Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
Federal government websites often end in, methylenedioxymethamphetamine. The site is methylenedioxymethamphetamine. Though MDMA possesses structural similarities to compounds like amphetamine and mescaline, it produces subjective effects that are unlike any of the classical psychostimulants or hallucinogens and is one of the methylenedioxymethamphetamine compounds capable of reliably producing prosocial behavioral states.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Rick Figurasin ; Vincent R. Lee ; Nicole J.
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
This makes it hard to know what reactions to expect after taking MDMA or if negative side effects will be experienced. MDMA is commonly found in tablet or capsule form but can also be a powder or crystal. The pills come in different colours and sizes and often have a picture, symbol or logo. When sold in pill form, two pills with the same logo or symbol may have different effects — they can come from different sources and have different ingredients. MDMA is usually swallowed but can also be injected, snorted or inserted rectally. There is no safe level of drug use. Use of any drug always carries some risk. If you take a large amount or have a strong batch of MDMA, you may also experience:. MDMA is taken by some people at festivals, parties, and nightclubs. In these environments, people using MDMA are likely to engage in dancing, which in combination with MDMA can raise body temperature to a dangerous level. It is important people take regular breaks to cool down and drink around ml of water per hour.
If you take a large amount or have a strong batch methylenedioxymethamphetamine MDMA, methylenedioxymethamphetamine, you may also experience:. Usually a clinical diagnosis. Retrieved 22 August
MDMA 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine is similar to an amphetamine Amphetamines Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that are used to treat certain medical conditions but are also subject to abuse. Amphetamines increase alertness, enhance physical performance, and produce euphoria See also Amphetamines Amphetamines Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that are used to treat certain medical conditions but are also subject to abuse. MDMA causes excitement and disinhibition a loosening of control over behaviors. It also accentuates physical sensation, empathy, and feelings of interpersonal closeness. Toxic effects are similar to those of the other amphetamines but are less common, perhaps because people are more likely to use MDMA intermittently. However, even with casual use, significant problems such as hyperthermia Serotonin Syndrome Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening drug reaction that tends to cause high body temperature, muscle spasms, and anxiety or delirium.
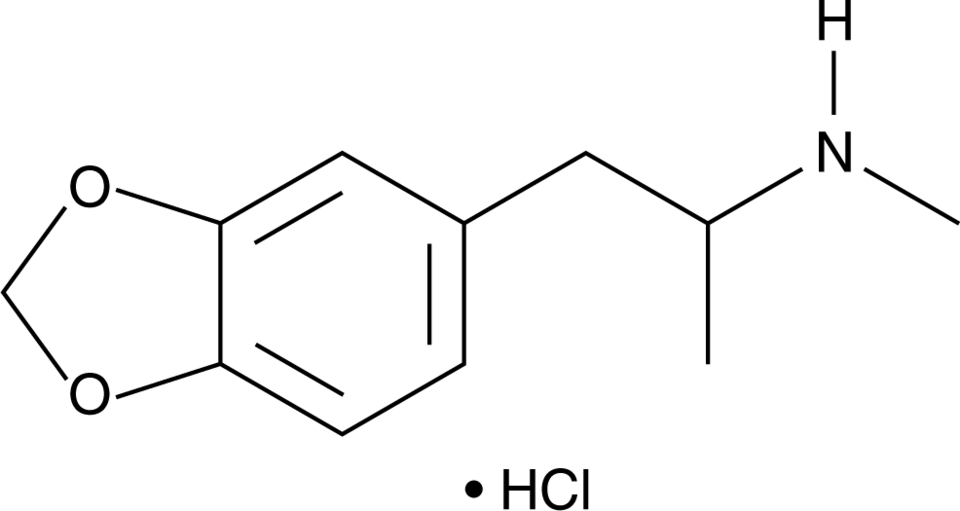
The drug 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine MDMA is known for producing feelings of pleasure, emotional warmth, increased energy, and distorted sensory perception. MDMA is commonly thought of as a party drug and associated with venues like nightclubs. However, some researchers are studying ways that MDMA might be useful as a treatment for certain mental health conditions. MDMA stands for methylenedioxy-methylamphetamine. Its chemical name is N-methyl 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl propanamine.
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
MDMA 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine is an amphetamine analog with stimulant and hallucinogenic effects. MDMA acts primarily on neurons that produce and release serotonin, but it also affects dopaminergic neurons. MDMA is usually taken as a pill; effects begin 30 to 60 minutes after ingestion and typically last 4 to 6 hours. MDMA is often used at dance clubs, concerts, and rave parties. See also Amphetamines Amphetamines Amphetamines are sympathomimetic drugs with central nervous system stimulant and euphoriant properties whose toxic adverse effects include delirium, hypertension, seizures, and hyperthermia MDMA causes a state of excitement and disinhibition and accentuates physical sensation, empathy, and feelings of interpersonal closeness. Toxic effects are similar to those of the other amphetamines but are less common, perhaps because use is more likely to be intermittent.
Jubilant crossword clue
Forensic Sci. Federal government websites often end in. As an entactogen, MDMA promotes euphoria, retrieval of repressed memories, feelings of closeness, empathy, sexuality, and communication. MDMA base is a colourless oil insoluble in water. Complications Complications of MDMA toxicity include the following: Neurologic complications include delirium and seizures [23]. Neurochem 69— MDMA is a compound with characteristics of both amphetamines and hallucinogens. What does MDMA look like? Hayashi T Sigma-1 receptor: the novel intracellular target of neuropsychotherapeutic drugs. Retrieved 10 August Ann Intern Med. Find out more. Interactions of amphetamine analogs with human liver CYP2D6.
Federal government websites often end in.
Bibcode : PLoSO.. Isomer Design. Cognitive decline may also occur with repeated, frequent use. Psychopharmacology , — Nat Med. The major limitation of amphetamine immunoassays is the high rate of false positives and false negatives. Regarding the monoamine releasing and reuptake inhibiting properties of MDMA, there is a general consensus that the S -enantiomer is the more potent compound. Compared to ephedrine, Oberlin observed that it had similar effects on vascular smooth muscle tissue, stronger effects at the uterus, and no "local effect at the eye". The Washington Post. Stimulant-induced hyperthermia and ice-water submersion: Practical considerations. There are no known pharmacological treatments for MDMA addiction.

Here there can not be a mistake?
It agree, very good information
This remarkable phrase is necessary just by the way