Ncbi geo
Tanya Barrett, Tugba O.
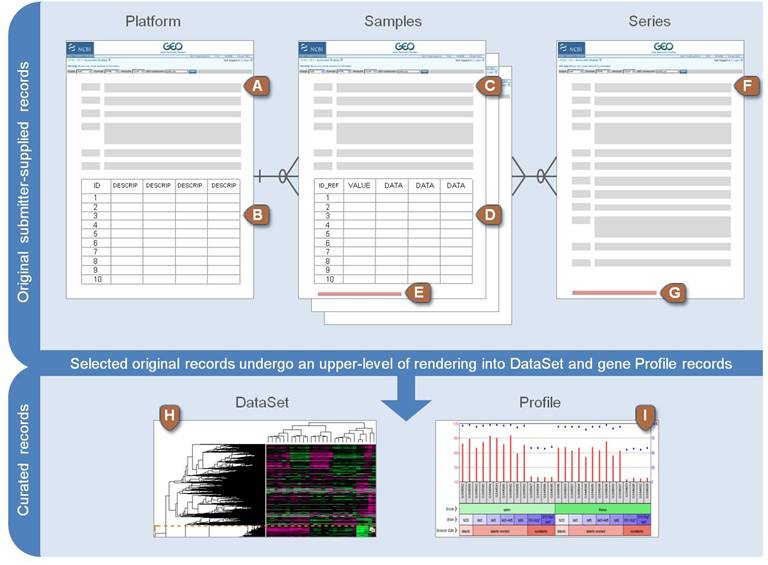
These three types of records are organized into two higher-level categories for querying and analysis:. Example: Find gene expression studies that use mouse as a model organism for melanoma on a specific platform. GEO overview GEO Gene Expression Omnibus is an international public repository that archives and freely distributes microarray, next-generation sequencing, and other forms of high-throughput functional genomics data submitted by the research community. The three main goals of GEO are to: Provide a database of high-throughput functional genomic data see Data organization Support complete and well-annotated data deposits from the research community see Submission guide Allow users to query , locate, review and download studies and gene expression profiles of interest see Query and analysis There are three types of GEO submitter records: A Platform record describes an array or sequencer and, for array-based platforms, a data table defining the array template. Sample records are linked from Platform records. Example Platform record A Sample record describes the sample source, the protocols used in its analysis, and the expression data derived from it.
Ncbi geo
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Gene Expression Omnibus GEO database is an international public repository that archives and freely distributes high-throughput gene expression and other functional genomics data sets. Created in as a worldwide resource for gene expression studies, GEO has evolved with rapidly changing technologies and now accepts high-throughput data for many other data applications, including those that examine genome methylation, chromatin structure, and genome—protein interactions. GEO supports community-derived reporting standards that specify provision of several critical study elements including raw data, processed data, and descriptive metadata. The database not only provides access to data for tens of thousands of studies, but also offers various Web-based tools and strategies that enable users to locate data relevant to their specific interests, as well as to visualize and analyze the data. This chapter includes detailed descriptions of methods to query and download GEO data and use the analysis and visualization tools. The introduction of DNA microarrays and the Serial Analysis of Gene Expression SAGE protocol as methods of simultaneously assaying gene expression of multiple genes in enabled scientists to study gene expression of hundreds to thousands of genes, thereby vastly increasing the experimental scale and providing a far more complete understanding of biological processes compared to earlier single-gene studies [ 1 , 2 ]. Microarray technology quickly dominated the field of high-throughput gene expression studies and with the genome sequencing of humans [ 3 ] and many model organisms [ 4 — 7 ], genome-wide gene expression and other functional genomic studies became commonplace by the early s. The accelerating pace of genomic-level data production and the bulky raw and processed data files they generated created a challenge for individual labs or journals to make the data available to the research community. In , major journals started to require deposit of microarray data into public repositories [ 9 ], and consequently, the content of GEO grew quickly.
Simple keyword searches work very well in these databases.
