Nmda receptors
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Kasper B. Hansen , Feng Yi , Riley E. Perszyk , Hiro Furukawa , Lonnie P. Wollmuth , Alasdair J. Gibb , Stephen F.
Nmda receptors
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English Spanish French. An increasing level of N-methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor hypofunction within the brain is associated with memory and learning impairments, with psychosis, and ultimately with excitotoxic brain injury. As the brain ages, the NMDA receptor system becomes progressively hypofunctional, contributing to decreases in memory and learning performance. In those individuals destined to develop Alzheimer's disease, other abnormalities eg, amyloidopathy and oxidative stress interact to increase the NMDA receptor hypofunction NRHypo burden. In these vulnerable individuals, the brain then enters into a severe and persistent NRHypo state, which can lead to widespread neurodegeneration with accompanying mental symptoms and further cognitive deterioration. If the hypotheses described herein prove correct, treatment implications may be considerable. Pharmacological methods for preventing the overstimulation of vulnerable corticolimbic pyramidal neurons developed in an animal model may be applicable to the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. The amino acid glutamate Glu plays a central role in both the normal and abnormal functioning of the central nervous system CNS. Glu is recognized to be the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, estimated to be released at. In addition, Glu is also an excitotoxin that can destroy CNS neurons by excessive activation of excitatory receptors on dendritic and somal surfaces. Two major classes of Glu receptors, ionotropic and metabotropic, have been identified. Glu exerts excitotoxic activity through three receptor subtypes, which belong to the ionotropic family. Progressive increases in the severity of NRHypo within the brain, which can be induced experimentally in vivo using NMDA receptor antagonist drugs, can produce a range of clinically relevant effects on brain function, which are discussed below.
Pharmacological characterization of ligands at recombinant NMDA receptor subtypes by electrophysiological recordings and intracellular calcium measurements. Much research remains to elucidate the precise mechanisms of the NMDA receptor on brain development. This is a preview of subscription content, nmda receptors, access via your institution.
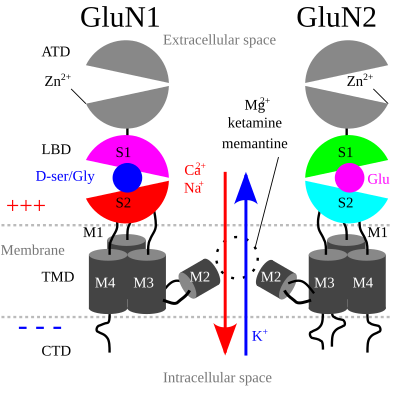
Depending on its subunit composition, its ligands are glutamate and glycine or D -serine. The NMDA receptor is ionotropic , meaning it is a protein which allows the passage of ions through the cell membrane. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of the ion channel that is nonselective to cations , with a combined reversal potential near 0 mV. While the opening and closing of the ion channel is primarily gated by ligand binding, the current flow through the ion channel is voltage-dependent. The anaesthetic and analgesic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are also partially due to their effects at blocking NMDA receptor activity.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Benjamin E.
Nmda receptors
You may have heard of NMDA receptors while learning about a disease or medication, but do you understand what they are and why they are important? First, it helps to understand what we mean by receptor. The brain contains cells called neurons. These are the cells that send and receive the electrical impulses that control your body. Neurons are specialized—each one only deals with certain types of information. So, for example, one neuron may process information on pain and temperature but have nothing to do with visual perception or learning new information. The chemicals that send information from neuron to neuron are called neurotransmitters. Some of the better-known ones include serotonin and dopamine. Neurotransmitters specialize in certain types of information, as well.
Is so2 polar
Mediators Inflamm. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. September Our hypothesis suggests that the neurodegenerative events in AD occur in two separate stages, by two separate mechanisms, and according to two separate patterns. Received: May 10 Chinese Medical Journal. Rezvani AH. Ann Neurol. The amino acid sequence of the intracellular CTD is highly variable among GluN2 subunits, thereby producing pronounced differences in interaction sites for phosphatases, kinases, and proteins responsible for anchoring at synaptic sites and surface trafficking Wenthold et al. Yuan, H. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics.
Federal government websites often end in.
The single-channel recordings demonstrate distinct open probabilities and channel conductances depending on the GluN2 subunit in the diheteromeric NMDA receptor. January Functional consequences of NR2 subunit composition in single recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. New York: Pergamon Press. Chemical structures of memantine and amantadine can be seen in figure 5. In addition, Glu is also an excitotoxin that can destroy CNS neurons by excessive activation of excitatory receptors on dendritic and somal surfaces. Disclosure: Benjamin Jewett declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Gray CW. J Psychiatr Res. NMDAR antagonists like ketamine , esketamine , tiletamine , phencyclidine , nitrous oxide , and xenon are used as general anesthetics.

0 thoughts on “Nmda receptors”