Kuffer cells
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions, kuffer cells. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Although macrophages contribute to cancer cell dissemination, immune evasion, and metastatic outgrowth, they have also been reported to coordinate tumor-specific immune responses. We therefore hypothesized that macrophage polarization could be modulated therapeutically to prevent metastasis.
Kuffer cells
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair. Multiple M2 phenotypes can be distinguished, each involved in the resolution of inflammation and wound healing. Here, we have provided an update on recent research that has contributed to the developing delineation of the contribution of Kupffer cells to different types of liver injury, with an emphasis on alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases. These recent advances in our understanding of Kupffer cell function and regulation will likely provide new insights into the potential for therapeutic manipulation of Kupffer cells to promote the resolution of inflammation and enhance wound healing in liver disease. Kupffer cells, the resident macrophage in the liver, comprise the largest population of resident tissue macrophages in the body. It was not until that Tadeusz Browiecz correctly identified them as macrophages Kupffer cells play a critical role in the innate immune response; their localization in the hepatic sinusoid allows them to efficiently phagocytize pathogens entering from the portal or arterial circulation. Kupffer cells also serve as a first line of defence against particulates and immunoreactive material passing from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal circulation and may be considered as a final component in gut barrier function.
Mosser, D.
AoH publishes editorials, opinions, concise reviews, original articles, brief reports, letters to the editor, news from affiliated associations, clinical practice guidelines and summaries of congresses in the field of Hepatology. Our journal seeks to publish articles on basic clinical care and translational research focused on preventing rather than treating the complications of end-stage liver disease. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD is considered to be a manifestation of liver metabolic damage and is related to insulin resistance and genetic susceptibility.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Tissue macrophages are highly adapted to their tissue of residence, but it is unclear how they become specialized from common progenitors. Now, complementary studies from the Guilliams and Glass laboratories detail many of the precise cellular and molecular interactions that promote Kupffer cell KC specialization in the liver.
