N2o lewis dot
Post by » Mon Nov 05, am. Post by chaggard » Mon Nov 05, am.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 53m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties. Intensive vs.
N2o lewis dot
Cronk Syllabus Topics. Lewis structures are structural formulas for molecules and polyatomic ions that represent all valence electrons. Since valence electrons are typically represented as dots, these structural formulas sometimes are called Lewis dot structures. These symbolic representations were introduced by Gilbert Newton Lewis , a prolific American chemist who was a pioneer in the theory of chemical bonding, thermodynamics, and other areas of chemistry. Lewis structures are of great utility as a tool that allows us to speak a "language" of chemical bonding and molecular structure. The structures, with their guiding rules principally the octet rule provide a basis to predict the chemistry of the elements. In other words, we can make a judgment of whether a particular combination of elements is likely to form a stable molecule or polyatomic ion. The further interpretation of Lewis structures in terms of their implied three-dimensional molecular structures and inferred molecular polarity broadens the scope of their usefulness and importance. Therefore, we will place great emphasis upon developing and practicing the skill of correctly drawing and interpreting Lewis structures. The starting point for Lewis structures are the Lewis symbols for the atoms that comprise the molecular or ionic species under consideration. This is specified by its molecular formula. Recall that a Lewis symbol includes the element symbol plus its valence electrons represented as dots.
Polyatomic Ions.
Previously, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. In some cases, however, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
But have we ever tried to know more about this gas that can make humans laugh? I guess no! After gaining some knowledge about laughing gas, I decided to share it with you, so that next time we can laugh with knowledge!! N2O or nitrous oxide is commonly known as laughing gas. There are several other names by which this compound is known like sweet air, protoxide of nitrogen, etc. N2O is a colorless gas with a molecular weight of The boiling point of this compound is Nitrous oxide, from being used as an oxidizer in a rocket motor to its usage in internal combustion engines, has immense use in different fields.
N2o lewis dot
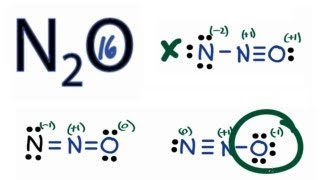
The Oxygen atom has 3 lone pairs and the outer nitrogen atom has 1 lone pair. Note: Take a pen and paper with you and try to draw this lewis structure along with me. I am sure you will definitely learn how to draw lewis structure of N2O. Here, the given molecule is N2O.
Menchies frozen yogurt near me
Equatorial and Axial Positions. Possible Lewis structures and the formal charges for each of the three possible structures for the thiocyanate ion are shown here:. If this cannot be done with the available valence electrons, one would infer a compound with this elemental composition is unlikely to form. From this point the electrons are moved if necessary in pairs in order that the octet rule is satisfied. What is a Lewis dot diagram? This creates a shared pair, or bonding pair, between the two fluorine atoms which completes an octet for both atoms as each also has three unshared pairs or lone pairs. Just as a rhinoceros is neither a dragon sometimes nor a unicorn at other times, a resonance hybrid is neither of its resonance forms at any given time. Carbon dioxide is a stable molecule with this skeletal structure, so it must be possible! Structural isomers of C 2 H 6 O. The convention for ions is to enclose the structure in brackets, and indicate the net charge at the upper right corner.
This article discusses N2O lewis structure and its hybridization, shape, bond angle, and relevant detailed explanations. N 2 O is covalent molecule. The central N atom is sp hybridized and terminal N and O are sp, and sp 3 hybridized respectively.
In many cases, following the steps for writing Lewis structures may lead to more than one possible molecular structure—different multiple bond and lone-pair electron placements or different arrangements of atoms, for instance. Intro to Henry's Law. Resonance Structures and Formal Charge. Benzene Reactions. Quantum Numbers: Magnetic Quantum Number. Electromagnetic Spectrum. The octet rule. Period 2 elements can accommodate at most eight electrons in their valence shells. Galvanic Cell. Cell Notation. Previously, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. This typical pattern of bonding can be referred to as the normal valence for an atom, "valence" being a general term for number of bonds an atom forms. These symbolic representations were introduced by Gilbert Newton Lewis , a prolific American chemist who was a pioneer in the theory of chemical bonding, thermodynamics, and other areas of chemistry. Extensive Properties. Consider the Lewis structures we might initially propose for diatomic helium: None of the structures we can draw for He 2 represent stable molecular forms of helium for the simple reason that helium is extremely unreactive.

It is scandal!