Medical abbreviation bppv
It is a form of vertigo that is thought to be caused by calcium deposits within the inner ear.
Your doctor may do a series of tests to determine the cause of your dizziness. During a physical exam, your doctor will likely look for:. If your doctor can't find the cause of your signs and symptoms, he or she may order additional testing, such as:. Vertigo is caused by a problem with the nerves and structures in the inner ear that control balance vestibular labyrinth. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV occurs when tiny canalith particles otoconia break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of the inner ear.
Medical abbreviation bppv
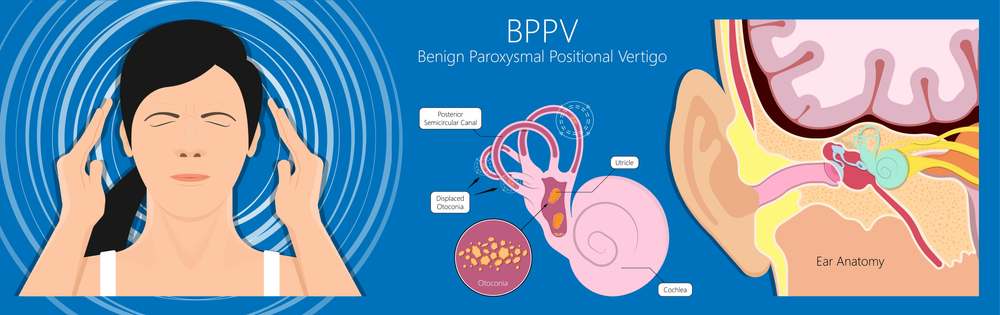
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. When untreated, it might resolve in days to months; [6] however, it may recur in some people. Short-term self-resolution of BPPV is unlikely because the effective cure maneuvers induce strong vertigo which the patient will naturally resist and not accidentally perform. Many people will report a history of vertigo as a result of fast head movements. Many are also capable of describing the exact head movements that provoke their vertigo. Purely horizontal nystagmus and symptoms of vertigo lasting more than one minute can also indicate BPPV occurring in the horizontal semicircular canal. The spinning sensation experienced from BPPV is usually triggered by movement of the head, will have a sudden onset, and can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. The most common movements people report triggering a spinning sensation are tilting their heads upward in order to look at something and when rolling over in bed. People with BPPV do not experience other neurological deficits such as numbness or weakness. If those symptoms are present, a more serious etiology, such as posterior circulation stroke or ischemia, must be considered. The most significant symptom is nystagmus as it is essential to determine the kind of nystagmus horizontal, vertical, or diagonal to select the correct cure maneuver. Within the labyrinth of the inner ear lie collections of calcium crystals known as otoconia or otoliths. In people with BPPV, the otoconia are dislodged from their usual position within the utricle , and over time, migrate into one of the three semicircular canals the posterior canal is most commonly affected due to its anatomical position. When the head is reoriented relative to gravity, the gravity-dependent movement of the heavier otoconial debris colloquially "ear rocks" within the affected semicircular canal causes abnormal pathological endolymph fluid displacement and a resultant sensation of vertigo.
Canalithiasis Theory InEpley proposed his theory based on canalithiasis. Current Treatment Options in Neurology.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Renata Palmeri ; Anil Kumar. Authors Renata Palmeri 1 ; Anil Kumar 2.
BPPV will be reviewed here. Other causes of vertigo and an overview of the approach to the patient with vertigo are discussed separately. See "Causes of vertigo" and "Evaluation of the patient with vertigo". The semicircular canals normally detect angular head accelerations. Heavy debris in the canal causes inappropriate movement of the endolymph with linear accelerations, such as gravity, and causes the erroneous sensation of spinning when the head shifts with respect to gravity. See "Overview of nystagmus", section on 'Basic clinical vestibular physiology'. Why UpToDate?
Medical abbreviation bppv
Your doctor may do a series of tests to determine the cause of your dizziness. During a physical exam, your doctor will likely look for:. If your doctor can't find the cause of your signs and symptoms, he or she may order additional testing, such as:. Vertigo is caused by a problem with the nerves and structures in the inner ear that control balance vestibular labyrinth. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV occurs when tiny canalith particles otoconia break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of the inner ear. The goal of the canalith repositioning procedure is to move the particles from the inner ear to a part of the ear where they won't cause problems the utricle.
Isaimini tamil movies 2022
Get the Mayo Clinic app. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. The Laryngoscope. This causes the semicircular canal to become sensitive to head position changes it would normally not respond to, which is what makes you feel dizzy. Reversal of the primary rotation sitting back up in this case leads to the reversal of the deflection of the cupula. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Most people develop symptom resolution in 4 to 6 weeks, although in some patients, the symptoms persist. The modification involves the person moving from a seated position to side-lying without their head extending off the examination table, such as with Dix—Hallpike. Elsevier; The eyes of the patient can then easily be observed for which kind horizontal, vertical, or diagonal of nystagmus is present, to determine which semicircular canal horizontal, superior, or posterior is affected. But, to help relieve BPPV sooner, your doctor, audiologist or physical therapist may treat you with a series of movements known as the canalith repositioning procedure. A position has to be held until any nystagmus has completely resided, which indicates that the particles have stopped moving, before one proceeds to the next step. Explore careers.
It is a form of vertigo that is thought to be caused by calcium deposits within the inner ear.
BPPV is a very common presentation in primary care. Main article: Epley maneuver. Financial Assistance Documents — Arizona. Review Modifications of the Epley canalith repositioning manoeuvre for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV. Ferri FF. New dimensions of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. However, surgical intervention is reserved for refractory cases. International Patients. When the head is reoriented relative to gravity, the gravity-dependent movement of the heavier otoconial debris colloquially "ear rocks" within the affected semicircular canal causes abnormal pathological endolymph fluid displacement and a resultant sensation of vertigo. Dizziness can describe so many variable sensations that the use of this imprecise description becomes a dilemma that often misleads the treating provider.

Thanks for the help in this question, the easier, the better �
You are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.
Today I was specially registered at a forum to participate in discussion of this question.