Kuffer cells
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Theater development fund
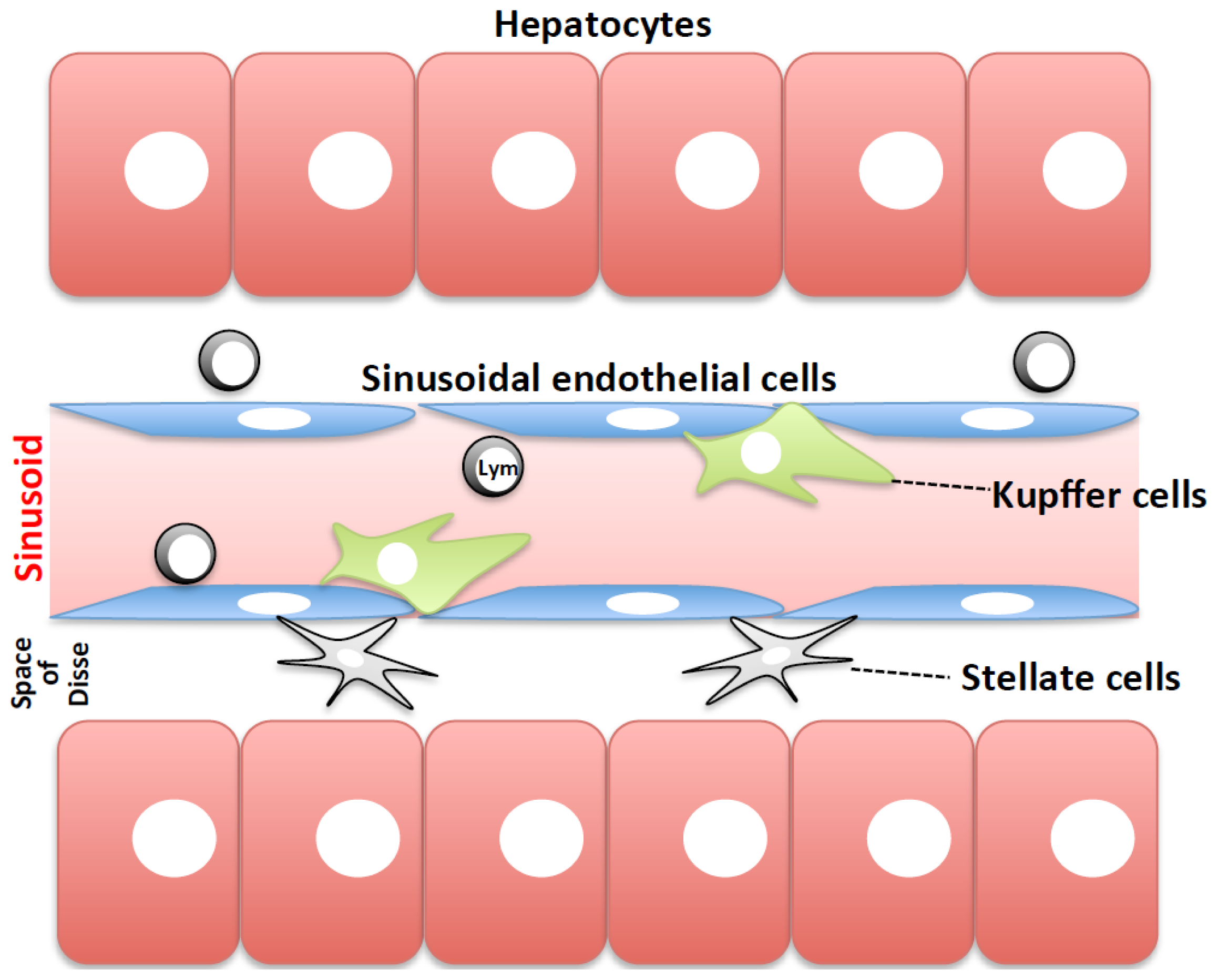
While the first hit is direct, mediated by the direct toxicity of ethanol and its metabolic byproducts, the second hit is indirect, mediated by increased uptake of lipopolysaccharide endotoxin from the intestine. Chronic ethanol-induced insulin resistance is associated with macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue and altered expression of adipocytokines. Results obtained by different research groups showed that: 1 chemical depletion of KCs prevents the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and alleviates hepatocellular damage [ 80 ] and 2 ablation of KCs protects against the development of hepatic insulin resistance in response to high-fat diets [ 79 ] and hepatic steatosis after longer feeding of high-fat diets [ 81 ]. Cancer 5 , 1—13 Tissue expression of human Toll-like receptors and differential regulation of Toll-like receptor mRNAs in leukocytes in response to microbes, their products, and cytokines. Peripheral blood monocytes can enter the liver and then mature into a phenotype characteristic of tissue macrophages. Aldred A, Nagy LE. Cell , — Granger DN. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Gordon S. The possibility to synthetize thalidomide analogs lacking these teratogenic effects could be a next step to modulate KC functions in pathological conditions. Their strategic position in liver allows to them discriminate and remove neoplastic cells that rich to liver.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. The hepatocytes were arranged radially around the central vein, the structure of the hepatic sinus was clear and there was no pathological change. Macrophage-derived Wnt opposes Notch signaling to specify hepatic progenitor cell fate in chronic liver disease. Dietary glycine prevents increases in hepatocyte proliferation caused by the peroxisome proliferator WY, Brahmer, J. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Interestingly, many of the same signaling pathways targeted by ethanol in neurons, resulting in the complex behavioral effects of ethanol, are also involved in TLRmediated signal transduction in macrophages. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 6 , pp. Brenner [ 72 ] identified the importance of the CCR2 receptor, which is expressed on the KC surface in liver fibrosis. These subclasses are induced by different regulators and exhibit distinct marker proteins on their cell surface, as well as distinct functional activity It indicated that the normal function of hepatocytes was impaired, and the liver microenvironment was severely imbalanced in patients with hepatic AE. Exp Mol Pathol.

0 thoughts on “Kuffer cells”