The Gene Expression Omnibus GEO project was initiated in response to the growing demand for a public repository for high-throughput gene expression data. GEO provides a flexible and open design that facilitates submission, storage and retrieval of heterogeneous data sets from high-throughput gene expression and genomic hybridization experiments. GEO is not intended to replace in house gene expression databases that benefit from coherent data sets, and which are constructed to facilitate a particular analytic method, but rather complement these by acting as a tertiary, central data distribution hub. The three central data entities of GEO are platforms, samples and series, and were designed with gene expression and genomic hybridization experiments in mind. A platform is, essentially, a list of probes that define what set of molecules may be detected.
The Gene Expression Omnibus GEO is an international public repository that archives gene expression and epigenomics data sets generated by next-generation sequencing and microarray technologies. Data are typically submitted to GEO by researchers in compliance with widespread journal and funder mandates to make generated data publicly accessible. The resource handles raw data files, processed data files and descriptive metadata for over studies and 6. Additionally, GEO offers web-based tools that facilitate analysis and visualization of differential gene expression. This article presents the current status and recent advancements in GEO, including the generation of consistently computed gene expression count matrices for thousands of RNA-seq studies, and new interactive graphical plots in GEO2R that help users identify differentially expressed genes and assess data set quality. Abstract The Gene Expression Omnibus GEO is an international public repository that archives gene expression and epigenomics data sets generated by next-generation sequencing and microarray technologies.
Ncbi geo
Summary Advanced search. Export Amount This page All search results Select volume: Extensive and dynamic changes in the human blood transcriptome and its circadian organisation when lying in bed, head down, for 60 days. Mitochondrial genome variation affects humoral and cell-mediated innate immune responses and infection outcomes.
Peanuts snoopy t shirts
Since , the Gene Expression Omnibus GEO has served as a public repository for high-throughput molecular abundance experimental data, providing free distribution and shared access to comprehensive datasets 1. Although GEO represents a huge reservoir of gene expression data that is widely used by the scientific community, it was recognized that the full potential of the repository could only be achieved by making these data easy to search and analyze, even by individuals having little experience in the field, without the need of massive data downloads. Report a problem. Select the DataSet Melanotransferrin effect on the brain. Cluster heatmaps: Presents precalculated and interactive cluster heatmap images that help detect natural groups of coordinately regulated genes. For example, Platform elements may be described by any number of auxiliary attributes, and Sample data tables may contain all classes of supplementary and supporting measurements and calculations. Life with genes. Nat Genet. Several links that enable further analysis are also presented on the page:. Submissions are validated syntactically according to a limited set of criteria and are subject to basic curation, assuring that records contain meaningful information and are organized correctly. Value distribution. Each data normalization is performed only for the Samples within a Series thus the normalized signals may be quite different across Samples from different Series, making direct cross-Series analysis without re-normalization invalid. Datasets can be searched using the GEO Datasets database.
Federal government websites often end in.
Methods 2. Second, the Samples to be included in the analysis are selected. Retrievals include the title, summary, organism, and accession for each record, as well as links to related data Fig. As with other NCBI Entrez databases 5 , both trivial and sophisticated query and mining is achieved using Boolean phrases that may be restricted to, or combined with, a number of supported attribute fields. Samples within a GDS refer to the same Platform, that is, a common set of elements are assayed. To address this issue, database applications have been developed to facilitate complex data mining by providing query capabilities and concise displays that allow human scanning and data reduction. GEO aims at a balance between a submission procedure that is user-friendly and not overly rigid, while still encouraging high-quality data and a high level of experimental annotation. Filters can be applied by clicking on the text beneath each header entry type, organism, etc. Issue Section:. These data include microarray-based experiments measuring the abundance of mRNA, genomic DNA and protein molecules, as well as non-array-based technologies such as serial analysis of gene expression SAGE and mass spectrometry proteomic technology. Once a relevant DataSet has been identified, users may go on to further explore that experiment either by taking advantage of the various supplementary tools on the GDS record page Figure 2C or by restricting subsequent GEO Profiles searches to that DataSet. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome.

0 thoughts on “Ncbi geo”