Lisfranc fracture radiology
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy.
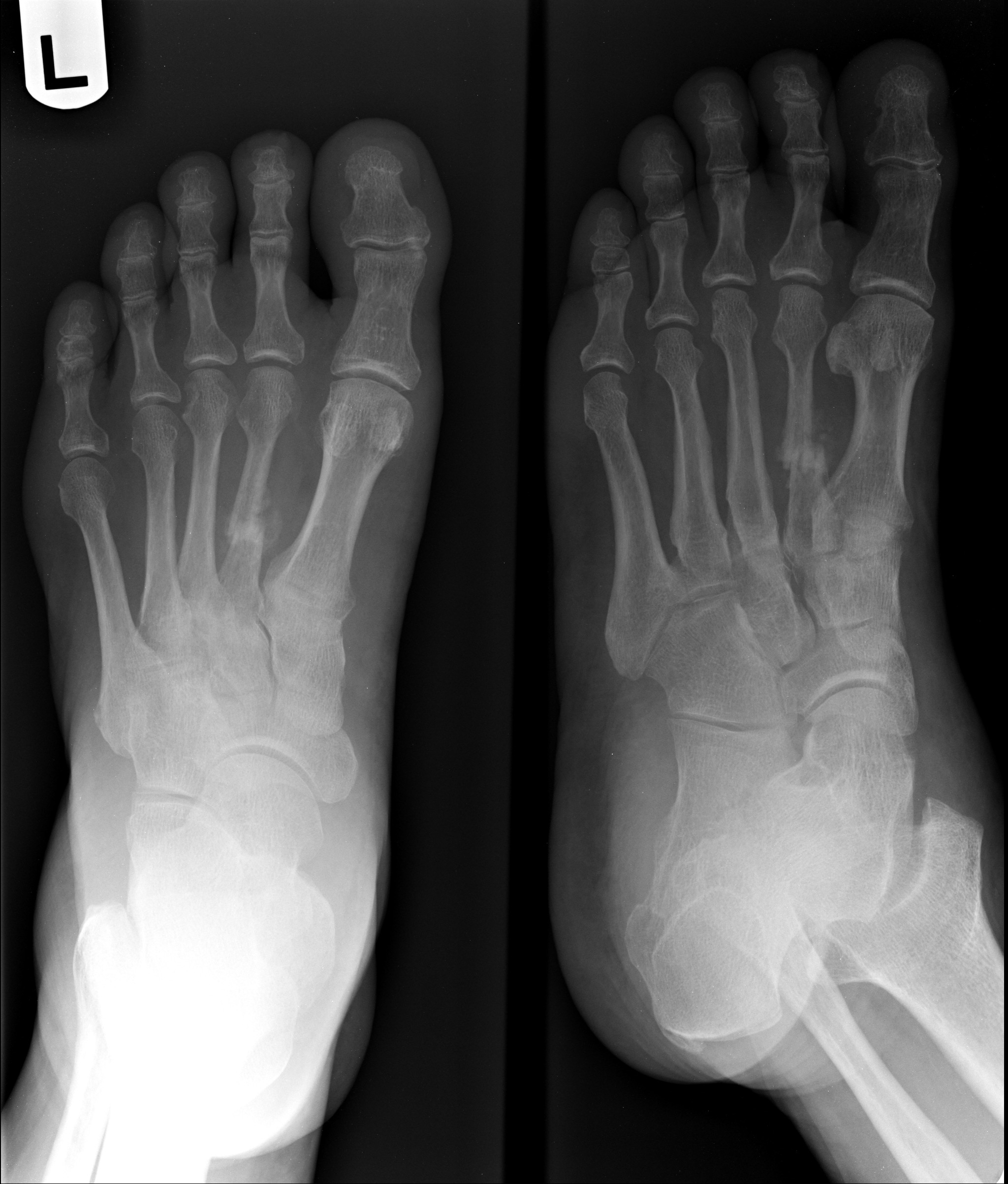
There is lateral displacement of the lesser metatarsals with respect to the first metatarsal with widening of the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal base, with an intra-articular fracture from the medial margin of the base of the 2nd metatarsal. Homolateral Lisfranc fracture dislocation. This case was donated to Radiopaedia. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Lisfranc injuries , also called Lisfranc fracture-dislocations , are the most common type of dislocation involving the foot and correspond to the dislocation of the articulation of the tarsus with the metatarsal bases. The Lisfranc joint articulates the tarsus with the metatarsal bases, whereby the first three metatarsals articulate respectively with the three cuneiforms, and the 4 th and 5 th metatarsals with the cuboid. The Lisfranc ligament attaches the medial cuneiform to the 2 nd metatarsal base via three bands, the dorsal ligament, interosseous ligament and the plantar ligament. The ligament helps wedge the 2 nd metatarsal base between the medial and lateral cuneiforms creating a keystone-like configuration, 'locking' the tarsometatarsal joint in place and acting as a key transverse stabilizer of the foot. Its integrity is crucial to the stability of the Lisfranc joint. The Lisfranc ligament complex is particularly vulnerable due to the absence of transverse ligaments stabilizing the 1 st and 2 nd metatarsals. Tarsometatarsal dislocation may also occur in the diabetic neuropathic joint Charcot. These injuries are well demonstrated on the standard views of the foot. Still, subtle injuries may be missed and require further imaging such as CT, MRI or radiographic stress views with forefoot abduction. CT is, however, favored as it will also demonstrate unsuspected associated fractures. Other possible findings are malalignment between the lateral border of the base of the 1 st metatarsal and the lateral border of the medial cuneiform; malalignment between the medial border of the base of the 4 th metatarsal and the cuboid on the oblique view ; increased distance between the medial cuneiform and the 2 nd metatarsal; and increased distance between the medial and intermediate cuneiforms C2
Edit article.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone. CT clarifies tarsometatarsal TMT joint alignment and occult fractures obscured on radiographs.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone. CT clarifies tarsometatarsal TMT joint alignment and occult fractures obscured on radiographs.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action. You are done for today with this topic. Cards Cards. Questions Questions. Cases Cases.
Cindy jr eastenders
Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. The diagnosis and treatment of injuries to the Lisfranc joint complex. At the time the article was last revised Ramon Olushola Wahab had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Type B2 Lisfranc injury. J Am Coll Radiol. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Crim J. Figure 4: This 3D graphic of the midfoot with the 1st metatarsal removed demonstrates the dorsal blue , interosseous red , and plantar green components of the Lisfranc ligament complex. Homolateral Lisfranc fracture dislocation. Standard treatment is open reduction and internal fixation, with non-weight-bearing for six to eight weeks for most types of Lisfranc injuries, commonly type B [2,9].
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
At the time the case was submitted for publication The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures. Abduction stress and AP weightbearing radiography of purely ligamentous injury in the tarsometatarsal joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Normal Alignment of Tarsal-Metatarsal Joints. Figure 2. Musculoskeletal , Trauma. ACR appropriateness criteria acute trauma to the foot. The location of tenderness to palpation to the tarsometatarsal joints and the reproduction of pain localized to the tarsometatarsal region by passive pronation and supination through the midfoot region were found to be the most reliable indicators of the minor sprains. Published Mar 1. Foot Ankle Int. Lisfranc injuries in sport. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.

Your phrase is magnificent
In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
Has not absolutely understood, that you wished to tell it.