoplastids, the trypanosomatids, is notable as it includes several genera which are exclusively parasitic. Bodo is a typical genus within kinetoplastida, which also includes various common free-living species which feed on bacteria.
Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kDNA is best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig. The kDNA circles are of two types, maxicircles and minicircles. Maxicircles usually range from 20 to 40 kb, depending on the species, and are present in a few dozen identical copies per network. Minicircles, present in several thousand copies per network, are usually nearly identical in size 0. Maxicircles encode typical mitochondrial gene products e. To generate functional mRNAs, the cryptic maxicircle transcripts undergo posttranscriptional modification via an intricate RNA editing process that involves insertion and deletion of uridine residues at specific sites in the transcripts. The genetic information for editing is provided by guide RNAs gRNAs that are mostly encoded by minicircles, although a few are encoded by maxicircles. Encoding gRNAs is the only known function of minicircles, and some organisms that edit extensively such as Trypanosoma brucei possess about different minicircle sequence classes in their network to provide sufficient gRNAs. For reviews on RNA editing, see references 13 , 17 , and
Introduction The kinetoplast is a diagnostic structure of kinetoplast Kinetoplastida order, which encompasses the Trypanosomatidae family.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They include free-living microorganisms, as well as parasites of diverse invertebrate, vertebrate, and plant species. Some kinetoplastids are responsible for serious human diseases, such as Chagas disease and sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei , respectively , and the various forms of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. The network of rings in kDNA forms a beautiful structure.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kDNA is best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig. The kDNA circles are of two types, maxicircles and minicircles. Maxicircles usually range from 20 to 40 kb, depending on the species, and are present in a few dozen identical copies per network. Minicircles, present in several thousand copies per network, are usually nearly identical in size 0.
Kinetoplast
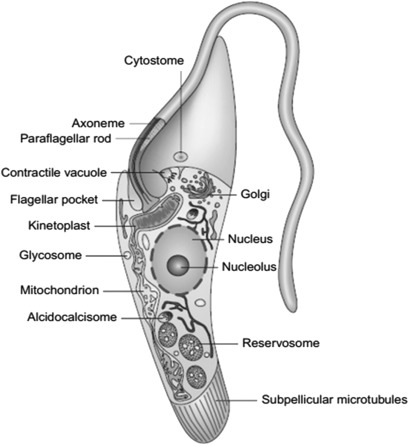
Situated near the nucleus, kinetoplasts are made up of a dense structure consisting of DNA kDNA within the mitochondria. As an extranuclear bundle of DNA, kinetoplast are distinguishing features among some eukaryotes that are collectively known as kinetoplastids members of the order Kinetoplastida. Based on molecular studies, kinetoplasts have been shown to contain two types of circular DNA. These include:. Kinetoplasts were first identified in the s by scientists like William Trager using the light microscope. At the time, they were described as tiny spherical or rod-shaped structures located behind the basal body of the flagellum. Using Feulgen stain studies also showed that it contained DNA. Through new studies, the kinetoplast was found to be specifically located within a specialized part of the mitochondrial matrix and perpendicular to the flagellum axis. Like some of the other organelles , the kinetoplast is self-replicating with its division preceding that of the nucleus. The kDNA of kinetoplastids, which is condensed and organized to form a disc-shaped structure makes up between 5 and 25 percent of the total cell DNA.
Circle k slurpee cost
The maxicircle is indicated by the arrow in b. Zuma A. The form and structure of kinetoplast DNA of Crithidia. Flagellum Cilium Pseudopodia Gliding motility. Observing the data of Table 1 , we note that the kDNA isolated from distinct trypanosomatids exhibited a very similar pattern of organization and sizes Figure 8. Schematic view of the primary structures and organelles found in the trypanosomatid T. Universal minicircle sequence-binding protein, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that recognizes the two replication origins of the kinetoplast DNA minicircle. The network of maxicircles and minicircles are catenated to form a planar network that resembles chain mail. By rotating, the minicircles of the daughter kinetoplast are assembled in a spiral fashion and begin moving inward toward the center of the disk as new minicircles are unlinked and moved into the KFZ for replication. Nucleotide sequences provide evidence of genetic exchange among distantly related lineages of Trypanosoma cruzi. American Naturalist 99 , — The circles are catenated to form a planar network that has a topology resembling that of chain mail in medieval armor Fig. The single flagellum extends from the anterior end of the cell to the right and does not run along the side of the cell.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms.
Open in a separate window. Molecular and Cellular Biology 6 , — For reviews on RNA editing, see references 13 , 17 , and Incredibly, the discovery of this new cellular mechanism did not catch the attention of biologists around the globe until , when Kenneth Stuart and his collaborators showed that over 50 percent of the T. Tsukubea Tsukubamonadida Tsukubamonadidae. Petalomonadea Petalomonadida Petalomonadidae Sphenomonadidae. Proposed evolution of kinetoplastids, emphasizing differences in kDNA organization and compaction. The Moving Kinetoplast. In recent years, AFM has been used to study kDNA topology and the effect of drugs on the kinetoplasts of trypanosomatids. Universal minicircle sequence-binding protein, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that recognizes the two replication origins of the kinetoplast DNA minicircle. Scientists were curious why the kinetoplast remained near the basal body. Taken together, the data presented here demonstrated that AFM is an excellent tool for analyzing the disruption of the kDNA network caused by drugs, as well as to evaluate the topology of kDNA networks, complementing the studies of electron microscopy. Within the KFZ, minicircles encounter key proteins that are localized specifically in this region. In addition, the authors suggested that maxicircles were equivalent to the mitochondrial DNA in other organisms.

I can ask you?
In my opinion it is obvious. I will refrain from comments.