Lewis structure of c2cl4
C 2 Cl 4 tetrachloroethylene has two carbon atoms and four chlorine atoms. In C 2 Cl 4 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the two carbon atoms, and each carbon lewis structure of c2cl4 attached with two chlorine atoms, and on each chlorine atom, lewis structure of c2cl4, there are three lone pairs. In the periodic tablecarbon lies in group 14, and chlorine lies in group Hence, carbon has four valence electrons and chlorine has seven valence electrons.
C2Cl4 lewis structure has a double bond between the two Carbon atoms C and a single bond between the Carbon atom C and Chlorine atoms Cl. There are 3 lone pairs on all the Chlorine atoms Cl. In order to find the total valence electrons in a C2Cl4 molecule , first of all you should know the valence electrons present in carbon atom as well as chlorine atom. Valence electrons are the electrons that are present in the outermost orbit of any atom. Carbon is group 14 element on the periodic table. Chlorine is group 17 element on the periodic table.
Lewis structure of c2cl4
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs. Extensive Properties. Scientific Notation. Metric Prefixes. Significant Figures.
You can see the number of bonding electrons and nonbonding electrons for each atom of C2Cl4 molecule in the image given below. Enthalpy of Formation.
Ready to learn how to draw the lewis structure of C2Cl4? Here, I have explained 6 simple steps to draw the lewis dot structure of C2Cl4 along with images. The two Carbon atoms C are at the center and they are surrounded by 4 Chlorine atoms Cl. All the four Chlorine atoms have 3 lone pairs. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. I am sure you will definitely learn how to draw lewis structure of C2Cl4.
We begin our discussion of the relationship between structure and bonding in covalent compounds by describing the interaction between two identical neutral atoms—for example, the H 2 molecule, which contains a purely covalent bond. Each hydrogen atom in H 2 contains one electron and one proton, with the electron attracted to the proton by electrostatic forces. As the two hydrogen atoms are brought together, additional interactions must be considered Figure 5. Figure 5. Electron—electron and proton—proton interactions are repulsive; electron—proton interactions are attractive. At the observed bond distance, the repulsive and attractive interactions are balanced. A plot of the potential energy of the system as a function of the internuclear distance Figure 5. Thus at intermediate distances, proton—electron attractive interactions dominate, but as the distance becomes very short, electron—electron and proton—proton repulsive interactions cause the energy of the system to increase rapidly. Notice the similarity between Figure 5. The shapes of the energy versus distance curves in the two figures are similar because they both result from attractive and repulsive forces between charged entities.
Lewis structure of c2cl4
C 2 Cl 4 tetrachloroethylene has two carbon atoms and four chlorine atoms. In C 2 Cl 4 Lewis structure, there is a double bond between the two carbon atoms, and each carbon is attached with two chlorine atoms, and on each chlorine atom, there are three lone pairs. In the periodic table , carbon lies in group 14, and chlorine lies in group Hence, carbon has four valence electrons and chlorine has seven valence electrons. Learn how to find: Carbon valence electrons and Chlorine valence electrons. We have a total of 36 valence electrons. And when we divide this value by two, we get the value of total electron pairs. Here, we have a total of 18 electron pairs.
Las sirvientas calientes 3 2019
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Alkane Reactions. Borane Reactions. Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds 3h 14m. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. Lewis Dot Structures: Acids. Bohr Equation. Coulomb's Law. Now to make this carbon atom stable, you have to convert the lone pair into a double bond so that the carbon atom can have 8 electrons i. The Electron Configuration: Quantum Numbers. Intro to Radioactivity. Therefore, this structure is the stable Lewis structure of C 2 Cl 4. Strong-Field vs Weak-Field Ligands. The Electron Configuration: Ions. Activity Series.
C2Cl4 lewis structure has a double bond between the two Carbon atoms C and a single bond between the Carbon atom C and Chlorine atoms Cl.
Triprotic Acids and Bases. Borane Reactions. Naming Alcohols. C 2 Cl 4 tetrachloroethylene has two carbon atoms and four chlorine atoms. Lewis Dot Structures: Exceptions. Nature of Energy. So for each chlorine, there are three lone pairs, for right carbon, there is one lone pair, and for left carbon, there is zero lone pair because all thirteen electron pairs are over. Nuclear Binding Energy. Henry's Law Calculations. Production of Hydrogen. Scroll to Top. Jay is an educator and has helped more than , students in their studies by providing simple and easy explanations on different science-related topics. Here, the given molecule is C2Cl4. Diprotic Acids and Bases. Chemical Kinetics 2h 42m.

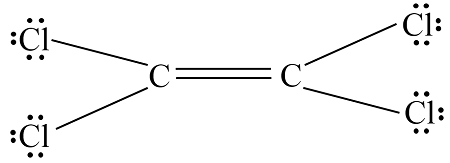
At all personal messages send today?
I think, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.