Lewis dot na
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines its chemical characteristics. We visualize valence electrons using Lewis dot structures to locate stable electron configurations.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side.
Lewis dot na
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot symbol or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. Figure 1. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium: Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown below for chlorine and sulfur: Figure 2 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Figure 2. Cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer Lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms gaining electrons. The total number of electrons does not change. The valence electron configuration for aluminum is 3 s 2 3 p 1. So it would have three dots around the symbol for aluminum, two of them paired to represent the 3 s electrons or three single dots around the atom :. The valence electron configuration for selenium is 4 s 2 4 p 4.
A single bond is represented by a line. For atoms with partially filled d or f subshells, lewis dot na, these electrons are typically omitted from Lewis electron dot diagrams. Lewis electron dot diagrams use dots to represent valence electrons around an atomic symbol.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is:.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram, or a Lewis diagram, or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. The order in which the positions are used does not matter. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is simply. Because the side is not important, the Lewis electron dot diagram could also be drawn as follows:. The electron dot diagram for helium, with two valence electrons, is as follows:. By putting the two electrons together on the same side, we emphasize the fact that these two electrons are both in the 1 s subshell; this is the common convention we will adopt, although there will be exceptions later.
Lewis dot na
Why are some substances chemically bonded molecules and others are an association of ions? The answer to this question depends upon the electronic structures of the atoms and nature of the chemical forces within the compounds. Although there are no sharply defined boundaries, chemical bonds are typically classified into three main types: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. In this chapter, each type of bond wil be discussed and the general properties found in typical substances in which the bond type occurs. Each bond classification is discussed in detail in subsequent sections of the chapter. Let's look at the preferred arrangements of electrons in atoms when they form chemical compounds. At the beginning of the 20 th century, the American chemist G.
V guard pump 0.5 hp price
A Lewis structure is a type of diagram used to represent the electron configuration of a molecule or ion. The valence electron configuration of thallium, whose symbol is Tl, is 6 s 2 5 d 10 6 p 1. So it would have three dots around the symbol for aluminum, two of them paired to represent the 3 s electrons or three single dots around the atom : The valence electron configuration for selenium is 4 s 2 4 p 4. Additional lone pairs can then be placed on the central atom. Licenses and Attributions. As such, the electron dot diagram for carbon is as follows:. Anions have extra electrons when compared to the original atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. The next atom, lithium, has an electron configuration of 1 s 2 2 s 1 , so it has only one electron in its valence shell. As a result, each atom acquires a charge. The next atom is boron. In the Lewis dot structure of sodium chloride, the valence electron from sodium forms a covalent bond with one of the valence electrons from chlorine. There is an ionic bond between sodium and chlorine, one atom donates an electron and the other accepts it. For carbon, there are four valence electrons, two in the 2 s subshell and two in the 2 p subshell. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table.
Here are some videos to help with this concept. They help you see what type of bonds form in molecules by just focusing on the outer electrons.
What column of the periodic table has Lewis electron dot symbol with two electrons? The remaining valence electrons from both sodium and chlorine are arranged around the atoms as lone pairs. Lewis structure for NaCl consists of two elements sodium Na metal and chlorine Cl atom. A Lewis structure is a type of diagram used to represent the electron configuration of a molecule or ion. The central atom of the molecule or ion is chosen because it has the lowest electronegative charge. The structure consists of a skeletal structure of the molecule, with atoms represented by their chemical symbols and electrons represented by dots. In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. Skip to content Draw a Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion. Lewis Dot structure of Sodium Chloride. Key Takeaways Lewis electron dot diagrams use dots to represent valence electrons around an atomic symbol.

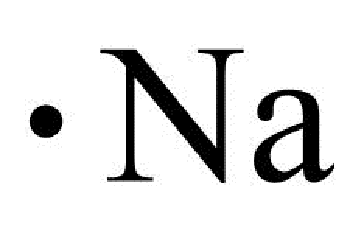
0 thoughts on “Lewis dot na”