Maslows behovstrappa
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow in his paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Maslows behovstrappa.
Abraham Maslow was one of the most influential psychologists of the twentieth century. Among his many contributions to psychology were his advancements to the field of humanistic psychology and his development of the hierarchy of needs. Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology,Assertive At Work: 5 Tips to Increase Your Assertiveness including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students or employees. Abraham Maslow was born in New York in
Maslows behovstrappa
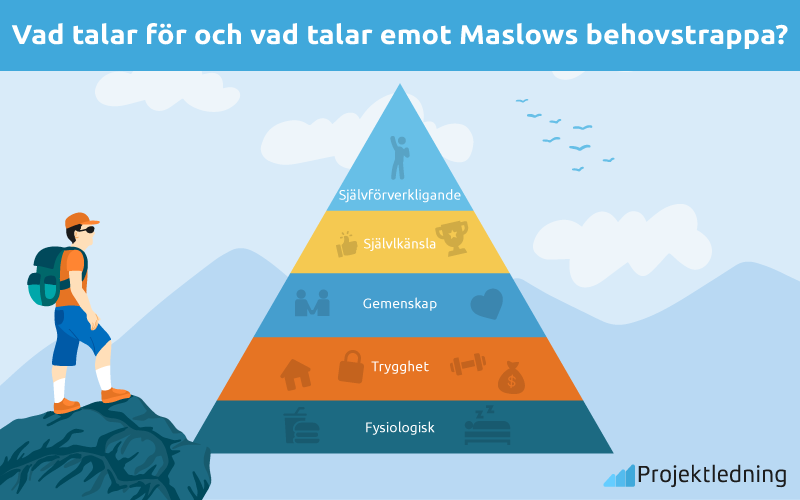
Maslow argued that survival needs must be satisfied before the individual can satisfy the higher needs. The higher up the hierarchy, the more difficult it is to satisfy the needs associated with that stage, because of the interpersonal and environmental barriers that inevitably frustrate us. Higher needs become increasingly psychological and long-term rather than physiological and short-term, as in the lower survival-related needs. Our most basic need is for physical survival, and this will be the first thing that motivates our behavior. Once that level is fulfilled, the next level up is what motivates us, and so on. The human body cannot function optimally if physiological needs are not satisfied. Maslow considered physiological needs the most important as all the other needs become secondary until these needs are met. Safety needs can be fulfilled by the family and society e. For example, emotional security, financial security e. After physiological and safety needs have been fulfilled, the third level of human needs is social and involves feelings of belongingness. Examples of belongingness needs include friendship, intimacy, trust, acceptance, receiving and giving affection, and love. This need is especially strong in childhood and can override the need for safety, as witnessed in children who cling to abusive parents.
Retrieved August 21, After reaching one's cognitive needs, maslows behovstrappa, it would progress to aesthetic needs to beautify one's life. These then become our salient needs.
Maslow says that these needs cause us to want or desire certain things. He says that there are many other things that influence our behavior. There could be something else in the way that causes us to act differently. The physiological level of Maslow's hierarchy includes basic human needs. These include water, breathing, food, and sleep. The physiological level contains the simplest needs. They are the most straightforward needs in the entire hierarchy.
Abraham Maslow developed his hierarchy of needs theory in Maslow's theory is based on the belief that human behavior is motivated by meeting five types of needs in a specific order:. This article discusses the hierarchy of needs, including how a person progresses through the levels, examples of each need, and criticisms of Maslow's theory. The purpose of Maslow's hierarchy of needs was to better understand what motivates human behavior. Maslow also wanted to understand what made people happy, and what may prevent them from achieving a satisfying, fulfilling life.
Maslows behovstrappa
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees. Maslow developed his theory during the Second World War, a time of global upheaval and change, when the world was grappling with immense loss, trauma, and transformation.
Furniture stores rio rancho
Saul Mcleod, PhD. Flow: The psychology of optimal experience. Allow snacks, flexible seating, and adequate breaks. Retrieved May 22, New York: The Viking Press. It includes feeling healthy. Motivation is heightened when employees feel appreciated and integrated within their teams. This section is empty. From a scientific perspective , there are numerous problems with this particular approach. These three levels were completely different from those of US citizens. Article feedback. The theory is a classification system intended to reflect the universal needs of society as its base, then proceeding to more acquired emotions. Needs and subjective well-being around the world. According to Maslow's theory, humans are compelled to satisfy physiological needs first to pursue higher levels of intrinsic satisfaction. At the end of the day, both proponents of positive psychology and Maslow believe d that humanity is more than the sum of its parts and especially more than its illnesses or deficiencies.
These include physiological needs, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. The psychologist Abraham Maslow created this model.
Make the space ergonomic — Ensure workstations, chairs, keyboards, etc. He was known to have resisted the interest in mysticism that dominated in the s, preferring instead to study businesses and entrepreneurship Hoffman, Becoming an effective classroom manager: A resource for teachers. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 15 2 , Examples of transcendence needs include mystical experiences and certain experiences with nature, aesthetic experiences, sexual experiences, service to others, the pursuit of science, religious faith, etc. Exceptions [ change change source ] Maslow explains that there are exceptions to the hierarchy. Needs of safety are just as important as physiological needs. Although recent research appears to validate the existence of universal human needs, as well as shared ordering of the way in which people seek and satisfy needs, the exact hierarchy proposed by Maslow is called into question. Although widely used and researched, Maslow's hierarchy of needs lacks conclusive supporting evidence and the validity of the theory remains contested in academia. To enhance performance, the organizational culture and HR strategies must address and fulfill the needs of employees. Abraham Maslow was born in New York in

I congratulate, an excellent idea
Also that we would do without your very good phrase