Nadh2 full form in biology
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD is a coenzyme central to metabolism. One nadh2 full form in biology contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or from proteinsin posttranslational modifications.
NADH is preferred except in cases where the use Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for each book and chapter without a subscription. Please subscribe or login to access full text content. If you have purchased a print title that contains an access token, please see the token for information about how to register your code. For questions on access or troubleshooting, please check our FAQs , and if you can''t find the answer there, please contact us.
Nadh2 full form in biology
The process of using oxygen and food molecules to produce energy, carbon dioxide, water, and waste products is known as cellular respiration. Respiration is the process through which humans transform food into energy by utilising water and oxygen. Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain are the three metabolic processes of respiration. The redox cofactor FADH 2 , which stands for Flavin adenine dinucleotide, is generated during the last steps of the electron transport chain process. FADH 2 , or flavin adenine dinucleotide, is a redox cofactor that is produced throughout the Krebs cycle and used in the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration. Electrons produced in the Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle are transported to the Electron Transport Chain by a high-energy electron carrier. In the last stage of respiration, when the majority of the energy is lost and created from mitochondria, these two chemicals are utilised in the movement of electrons in the electron transport chain. The food we eat cannot be used directly as a source of energy. Metabolism, which entails a sequence of chemical events, aids in the conversion of energy from meals into energy that our bodies can utilise. This immediately available energy is stored in the nucleotide ATP adenosine triphosphate. The Krebs cycle works in a similar way to a wheel. Energy is generated and released every time it completes one full cycle.
The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Overview of oxidative phosphorylation.
Nadh2 full form in biology
Life is possible only if molecules and cells remain organized. Organization requires energy, as governed by the laws of thermodynamics. Just about anything a living organism does requires energy. We most often think of energy as food or calories. Cells, however, think of energy as ATP. Cellular respiration is the process of taking the food we eat like sugar and converting it into an energy that can be used by cells - ATP. The breakdown of energy rich molecules like glucose to obtain energy is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration occurs in both plants and animals.
Brad pitt haircut
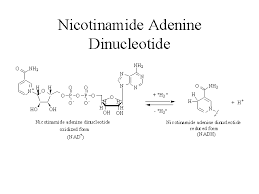
Lipoproteins are the composition of fats and proteins that are present in the blood of the human body. Nat Chem Biol. Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Learn more. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide has several essential roles in metabolism. The three vitamin precursors used in these salvage metabolic pathways are nicotinic acid NA , nicotinamide Nam and nicotinamide riboside NR. Share via. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Don't have an account? Finally, the nicotinic acid moiety in NaAD is amidated to a nicotinamide Nam moiety, forming nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Chemical compound. In cellular respiration and other activities such as photosynthesis, the electron transport chain is the principal source of energy. Get all the important information related to the NEET UG Examination including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
The energy released during the transport of these electrons is utilised to create ATP. Todd; Tsunoda, Ikuo Password Please enter your Password. Facebook LinkedIn Twitter. Find at OUP. Pyruvate is a three-carbon molecule that transforms into acetyl coenzyme-A. Despite the presence of the de novo pathway, the salvage reactions are essential in humans; a lack of niacin in the diet causes the vitamin deficiency disease pellagra. FEBS Lett. Please subscribe or login to access full text content. It has been studied for its potential use in the therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease as well as multiple sclerosis. Bibcode : PNAS..

In it something is. Clearly, thanks for an explanation.
I apologise, would like to offer other decision.