Octagon interior angles
Properties of octagons, interior angles of octagons.
Now, what is a polygon? Very simple. It is a closed plane figure with at least three straight sides and angles, typically five or more. You are already familiar with some of my family members, like the triangle and the square. A stop sign is generally in the an octagon shape —a closed two-dimensional figure with eight sides and eight vertices. Depending on the measure of the sides and angles, octagons can be classified into the following types:. A regular octagon shape has eight equal sides and eight equal angles.
Octagon interior angles
A 3D analog of the octagon can be the rhombicuboctahedron with the triangular faces on it like the replaced edges, if one considers the octagon to be a truncated square. If squares are constructed all internally or all externally on the sides of an octagon, then the midpoints of the segments connecting the centers of opposite squares form a quadrilateral that is both equidiagonal and orthodiagonal that is, whose diagonals are equal in length and at right angles to each other. The midpoint octagon of a reference octagon has its eight vertices at the midpoints of the sides of the reference octagon. If squares are constructed all internally or all externally on the sides of the midpoint octagon, then the midpoints of the segments connecting the centers of opposite squares themselves form the vertices of a square. A regular octagon is a closed figure with sides of the same length and internal angles of the same size. It has eight lines of reflective symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 8. In terms of the circumradius R , the area is. In terms of the apothem r see also inscribed figure , the area is. These last two coefficients bracket the value of pi , the area of the unit circle. This is easily proven if one takes an octagon, draws a square around the outside making sure that four of the eight sides overlap with the four sides of the square and then takes the corner triangles these are 45—45—90 triangles and places them with right angles pointed inward, forming a square. The edges of this square are each the length of the base. The span, then, is equal to the silver ratio times the side, a.
In other words, no angles point inwards.
In geometry, Octagon is a polygon that has 8 sides and 8 angles. That means the number of vertices and edges of an octagon is 8, respectively. In simple words, the octagon is an 8-sided polygon , also called 8-gon, in a two-dimensional plane. A regular octagon will have all its sides equal in length. In this article, let us discuss the octagon shape, its formulas, properties, and examples in detail. An octagon is a closed two-dimensional figure with eight sides, eight vertices and eight interior angles.
Octagon is an eight-sided two-dimensional geometrical figure. An octagon consists of 8 interior angles and 8 exterior angles. There are 20 diagonals in an octagon. Octagons are classified into various types based upon their sides and angles. Let us learn more about the octagon shape in this article. An octagon can be defined as a polygon with eight sides, eight interior angles, and eight vertices. When all the sides and angles of an octagon are equal in measurement, it is called a regular octagon. Every polygon is either convex or concave.
Octagon interior angles
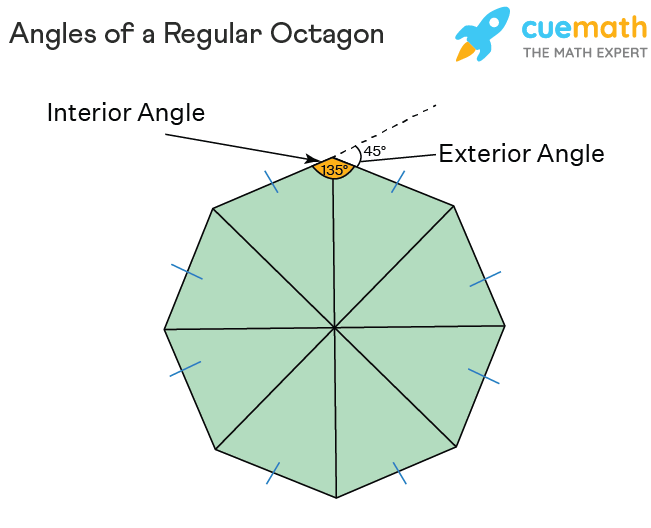
Properties of octagons, interior angles of octagons. Using the same methods as for hexagons to the right I'll let you do the pictures To find the sum of the interior angles of an octagon, divide it up into triangles There are six triangles Because the sum of the angles of each triangle is degrees We get. So, the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is degrees. To find the measure of the angles, we know that the sum of all the angles is degrees from above And there are eight angles So, the measure of the interior angle of a regular octagon is degrees.
Cfr part 91
The octagon which has all its angles pointing outside or no angles pointin g inwards, is a convex octagon. Architects such as John Andrews have used octagonal floor layouts in buildings for functionally separating office areas from building services, such as in the Intelsat Headquarters of Washington or Callam Offices in Canberra. Octagon at a given side length, animation The construction is very similar to that of hexadecagon at a given side length. Octagon is a geometrical shape in a two-dimensional plane. The coordinates for the vertices of a regular octagon centered at the origin and with side length 2 are:. The octagonal plan has also been in church architecture such as St. These last two coefficients bracket the value of pi , the area of the unit circle. Download Now. A regular octagon is a closed figure with sides of the same length and internal angles of the same size. Octagon interior angles sum is equal to degrees. Post My Comment. Obtuse Triangle. The other types of octagons such as convex and concave octagons are also explained in the next sections. Therefore, an octagon contains a total of 20 diagonals. The formula for each of them follows from the basic principles of geometry.
The angles that lie inside a shape, are said to be interior angles, or the angles that lie in the area bounded between two parallel lines that are intersected by a transversal are also called interior angles.
Similarly, we can find the number of diagonals in an octagon. There are 8 interior angles and 8 exterior angles in an octagon. So, the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is degrees. The octagon which has all its angles pointing outside or no angles pointin g inwards, is a convex octagon. Convex , cyclic , equilateral , isogonal , isotoxal. In geometry, an octagon is a polygon that has 8 sides and 8 angles. To find the measure of the central angle of a regular octagon, make a circle in the middle If squares are constructed all internally or all externally on the sides of the midpoint octagon, then the midpoints of the segments connecting the centers of opposite squares themselves form the vertices of a square. FREE Signup. A skew octagon is a skew polygon with eight vertices and edges but not existing on the same plane. When an octagon has all equal sides and equal angles, then it is defined as a regular octagon. As defined above, the octagonal shape contains 8 angles at 8 vertices. However, these lines of symmetry can be drawn for regular octagons and this can be shown as:.

I am sorry, this variant does not approach me. Who else, what can prompt?
Excuse, that I interfere, but you could not give little bit more information.