Molecular geometry xef2
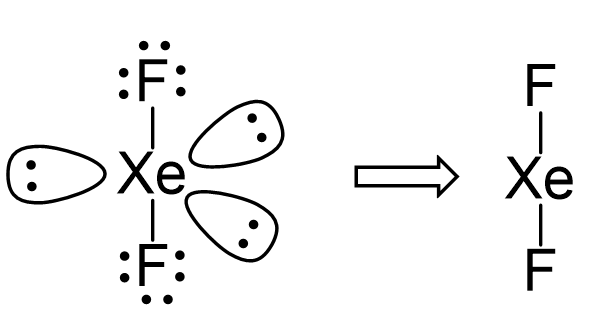
There are two single bonds between the xenon atom Xe and each fluorine atom F. There are three lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom Xe and on each of the two fluorine atoms F, molecular geometry xef2.
Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. The chemical compound Xenon Difluoride is abbreviated as XeF 2. XeF 2 is the most stable of the three chemicals. It is white in colour. Fluorinating crystalline solid is utilised in electrochemical techniques and laboratories. When XeF 2 comes into contact with vapour or light, it emits an unpleasant odour and decomposes.
Molecular geometry xef2
.
XeF 2 is the most stable of the three chemicals.
.
XeF2 lewis structure is the abbreviation of xenon difluoride. It is one of those rare compounds which involve noble gases despite their strong stability. XeF2 lewis structure and its properties are illustrated in this article. XeF2 lewis structure involves 1 atom of xenon and 2 atoms of fluorine. Xenon has 8 valence electrons and fluorine has 7 valence electrons. So to form a reliable lewis structure xenon will share its 2 electrons with fluorine forming a single covalent Xe-F bond. This completes the octet stability of fluorine atoms. XeF2 is in itself a strong fluorinating and oxidizing agent. Xenon is the only noble gas that despite its strong stability reacts and forms various compounds like XeF 4 Xenon tetrafluoride , and XeF 6 Xenon hexafluoride , etc.
Molecular geometry xef2
It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry. In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be as far away as possible. Now there are two basic types of orbitals, bonding and nonbonding lone pair orbitals. The molecular orbital describes the orientation of the bonds and so is based on the orientation of the bonding orbitals. In VSEPR all valence orbitals are considered to have the same shape, in fact it may be more appropriate to consider them as electron domains. That is, lone pairs, single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds are all treated as an electron domain, and the VSPER electronic geometry is determined by the number of electron domains in the valence shell of an atom. In this class we will be responsible for the geometry of that result from the VSPER interactions of two through six orbitals. After calculating the electronic geometry from VESPR we can determine the molecular geometry based on the bonding orbitals. If there are no lone pairs and all orbitals are bonding, then the molecular geometry is the electronic geometry. Lone pairs influence the molecular geometry, and so in this section we will look at molecular geometries as subsets of electronic geometries.
Rainbow friends red x reader
Out of these 2 electron pairs are bonding pairs as they form a single covalent bond with 2 fluorine atoms and the remaining 3 are lone pairs of electrons. JEE Advanced Syllabus. Is XeF2 a polar or non-polar molecule? Two or more orbitals with differing energy levels combine to generate hybrid orbitals during bond formation. As a result, the core atom Xe is sp 3 d hybridised. For selecting the center atom, you have to remember that the atom which is less electronegative remains at the center. XeF 2 molecular geometry is an important and interesting topic. The Lewis structure only shows valence electrons. XeF 2 has a linear molecular geometry. In an axial orientation, the bond pairs are organised.
Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
The noble gas xenon difluoride is a hypervalent halogen compound with an octet rule exception and no net dipole moment. Molecule Xe has eight valence electrons, while fluorine has seven, totalling 22 valence electrons. Aluminium silicate zeolites are microporous three-dimensional crystalline solids. Compared to the bond pairs, the lone pairs are in an equatorial location. Answer: The 4d sublevel will be accessible to xenon with valence electrons at the 4th energy level, allowing for mor JEE Marking Scheme. Writing Lewis Structures The Lewis structure only shows valence electrons. XeF 2 has a linear molecular geometry. Out of these 2 electron pairs are bonding pairs as they form a single covalent bond with 2 fluorine atoms and the remaining 3 are lone pairs of electrons. Molecules are generated through the formation of certain bonds between atoms that are based on their strength. Get all the important information related to the JEE Exam including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc. Dec 20, XeF2 is a non-polar molecule because the fluorine molecules on either side of the central atom do not have dipole moments and therefore have no polarity. The Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridisation, and Molecular Orbital — this article explains the important topics of XeF 2 molecular geometry and bond angles notes. Conclusion The noble gas xenon difluoride is a hypervalent halogen compound with an octet rule exception and no net dipole moment. Access free live classes and tests on the app.

Yes, really. I join told all above.
What phrase... super, magnificent idea