Norleucine
Quantitative metabolomics services for biomarker discovery and validation.
A systematic name for this compound is 2-aminohexanoic acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Together with norvaline , norleucine is found in small amounts in some bacterial strains where its concentration can approach millimolar. Its biosynthesis has been examined. The incorporation of Nle into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. In Miller—Urey experiments probing prebiotic synthesis of amino acids, norleucine and especially norvaline are formed. It is nearly isosteric with methionine , even though it does not contain sulfur.
Norleucine
.
Related compounds. Ornithine Citrulline, norleucine. A systematic name for this compound is 2-aminohexanoic acid.
.
We are working on a new version of ChemSpider — if you want to try the new interface go to beta. Simple Structure Advanced History. Comment on this record. Featured data source. S Aminocaproic acid. S amino-Hexanoi c acid. S Aminohexanoic acid. S -a-Aminocaproic acid. S -Aminohexanoic a cid. S -Norleucine.
Norleucine
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The broadly active glutamine antagonist 6-diazooxo-L-norleucine DON has been studied for sixty years as a potential anticancer therapeutic. Clinical studies of DON in the s using low daily doses suggested antitumor activity, but later phase I and II trials of DON given intermittently at high doses were hampered by dose-limiting nausea and vomiting. Further clinical development of DON was abandoned. Recently the recognition that multiple tumor types are glutamine dependent has renewed interest in metabolic inhibitors such as DON. Here we describe the prior experience with DON in humans. Evaluation of past studies suggests that the major impediments to successful clinical use included unacceptable gastrointestinal GI toxicities, inappropriate dosing schedules for a metabolic inhibitor, and lack of targeted patient selection. When these prodrugs are administered in a low daily dosing regimen, appropriate for metabolic inhibition, they are robustly effective without significant toxicity.
Allthefalle
Fermentative production of L-norleucine. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Human Metabolome Database. Norvaline 2-amino-pentanoic Aminocaproic acid 6-amino-hexanoic Leucine 2-aminomethyl-pentanoic Isoleucine 2-aminomethyl-pentanoic Lysine 2,6-diamino-hexanoic. Hidden categories: All articles with dead external links Articles with dead external links from February Articles with permanently dead external links ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes Chembox image size set Articles with short description Short description matches Wikidata. Toggle limited content width. Medium-chain fatty acids Amino fatty acids Amino acids Monocarboxylic acids and derivatives Carboxylic acids Organopnictogen compounds Organic oxides Monoalkylamines Hydrocarbon derivatives Carbonyl compounds. Solubility in water. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Property Value Source Water Solubility. The incorporation of Nle into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. L-alpha-amino acid Medium-chain fatty acid Amino fatty acid Fatty acid Fatty acyl Amino acid Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives Carboxylic acid Organic oxide Organopnictogen compound Organic oxygen compound Primary amine Organooxygen compound Organonitrogen compound Primary aliphatic amine Carbonyl group Organic nitrogen compound Amine Hydrocarbon derivative Aliphatic acyclic compound. Acidity p K a. Other names Caprine Glycoleucine. Carboxylic acids and derivatives.
A systematic name for this compound is 2-aminohexanoic acid.
L-Norleucine exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. Chemical compound. Aminolevulinic acid 5-ALA Cystine. Acidity p K a. Pure and Applied Chemistry. Wikimedia Commons. Beilstein Reference. Property Value Reference Melting Point. Download PDF. L-Norleucine, also known as L-aminohexanoate or caprine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. In other projects.

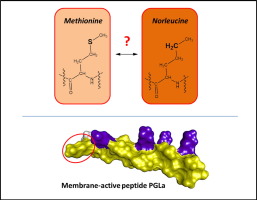
Interesting theme, I will take part.